Abstract
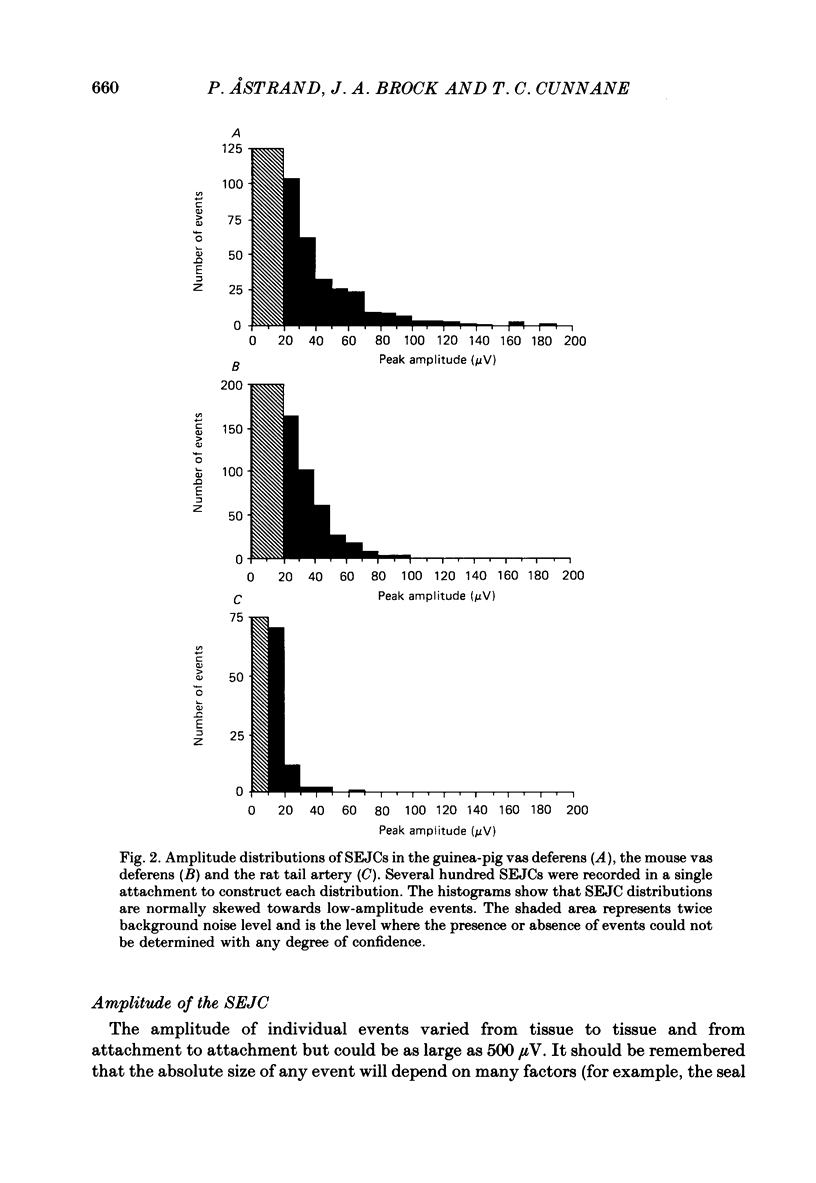
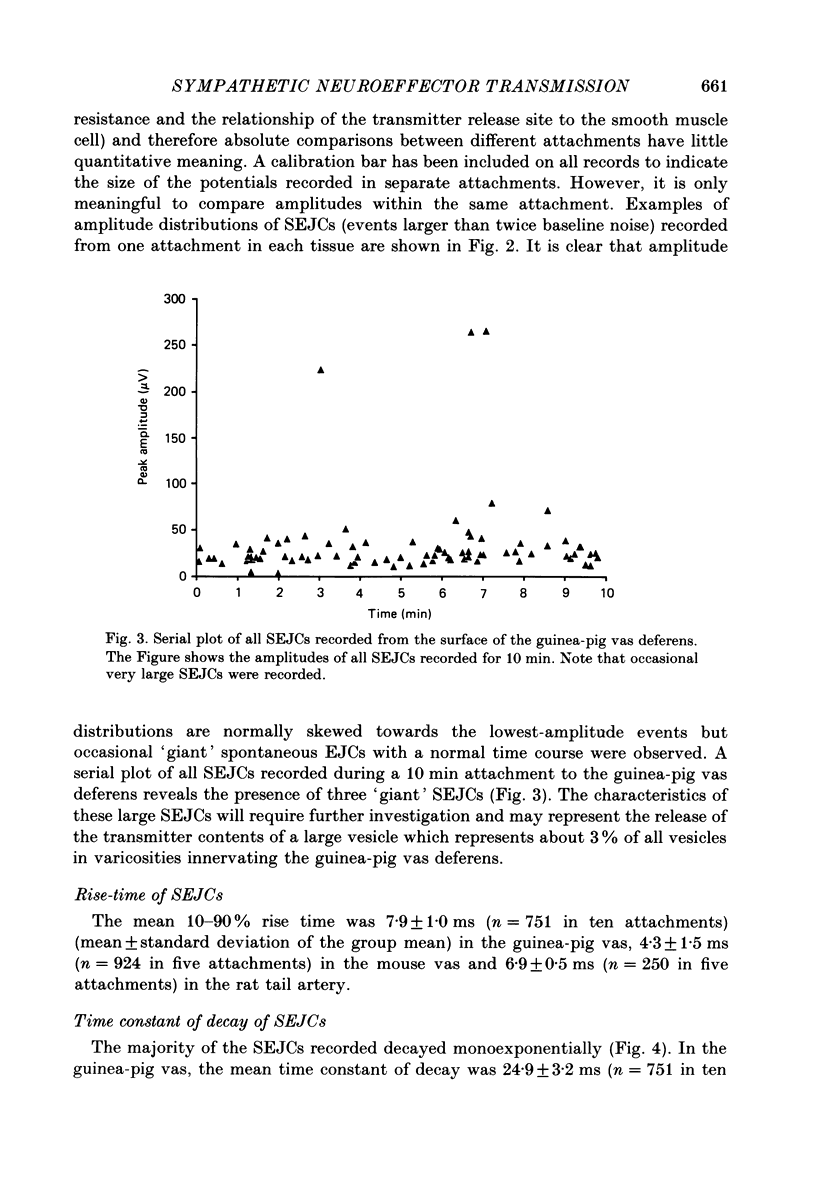
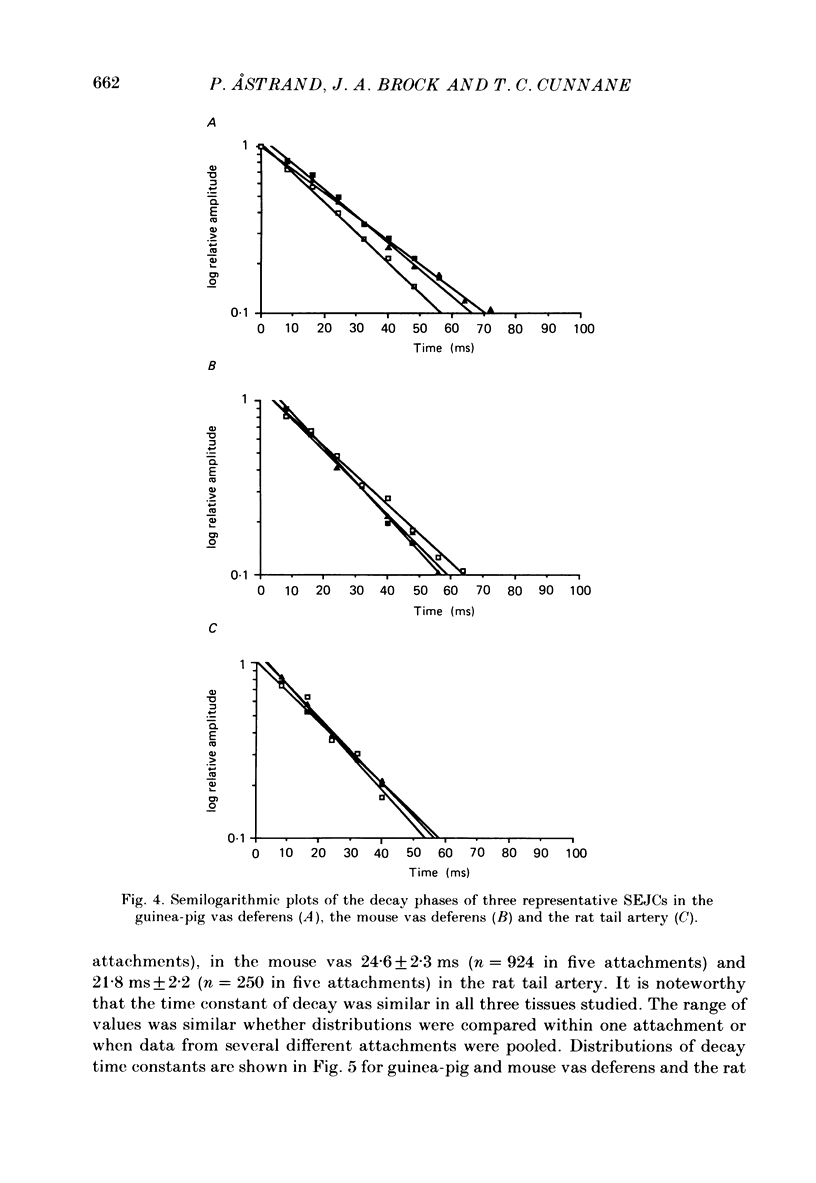
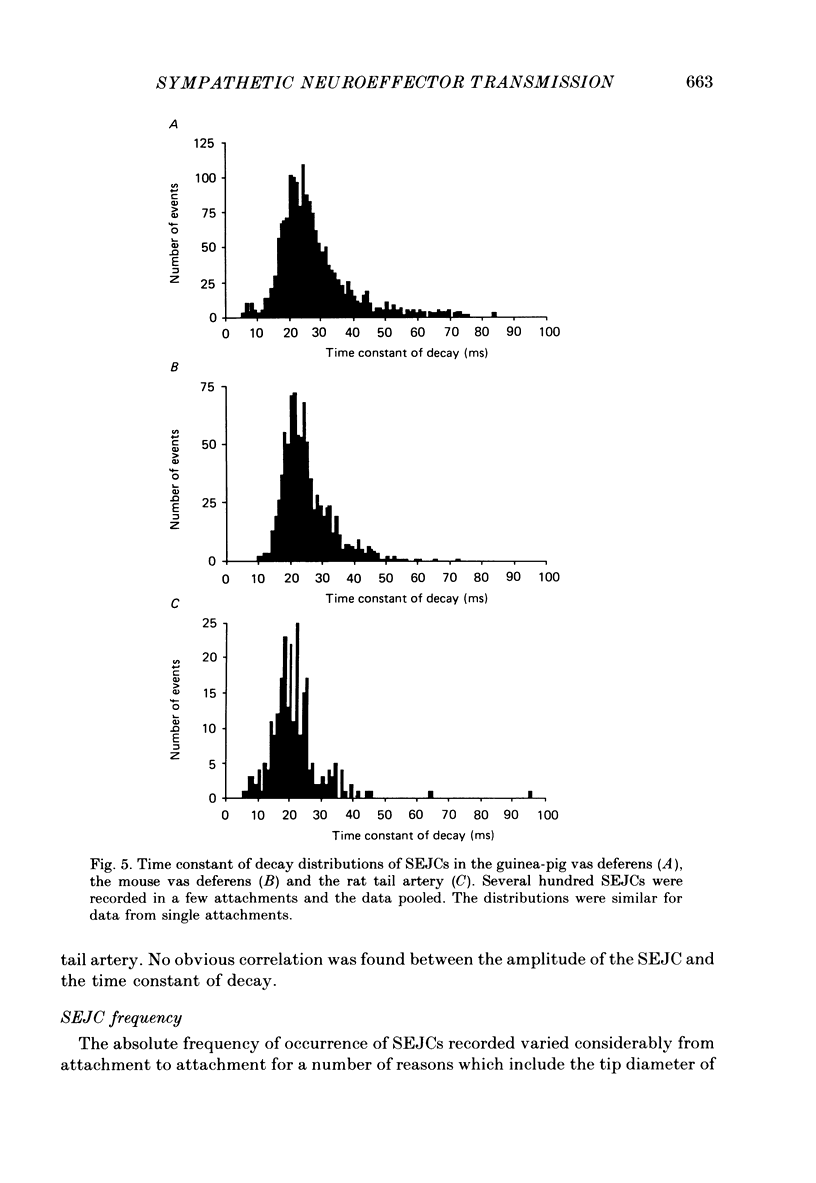
1. Transmitter release from sympathetic postganglionic nerve terminals innervating the guinea-pig and mouse vas deferens and the rat tail artery has been studied in vitro by focal extracellular recording with particular emphasis on the time course of transmitter action underlying the intracellular potential changes. 2. In the absence of stimulation, spontaneous excitatory junction currents (SEJCs) were recorded with amplitudes up to 500 microV and durations between 40 and 100 ms. SEJCs were unaffected by the competitive alpha-adrenoceptor antagonist prazosin but blocked by alpha, beta-methylene ATP which desensitizes P2-purinoceptors. 3. During trains of supramaximal stimuli at 0.1-4 Hz stimulus locked excitatory junction currents (EJCs) were evoked intermittently from the population of varicosities located under the suction electrode. 4. SEJCs were similar in amplitude and time course to EJCs evoked by low-frequency stimulation in the same attachment in all three tissues. 5. SEJCs recorded using either a conventional AC amplifier or a patch clamp amplifier had the same time course. 6. These studies show that the time course of the current underlying the excitatory junction potential is brief and essentially the same in three different tissues. The prolonged time course of the excitatory junction potential in different tissues can be accounted for by the passive membrane properties.
Full text
PDF


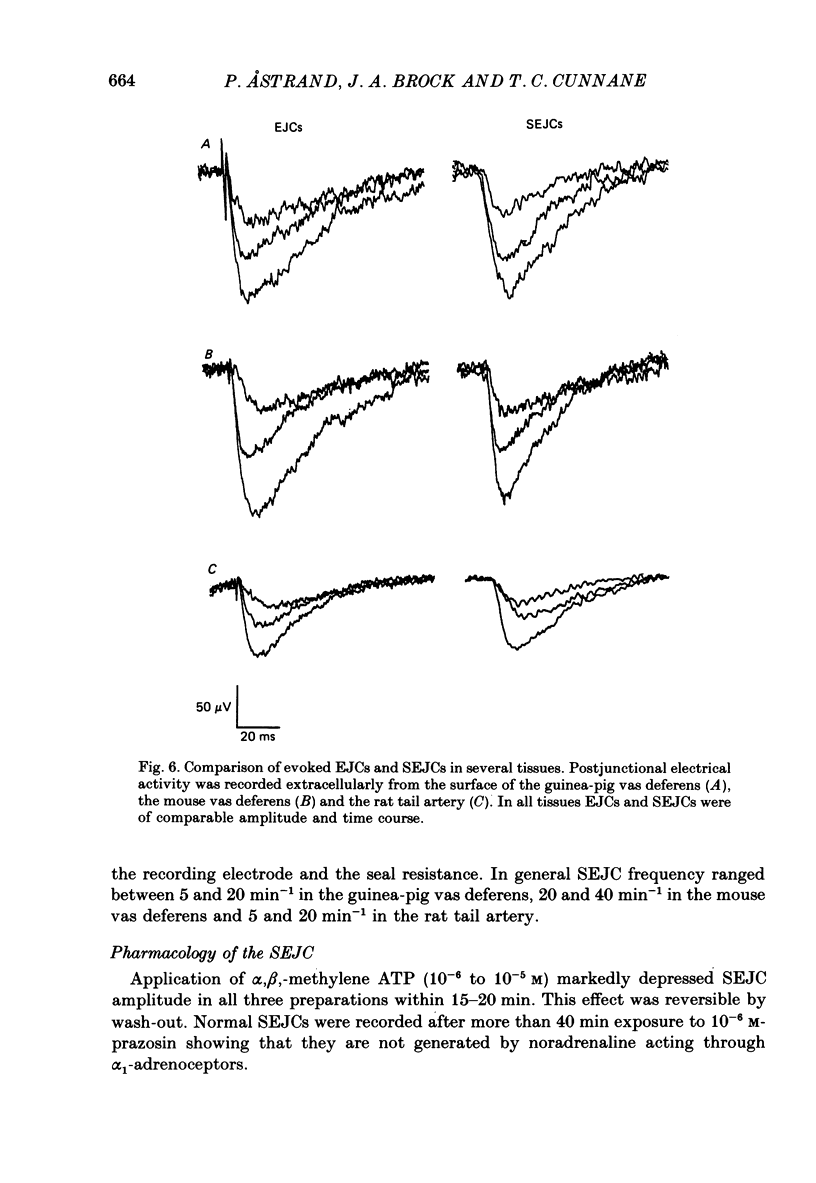

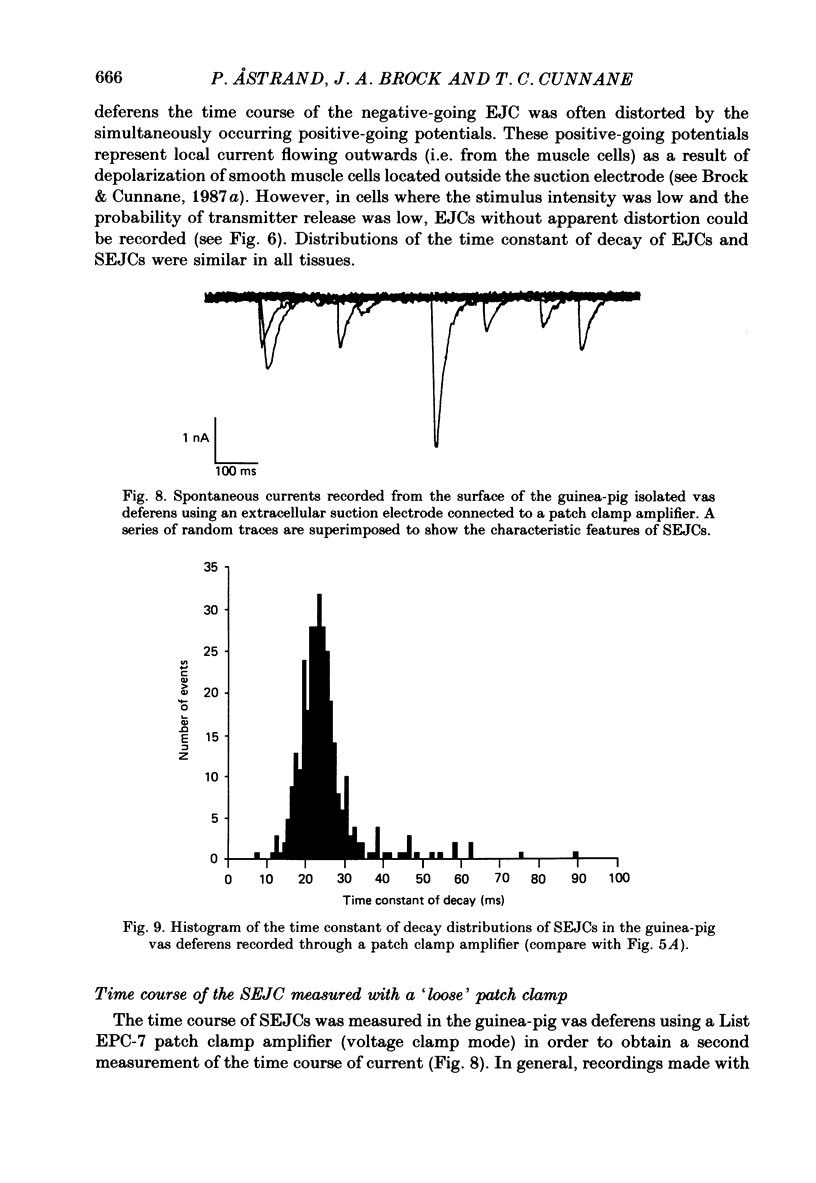
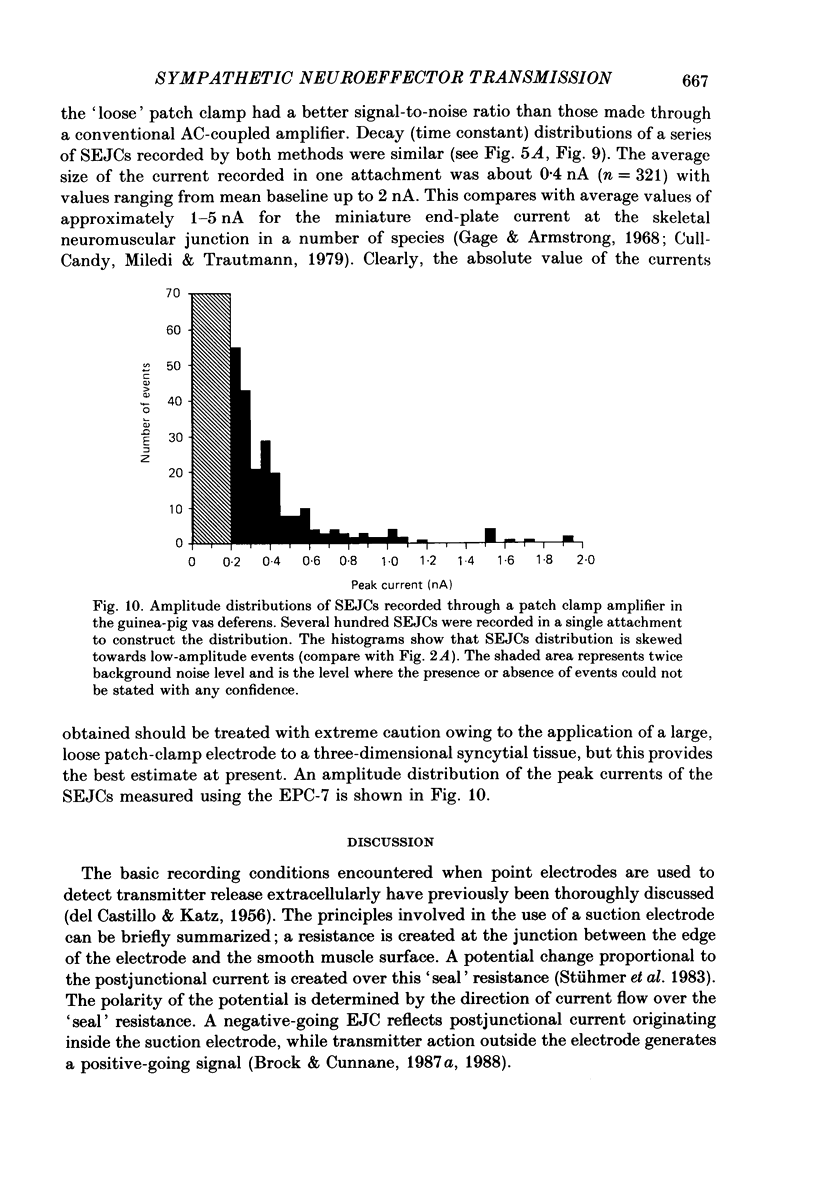



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allcorn R. J., Cunnane T. C., Kirkpatrick K. Actions of alpha, beta-methylene ATP and 6-hydroxydopamine on sympathetic neurotransmission in the vas deferens of the guinea-pig, rat and mouse: support for cotransmission. Br J Pharmacol. 1986 Dec;89(4):647–659. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1986.tb11169.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURNSTOCK G., HOLMAN M. E. Spontaneous potential at sympathetic nerve endings in smooth muscle. J Physiol. 1962 Mar;160:446–460. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1962.sp006858. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURNSTOCK G., HOLMAN M. E. The transmission of excitation from autonomic nerve to smooth muscle. J Physiol. 1961 Jan;155:115–133. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1961.sp006617. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blakeley A. G., Cunnane T. C. The packeted release of transmitter from the sympathetic nerves of the guinea-pig vas deferens: an electrophysiological study. J Physiol. 1979 Nov;296:85–96. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brock J. A., Cunnane T. C. Electrical activity at the sympathetic neuroeffector junction in the guinea-pig vas deferens. J Physiol. 1988 May;399:607–632. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017099. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brock J. A., Cunnane T. C. Relationship between the nerve action potential and transmitter release from sympathetic postganglionic nerve terminals. Nature. 1987 Apr 9;326(6113):605–607. doi: 10.1038/326605a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byrne N. G., Large W. A. The effect of alpha, beta-methylene ATP on the depolarization evoked by noradrenaline (gamma-adrenoceptor response) and ATP in the immature rat basilar artery. Br J Pharmacol. 1986 May;88(1):6–8. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1986.tb09464.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bywater R. A., Taylor G. S. The passive membrane properties and excitatory junction potentials of the guinea pig deferens. J Physiol. 1980 Mar;300:303–316. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cull-Candy S. G., Miledi R., Trautmann A. End-plate currents and acetylcholine noise at normal and myasthenic human end-plates. J Physiol. 1979 Feb;287:247–265. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012657. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunnane T. C., Muir T. C., Wardle K. A. Is co-transmission involved in the excitatory responses of the rat anococcygeus muscle? Br J Pharmacol. 1987 Sep;92(1):39–46. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1987.tb11293.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEL CASTILLO J., KATZ B. Localization of active spots within the neuromuscular junction of the frog. J Physiol. 1956 Jun 28;132(3):630–649. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1956.sp005554. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finkel A. S., Hirst G. D., Van Helden D. F. Some properties of excitatory junction currents recorded from submucosal arterioles of guinea-pig ileum. J Physiol. 1984 Jun;351:87–98. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015234. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fried G. Small noradrenergic storage vesicles isolated from rat vas deferens--biochemical and morphological characterization. Acta Physiol Scand Suppl. 1980;493:1–28. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gage P. W., Armstrong C. M. Miniature end-plate currents in voltage-clamped muscle fibre. Nature. 1968 Apr 27;218(5139):363–365. doi: 10.1038/218363b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirst G. D., Neild T. O. An analysis of excitatory junctional potentials recorded from arterioles. J Physiol. 1978 Jul;280:87–104. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012374. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasakov L., Burnstock G. The use of the slowly degradable analog, alpha, beta-methylene ATP, to produce desensitisation of the P2-purinoceptor: effect on non-adrenergic, non-cholinergic responses of the guinea-pig urinary bladder. Eur J Pharmacol. 1982 Dec 24;86(2):291–294. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(82)90330-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sneddon P., Burnstock G. ATP as a co-transmitter in rat tail artery. Eur J Pharmacol. 1984 Oct 30;106(1):149–152. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(84)90688-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sneddon P., Burnstock G. Inhibition of excitatory junction potentials in guinea-pig vas deferens by alpha, beta-methylene-ATP: further evidence for ATP and noradrenaline as cotransmitters. Eur J Pharmacol. 1984 Apr 13;100(1):85–90. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(84)90318-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sneddon P., Westfall D. P., Fedan J. S. Cotransmitters in the motor nerves of the guinea pig vas deferens: electrophysiological evidence. Science. 1982 Nov 12;218(4573):693–695. doi: 10.1126/science.6291151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sneddon P., Westfall D. P. Pharmacological evidence that adenosine triphosphate and noradrenaline are co-transmitters in the guinea-pig vas deferens. J Physiol. 1984 Feb;347:561–580. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015083. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stjärne L., Astrand P. Discrete events measure single quanta of adenosine 5'-triphosphate secreted from sympathetic nerves of guinea-pig and mouse vas deferens. Neuroscience. 1984 Sep;13(1):21–28. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(84)90256-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Surprenant A. A comparative study of neuromuscular transmission in several mammalian muscular arteries. Pflugers Arch. 1980 Jul;386(1):85–91. doi: 10.1007/BF00584192. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


