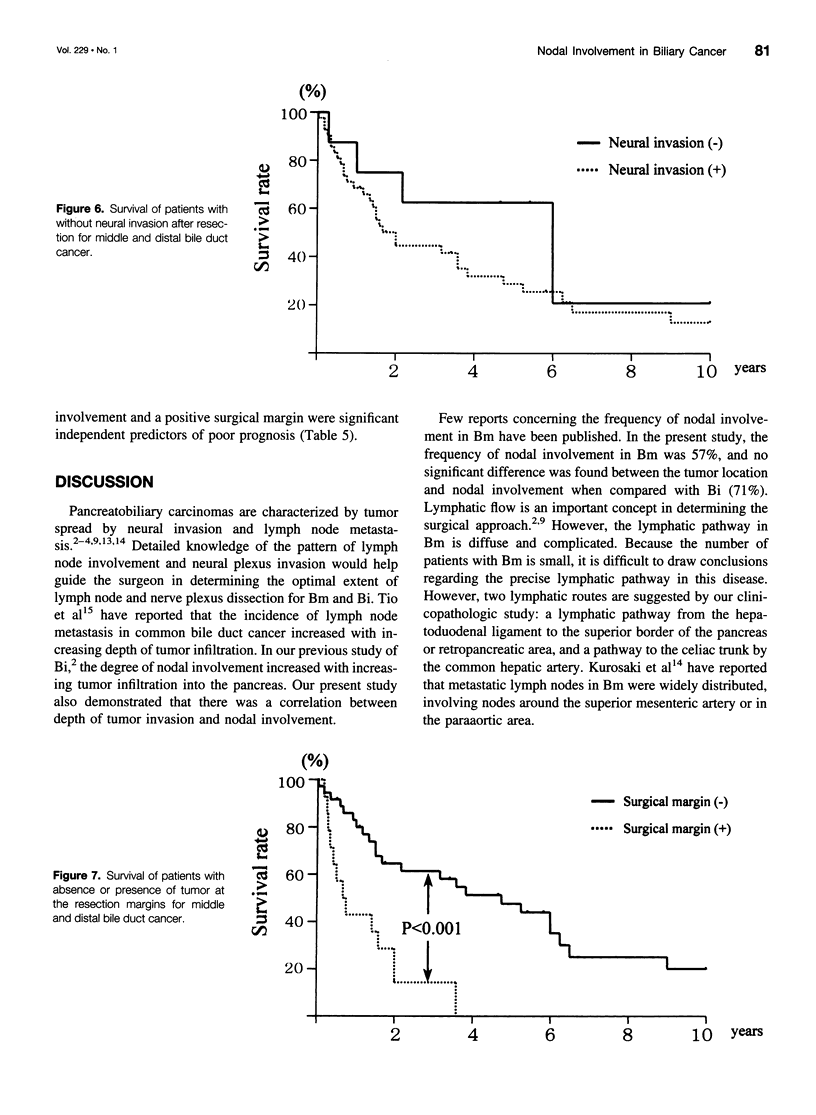
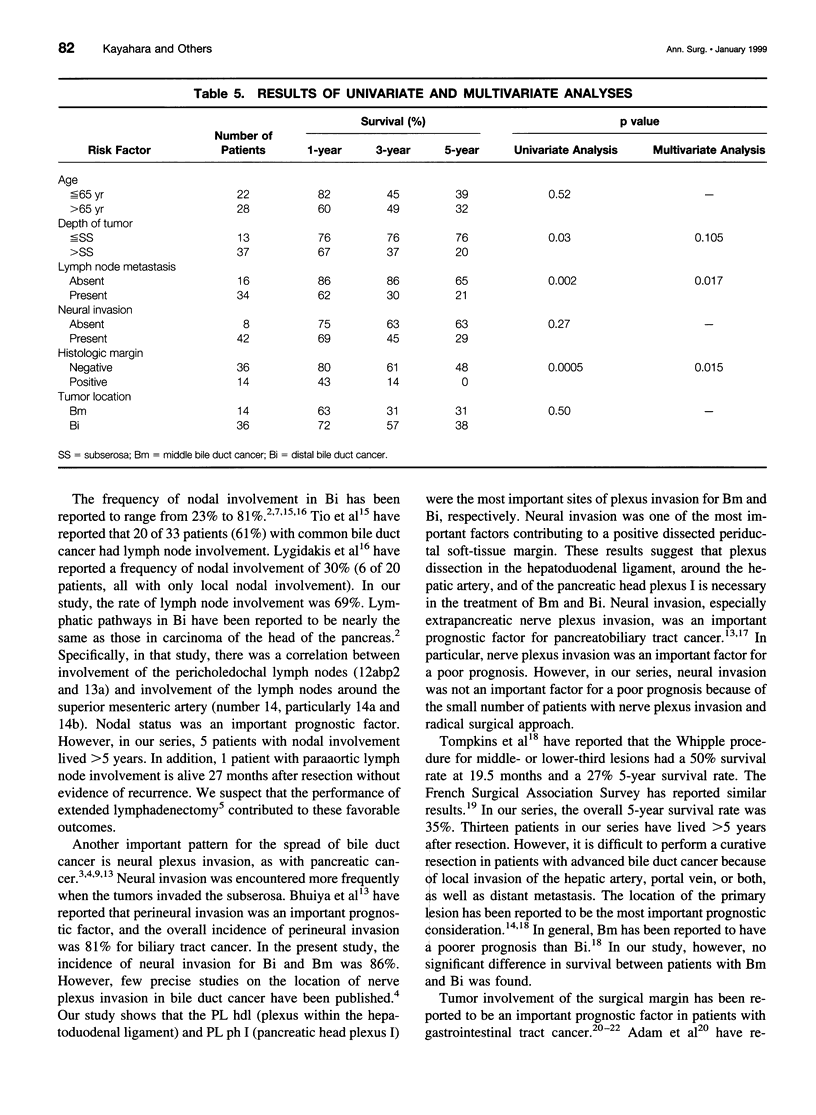
Abstract
OBJECTIVE: To determine the pattern of middle (Bm) and distal (Bi) bile duct cancers in an attempt to optimize surgical treatment. SUMMARY BACKGROUND DATA: Lymph node involvement and neural plexus invasion are the prognostic factors most amenable to surgery in Bm and Bi disease. However, a detailed analysis of these factors has not been conducted. METHODS: Fifty patients with Bm and Bi disease (Bm 14 patients, Bi 36 patients) were examined histopathologically. A precise determination was made of lymph node involvement and neural plexus invasion. Important prognostic factors were examined by clinicopathologic study to apply these findings to surgical management. RESULTS: Frequencies of nodal involvement for Bm and Bi disease were 57% and 71%, respectively. The inferior periductal and superior pancreaticoduodenal lymph nodes were most commonly involved. Neural plexus invasion occurred in 20% of patients, particularly involving the plexus in the hepatoduodenal ligament and pancreatic head. Tumor was present at the surgical margin in 50% and 14% of patients with Bm and Bi disease, respectively. Five-year survival rates were 65% in the absence of nodal metastasis and 21% with nodal metastasis. A significant correlation existed between absence of tumor at the surgical margin and survival. A Cox proportional hazard model projected absence of tumor at the surgical margin, followed by nodal involvement, as the strongest prognostic variables. CONCLUSIONS: Absence of tumor at the surgical margin and nodal involvement are important independent prognostic factors in Bm and Bi disease. Skeletonization of the hepatoduodenal ligament, including portal vein resection, is necessary for patients with Bm disease, and a wide nodal dissection is essential in all patients.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adam I. J., Mohamdee M. O., Martin I. G., Scott N., Finan P. J., Johnston D., Dixon M. F., Quirke P. Role of circumferential margin involvement in the local recurrence of rectal cancer. Lancet. 1994 Sep 10;344(8924):707–711. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(94)92206-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhuiya M. R., Nimura Y., Kamiya J., Kondo S., Fukata S., Hayakawa N., Shionoya S. Clinicopathologic studies on perineural invasion of bile duct carcinoma. Ann Surg. 1992 Apr;215(4):344–349. doi: 10.1097/00000658-199204000-00007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kayahara M., Nagakawa T., Futagami F., Kitagawa H., Ohta T., Miyazaki I. Lymphatic flow and neural plexus invasion associated with carcinoma of the body and tail of the pancreas. Cancer. 1996 Dec 15;78(12):2485–2491. doi: 10.1002/(sici)1097-0142(19961215)78:12<2485::aid-cncr6>3.0.co;2-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kayahara M., Nagakawa T., Konishi I., Ueno K., Ohta T., Miyazaki I. Clinicopathological study of pancreatic carcinoma with particular reference to the invasion of the extrapancreatic neural plexus. Int J Pancreatol. 1991 Oct;10(2):105–111. doi: 10.1007/BF02924113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kayahara M., Nagakawa T., Tsukioka Y., Ohta T., Ueno K., Miyazaki I. Neural invasion and nodal involvement in distal bile duct cancer. Hepatogastroenterology. 1994 Apr;41(2):190–194. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurosaki I., Tsukada K., Hatakeyama K., Muto T. The mode of lymphatic spread in carcinoma of the bile duct. Am J Surg. 1996 Sep;172(3):239–243. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9610(96)00156-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langer J. C., Langer B., Taylor B. R., Zeldin R., Cummings B. Carcinoma of the extrahepatic bile ducts: results of an aggressive surgical approach. Surgery. 1985 Oct;98(4):752–759. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lygidakis N. J., van der Heyde M. N., van Dongen R. J., Kromhout J. G., Tytgat G. N., Huibregtse K. Surgical approaches for unresectable primary carcinoma of the hepatic hilus. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1988 Feb;166(2):107–114. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michelassi F., Erroi F., Dawson P. J., Pietrabissa A., Noda S., Handcock M., Block G. E. Experience with 647 consecutive tumors of the duodenum, ampulla, head of the pancreas, and distal common bile duct. Ann Surg. 1989 Oct;210(4):544–556. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198910000-00015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mimura H., Kim H., Ochiai Y., Takakura N., Hamazaki K., Tsuge H., Sakagami K., Orita K. Radical block resection of hepatoduodenal ligament for carcinoma of the bile duct with double catheter bypass for portal circulation. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1988 Dec;167(6):527–529. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagakawa T., Kurachi M., Konishi K., Miyazaki I. Translateral retroperitoneal approach in radical surgery for pancreatic carcinoma. Jpn J Surg. 1982;12(3):229–233. doi: 10.1007/BF02469594. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagakawa T., Nagamori M., Futakami F., Tsukioka Y., Kayahara M., Ohta T., Ueno K., Miyazaki I. Results of extensive surgery for pancreatic carcinoma. Cancer. 1996 Feb 15;77(4):640–645. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakao A., Harada A., Nonami T., Kaneko T., Takagi H. Clinical significance of carcinoma invasion of the extrapancreatic nerve plexus in pancreatic cancer. Pancreas. 1996 May;12(4):357–361. doi: 10.1097/00006676-199605000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reding R., Buard J. L., Lebeau G., Launois B. Surgical management of 552 carcinomas of the extrahepatic bile ducts (gallbladder and periampullary tumors excluded). Results of the French Surgical Association Survey. Ann Surg. 1991 Mar;213(3):236–241. doi: 10.1097/00000658-199103000-00010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tio T. L., Cheng J., Wijers O. B., Sars P. R., Tytgat G. N. Endosonographic TNM staging of extrahepatic bile duct cancer: comparison with pathological staging. Gastroenterology. 1991 May;100(5 Pt 1):1351–1361. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tompkins R. K., Thomas D., Wile A., Longmire W. P., Jr Prognostic factors in bile duct carcinoma: analysis of 96 cases. Ann Surg. 1981 Oct;194(4):447–457. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198110000-00008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willett C. G., Lewandrowski K., Warshaw A. L., Efird J., Compton C. C. Resection margins in carcinoma of the head of the pancreas. Implications for radiation therapy. Ann Surg. 1993 Feb;217(2):144–148. doi: 10.1097/00000658-199302000-00008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YOSHIOKA H., WAKABAYASHI T. Therapeutic neurotomy on head of pancreas for relief of pain due to chronic pancreatitis; a new technical procedure and its results. AMA Arch Surg. 1958 Apr;76(4):546–554. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1958.01280220066013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


