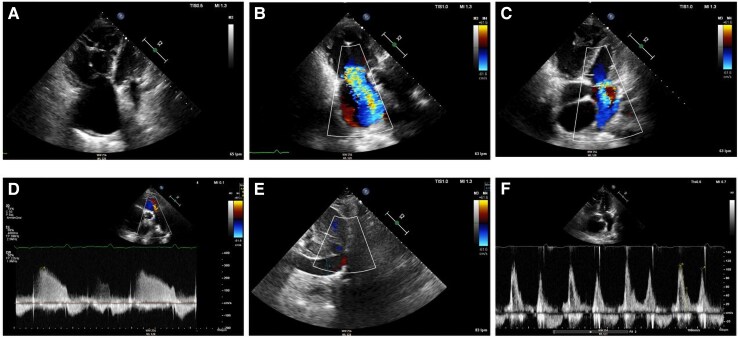
Figure 3.
Transthoracic echocardiography during follow-up of Case 2 at time of hospital admission. (A) Apical four chamber view depicting a severely dilated right ventricle with the following dimensions: end-diastolic right ventricular basal diameter 52 mm, end-diastolic right ventricular mid diameter 55 mm, end-diastolic right ventricular longitudinal diameter 85 mm, right ventricular end-diastolic area 41.5 cm2. Right ventricular systolic dysfunction was severely reduced (fractional area change 19%, tricuspid annular plane systolic excursion 12 mm with severe tricuspid regurgitation, pulsed Doppler S wave of the tricuspid annulus 6.9 cm/s). Severe right atrial dilation (33 cm2). (B) Right ventricular-focused apical four chamber view showing severe functional tricuspid regurgitation. (C) Apical four chamber view depicting moderate mitral regurgitation due to anterior leaflet prolapse. (D) Moderate functional pulmonary regurgitation allows for estimation of a mean pulmonary artery pressure of 45 mmHg. (E) Dilated inferior vena cava of 24 mm without respiratory variation, estimated right atrial pressure of 15 mmHg. (F) Mitral inflow shows pseudonormal left ventricular filling pattern consistent with Grade 2 diastolic dysfunction (elevated left ventricular filling pressures). Mitral E-wave was 109 cm/s; mitral A-wave was 102 cm/s. Valsalva manoeuvre increased A-wave velocity. Lateral E/e′ ratio was 12.