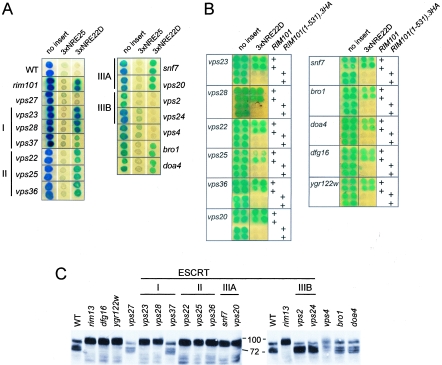
FIG. 8.
Involvement of ESCRT components, Dfg16, and Ygr122w in 3×NRE22D-mediated repression and processing of Rim101. (A) Colonies of the BY4741-derived deletion strains, as indicated on the sides of the panels, containing pLG312n (no insert), pLGn+3×NRE25, or pLGn+ 3×NRE22D, as indicated above the panels, were overlaid with X-Gal-containing agar. I, II, IIIA, and IIIB refer to ESCRT complexes. (B) Repression of the CYC1-3×NRE22D-lacZ reporter gene can be restored in the mutant strains by expression of a truncated version of Rim101. For each mutant strain identified on the left of the panel, the top two rows of colonies were from cells that contained the wild-type (WT) RIM101 gene, and the bottom two rows of colonies were from cells that contained the RIM101(1-531).3HA-HIS3MX6 allele, as indicated on the right. The cells also contained pLG312n (no insert) or pLGn+3×NRE22D, as indicated above the panels. For panels A and B, composite images were prepared from scans of plates that had been overlaid with X-Gal-containing agar after color development. Each plate had control colonies consisting of wild-type cells and rim101Δ cells containing pLG312n or pLG+3×NRE22D to ensure equivalent color development. (C) Western blot of an SDS-polyacrylamide gel containing aliquots of crude lysates prepared from the indicated BY4741-derived deletion strains that expressed a full-length internally HA-epitope-tagged Rim101 protein. The blot was probed with HRP-conjugated anti-HA antibodies.