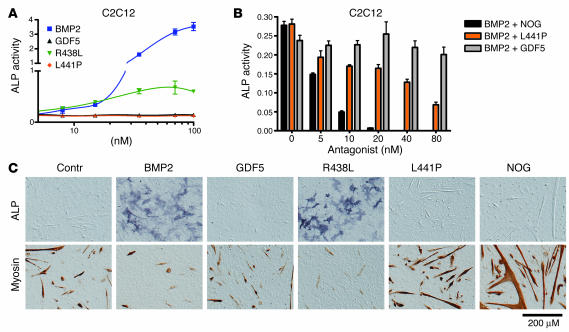
Figure 5.
Effects of GDF5 mutants on the differentiation of premyoblastic C2C12 cells. ALP activity was analyzed after stimulation of C2C12 cells with the recombinant proteins for 3 days. Differentiation markers ALP and myosin were assayed 5 days after addition of the proteins. (A) WT GDF5 and the L441P mutant did not induce significant ALP activity in C2C12 cells. In contrast, treatment with BMP2 resulted in a strong induction, and the R438L mutant induced significant ALP activity, albeit to a lower degree than BMP2. (B) Addition of NOG inhibited BMP2-induced ALP activity in a dose-dependent fashion. A similar antagonism was observed with the addition of L441P mutant. The addition of WT GDF5 had no major effect. (C) Differentiation of C2C12 cells was determined using ALP staining (osteoblastic lineage) or immunohistochemical analysis of myosin expression (muscle lineage). Treatment of C2C12 cells with WT GDF5 had a slightly negative effect on their spontaneous differentiation along the muscle lineage, as indicated by the reduced size of myoblasts. L441P treatment increased muscle formation with results similar to the effects of the BMP inhibitor NOG. Incubation with BMP2, in contrast, resulted in strong induction of ALP activity and suppression of muscle differentiation. Similar results were obtained for the R438L mutant, indicating that this mutant displayed BMP2-like activity in this assay. Magnification, ×10 objective (AxioCam HRc camera; Zeiss).