Abstract
OBJECTIVE: The purpose of this report is to describe the authors' technique for the laparoscopic repair of paraesophageal hernias and the outcome in their series of patients. METHODS: Thirty patients underwent elective laparoscopic repair of paraesophageal hernias. All were pure type II paraesophageal hernias as defined by upper gastrointestinal contrast studies. All operations were performed by a single surgeon (JKE) assisted by five different chief surgical residents. The authors have used various prototypes of a laparoscopic utility belt to reduce the physician requirement to the surgeon and a first assistant. The operative setup and specific techniques of the repair are described and illustrated. A concomitant anti-reflux procedure was performed in the last 23 patients. RESULTS: Satisfactory repair using video-laparoscopic techniques was achieved in all cases. There were no deaths. Complications occurred in 8 of 30 patients. Postoperative gastroesophageal reflux developed in three of the first seven patients in whom fundoplication was not performed. Three consecutive patients had left lower lobe atelectasis believed to be related to endotracheal tube displacement during the passage of the bougie. One patient had postoperative dysphagia. There was one case of major deep venous thrombosis with pulmonary embolism. Twenty-eight of 30 patients were discharged home by postoperative day 3. Twenty-four of 30 patients had returned to normal activity by the time of their first postoperative office visit 1 week after surgery.
Full text
PDF
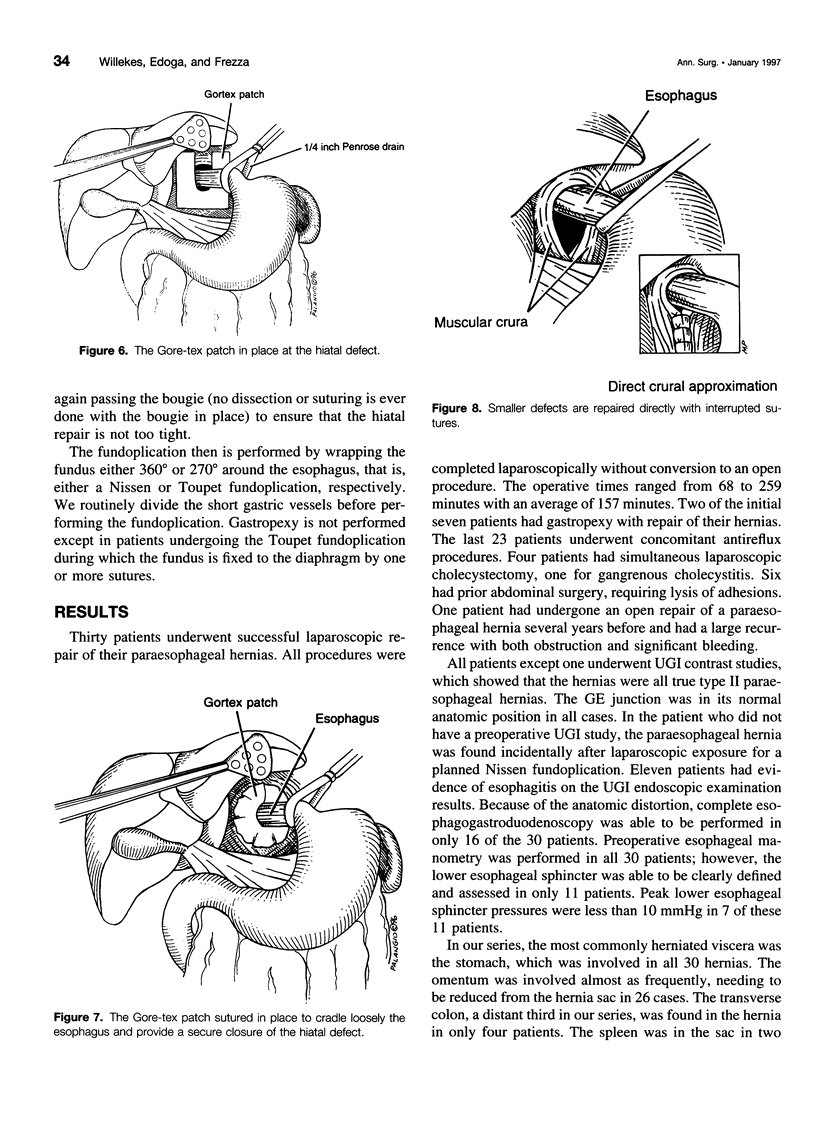




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Casabella F., Sinanan M., Horgan S., Pellegrini C. A. Systematic use of gastric fundoplication in laparoscopic repair of paraesophageal hernias. Am J Surg. 1996 May;171(5):485–489. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9610(97)89609-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis F. H., Jr, Crozier R. E., Shea J. A. Paraesophageal hiatus hernia. Arch Surg. 1986 Apr;121(4):416–420. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1986.01400040052007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuller C. B., Hagen J. A., DeMeester T. R., Peters J. H., Ritter M., Bremmer C. G. The role of fundoplication in the treatment of type II paraesophageal hernia. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1996 Mar;111(3):655–661. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5223(96)70319-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter J. G., Trus T. L., Branum G. D., Waring J. P., Wood W. C. A physiologic approach to laparoscopic fundoplication for gastroesophageal reflux disease. Ann Surg. 1996 Jun;223(6):673–687. doi: 10.1097/00000658-199606000-00006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jamieson G. G., Watson D. I., Britten-Jones R., Mitchell P. C., Anvari M. Laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication. Ann Surg. 1994 Aug;220(2):137–145. doi: 10.1097/00000658-199408000-00004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karasick S., O'Hara A. E., Karasick D., Rangarathnam C. S. Supradiaphragmatic cyst following surgical repair of congenital diaphragmatic hernia. Radiology. 1978 Oct;129(1):142–142. doi: 10.1148/129.1.142. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LARSON N. E., LARSON R. H., DORSEY J. M. MECHANISM OF OBSTRUCTION AND STRANGULATION IN HERNIAS OF THE ESOPHAGEAL HIATUS. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1964 Oct;119:835–841. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landreneau R. J., Johnson J. A., Marshall J. B., Hazelrigg S. R., Boley T. M., Curtis J. J. Clinical spectrum of paraesophageal herniation. Dig Dis Sci. 1992 Apr;37(4):537–544. doi: 10.1007/BF01307577. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matloub H. S., Jensen P., Grunert B. K., Sanger J. R., Yousif N. J. Characteristics of prosthetic mesh and autogenous fascia in abdominal wall reconstruction after prolonged implantation. Ann Plast Surg. 1992 Dec;29(6):508–511. doi: 10.1097/00000637-199212000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson F. G., Cooper J. D., Ilves R., Todd T. R., Jamieson W. R. Massive hiatal hernia with incarceration: a report of 53 cases. Ann Thorac Surg. 1983 Jan;35(1):45–51. doi: 10.1016/s0003-4975(10)61430-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rakic S., Pesko P., Dunjic M., Gerzic Z. Healing of gastric ulcer associated with paraesophageal hernia after hernial reduction. Am J Surg. 1992 Apr;163(4):443–445. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(92)90051-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skinner D. B., Belsey R. H. Surgical management of esophageal reflux and hiatus hernia. Long-term results with 1,030 patients. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1967 Jan;53(1):33–54. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treacy P. J., Jamieson G. G. An approach to the management of para-oesophageal hiatus hernias. Aust N Z J Surg. 1987 Nov;57(11):813–817. doi: 10.1111/j.1445-2197.1987.tb01271.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weerts J. M., Dallemagne B., Hamoir E., Demarche M., Markiewicz S., Jehaes C., Lombard R., Demoulin J. C., Etienne M., Ferron P. E. Laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication: detailed analysis of 132 patients. Surg Laparosc Endosc. 1993 Oct;3(5):359–364. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williamson W. A., Ellis F. H., Jr, Streitz J. M., Jr, Shahian D. M. Paraesophageal hiatal hernia: is an antireflux procedure necessary? Ann Thorac Surg. 1993 Sep;56(3):447–452. doi: 10.1016/0003-4975(93)90878-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]