Abstract
OBJECTIVE: The goals were to summarize the results of liver transplantation for chronic hepatitis B disease (HBV) at the University of Virginia, correlate pretransplant viral markers with posttransplant hepatitis B immunoglobulin (HBIg) requirements, and identify the relation between viral protein in the liver and clinical reinfection. SUMMARY BACKGROUND DATA: Liver transplantation is an accepted treatment for end-stage liver disease from chronic HBV infection, although lifelong antiviral treatment (with HBIg or antiviral agents) is still necessary. Patients with evidence of active viral replication (detectable serum HBV-DNA or e antigen) at the time of transplant have a higher rate of allograft infection. Whether clinically stable patients receiving HBIg immunoprophylaxis have detectable viral products in their grafts remains unknown. METHODS: Forty-four transplants performed for HBV disease at the University of Virginia since March 1990 were reviewed. Most patients underwent aggressive passive immunoprophylaxis with HBIg to maintain serum HBV surface antibody (HBsAb) levels > or =500 IU/l for the first 6 months after the transplant, and > or =150 IU/l thereafter. Patients had viral markers quantified, underwent pharmacokinetic analysis of HBsAb levels to adjust dosing, and were biopsied routinely every 3 to 6 months and when indicated. RESULTS: Forty-four transplants were performed in 39 patients. Actual 1-year and 3-year graft survival was 95% and 81%, respectively, and 1-year and 3-year patient survival was 98% and 96%, respectively. After the adoption of indefinite HBIg prophylaxis, nine grafts became infected (all in recipients positive for HBV e antigen). Three occurred within 8 weeks of transplantation and were associated with a short HBsAb half-life and a wild-type virus. Six occurred >8 months after the transplant, and most of these were associated with viral mutation. Quantification of pretransplant markers was an overall poor predictor of HBIg requirements after the transplant. Immunohistochemistry demonstrated transient low-level expression of core protein in the liver in 23% of patients without serum or clinical evidence of recurrent hepatitis. CONCLUSIONS: An excellent outcome is possible after liver transplantation for chronic HBV disease using HBIg dosed by pharmacokinetic parameters. Currently, quantification of pretransplant serum markers of the HBV antigen load does not predict the intensity of posttransplant treatment required for good clinical outcomes. Because HBV is not eradicated from the patient, some form of indefinite antiviral therapy continues to be warranted.
Full text
PDF

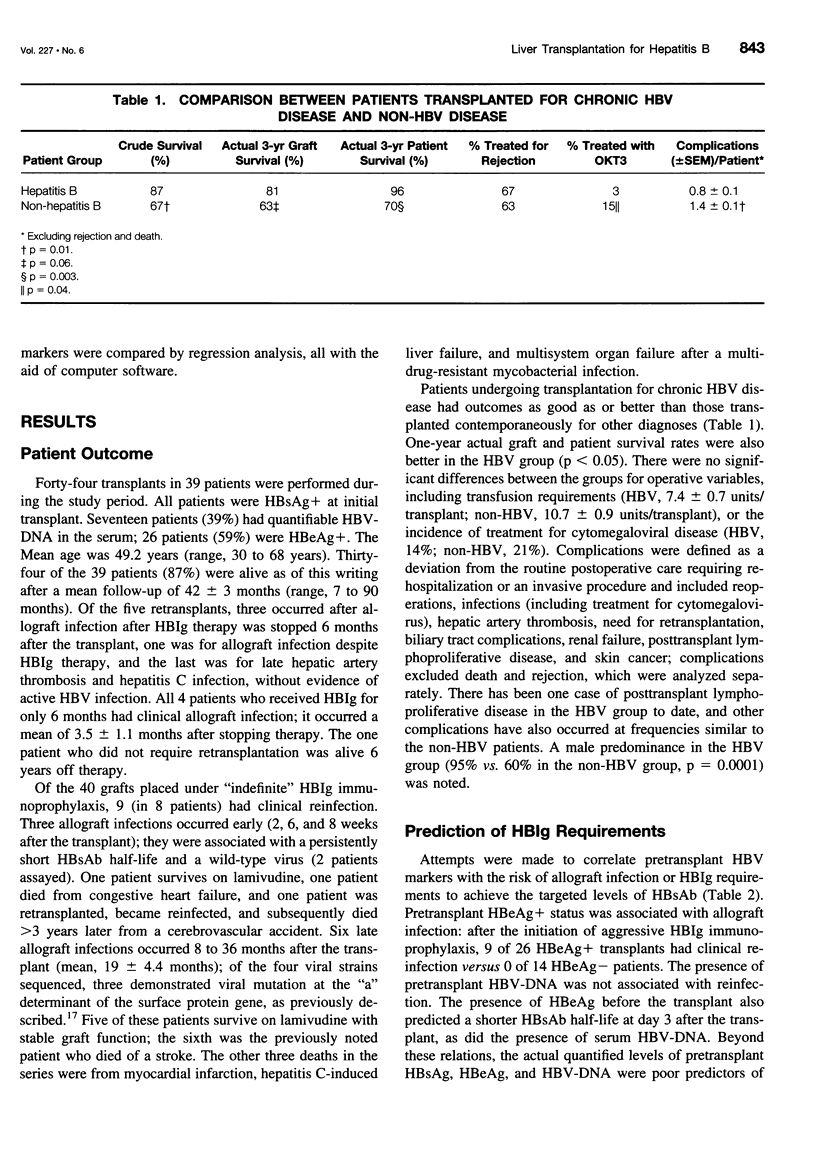
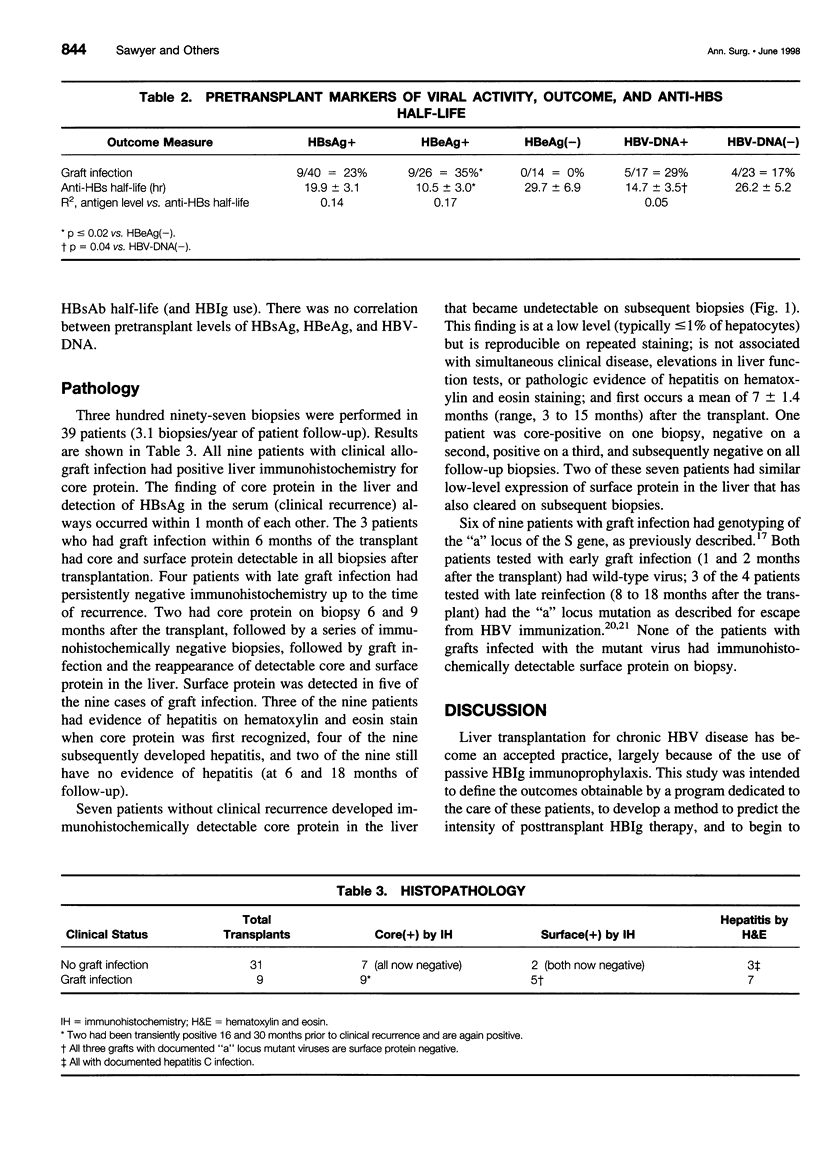
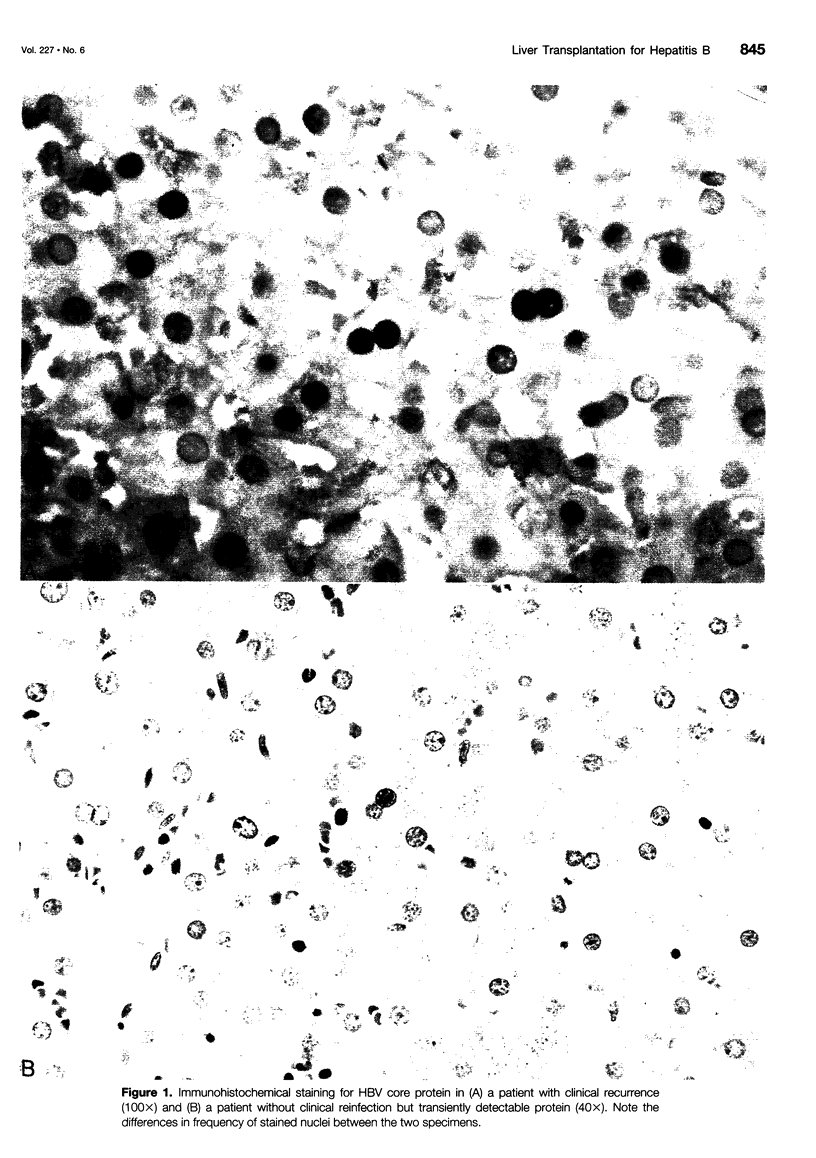


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bain V. G., Kneteman N. M., Ma M. M., Gutfreund K., Shapiro J. A., Fischer K., Tipples G., Lee H., Jewell L. D., Tyrrell D. L. Efficacy of lamivudine in chronic hepatitis B patients with active viral replication and decompensated cirrhosis undergoing liver transplantation. Transplantation. 1996 Nov 27;62(10):1456–1462. doi: 10.1097/00007890-199611270-00013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartholomew M. M., Jansen R. W., Jeffers L. J., Reddy K. R., Johnson L. C., Bunzendahl H., Condreay L. D., Tzakis A. G., Schiff E. R., Brown N. A. Hepatitis-B-virus resistance to lamivudine given for recurrent infection after orthotopic liver transplantation. Lancet. 1997 Jan 4;349(9044):20–22. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(96)02266-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cariani E., Ravaggi A., Tanzi E., Romanò L., Fiordalisi G., Bellati G., Caccamo L., Galmarini D., Albertini A., Zanetti A. Emergence of hepatitis B virus S gene mutant in a liver transplant recipient. J Med Virol. 1995 Dec;47(4):410–415. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890470419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carman W. F., Trautwein C., van Deursen F. J., Colman K., Dornan E., McIntyre G., Waters J., Kliem V., Müller R., Thomas H. C. Hepatitis B virus envelope variation after transplantation with and without hepatitis B immune globulin prophylaxis. Hepatology. 1996 Sep;24(3):489–493. doi: 10.1002/hep.510240304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carman W. F., Zanetti A. R., Karayiannis P., Waters J., Manzillo G., Tanzi E., Zuckerman A. J., Thomas H. C. Vaccine-induced escape mutant of hepatitis B virus. Lancet. 1990 Aug 11;336(8711):325–329. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)91874-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freeman R. B., Sanchez H., Lewis W. D., Sherburne B., Dzik W. H., Khettry U., Hing S., Zeldis J. B., Jenkins R. L. Serologic and DNA follow-up data from HBsAg-positive patients treated with orthotopic liver transplantation. Transplantation. 1991 Apr;51(4):793–797. doi: 10.1097/00007890-199104000-00011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grellier L., Mutimer D., Ahmed M., Brown D., Burroughs A. K., Rolles K., McMaster P., Beranek P., Kennedy F., Kibbler H. Lamivudine prophylaxis against reinfection in liver transplantation for hepatitis B cirrhosis. Lancet. 1996 Nov 2;348(9036):1212–1215. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(96)04444-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkins A. E., Gilson R. J., Gilbert N., Wreghitt T. G., Gray J. J., Ahlers-de Boer I., Tedder R. S., Alexander G. J. Hepatitis B virus surface mutations associated with infection after liver transplantation. J Hepatol. 1996 Jan;24(1):8–14. doi: 10.1016/s0168-8278(96)80179-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- König V., Hopf U., Neuhaus P., Bauditz J., Schmidt C. A., Blumhardt G., Bechstein W. O., Neuhaus R., Lobeck H. Long-term follow-up of hepatitis B virus-infected recipients after orthotopic liver transplantation. Transplantation. 1994 Sep 15;58(5):553–559. doi: 10.1097/00007890-199409150-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lauchart W., Müller R., Pichlmayr R. Long-term immunoprophylaxis of hepatitis B virus reinfection in recipients of human liver allografts. Transplant Proc. 1987 Oct;19(5):4051–4053. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ling R., Mutimer D., Ahmed M., Boxall E. H., Elias E., Dusheiko G. M., Harrison T. J. Selection of mutations in the hepatitis B virus polymerase during therapy of transplant recipients with lamivudine. Hepatology. 1996 Sep;24(3):711–713. doi: 10.1002/hep.510240339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowell J. A., Burgess S., Shenoy S., Peters M., Howard T. K. Mercury poisoning associated with hepatitis-B immunoglobulin. Lancet. 1996 Feb 17;347(8999):480–480. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(96)90061-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann S. P., Painter D. M., McCaughan G. W. Histopathological prediction of hepatitis B recurrence in liver allografts. Pathology. 1994 Jul;26(3):251–256. doi: 10.1080/00313029400169591. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGory R. W., Ishitani M. B., Oliveira W. M., Stevenson W. C., McCullough C. S., Dickson R. C., Caldwell S. H., Pruett T. L. Improved outcome of orthotopic liver transplantation for chronic hepatitis B cirrhosis with aggressive passive immunization. Transplantation. 1996 May 15;61(9):1358–1364. doi: 10.1097/00007890-199605150-00013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMahon G., Ehrlich P. H., Moustafa Z. A., McCarthy L. A., Dottavio D., Tolpin M. D., Nadler P. I., Ostberg L. Genetic alterations in the gene encoding the major HBsAg: DNA and immunological analysis of recurrent HBsAg derived from monoclonal antibody-treated liver transplant patients. Hepatology. 1992 May;15(5):757–766. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840150503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller R., Gubernatis G., Farle M., Niehoff G., Klein H., Wittekind C., Tusch G., Lautz H. U., Böker K., Stangel W. Liver transplantation in HBs antigen (HBsAg) carriers. Prevention of hepatitis B virus (HBV) recurrence by passive immunization. J Hepatol. 1991 Jul;13(1):90–96. doi: 10.1016/0168-8278(91)90869-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Grady J. G., Smith H. M., Davies S. E., Daniels H. M., Donaldson P. T., Tan K. C., Portmann B., Alexander G. J., Williams R. Hepatitis B virus reinfection after orthotopic liver transplantation. Serological and clinical implications. J Hepatol. 1992 Jan;14(1):104–111. doi: 10.1016/0168-8278(92)90138-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rizzetto M., Recchia S., Salizzoni M. Liver transplantation in carriers of the HBsAg. J Hepatol. 1991 Jul;13(1):5–7. doi: 10.1016/0168-8278(91)90855-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuel D., Bismuth A., Mathieu D., Arulnaden J. L., Reynes M., Benhamou J. P., Brechot C., Bismuth H. Passive immunoprophylaxis after liver transplantation in HBsAg-positive patients. Lancet. 1991 Apr 6;337(8745):813–815. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(91)92515-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuel D., Muller R., Alexander G., Fassati L., Ducot B., Benhamou J. P., Bismuth H. Liver transplantation in European patients with the hepatitis B surface antigen. N Engl J Med. 1993 Dec 16;329(25):1842–1847. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199312163292503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terrault N. A., Zhou S., Combs C., Hahn J. A., Lake J. R., Roberts J. P., Ascher N. L., Wright T. L. Prophylaxis in liver transplant recipients using a fixed dosing schedule of hepatitis B immunoglobulin. Hepatology. 1996 Dec;24(6):1327–1333. doi: 10.1002/hep.510240601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waters J. A., Kennedy M., Voet P., Hauser P., Petre J., Carman W., Thomas H. C. Loss of the common "A" determinant of hepatitis B surface antigen by a vaccine-induced escape mutant. J Clin Invest. 1992 Dec;90(6):2543–2547. doi: 10.1172/JCI116148. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- al-Hemsi B., McGory R. W., Shepard B., Ishitani M. B., Stevenson W. C., McCullough C., Pruett T. L. Liver transplantation for hepatitis B cirrhosis: clinical sequela of passive immunization. Clin Transplant. 1996 Dec;10(6 Pt 2):668–675. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



