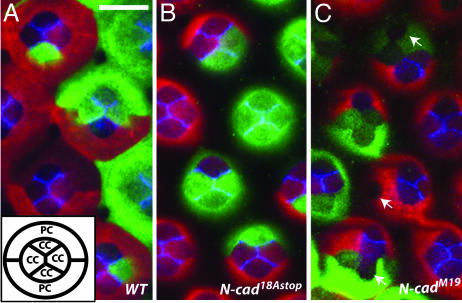
Fig. 5.
Cone cell patterning in midpupal retinas does not require 18A-containing N-cadherin isoforms. (A-C) N-cad phenotypes in clones in midpupal retinas (40-50% APF). (A) (Inset) The arrangement of cone cells (cc) and primary pigment cells (pc) as seen from above. Cells homozygous for a wild-type control (A), N-cad18Astop (B), or N-cadM19 (C) were labeled with GFP (green) using MARCM whereas all other retinal cells expressed RFP (red). Within a single confocal section GFP and RFP staining were occasionally difficult to see in some cone cells. Retinas also were stained with an N-cadherin Ab (blue). (A) N-Cadherin is expressed in cone cells but not pigment cells and localizes to regions of contact between cone cells. (Scale bar, 10 μm.) (C) When one or more cone cells in a cluster lacks N-cadherin their precise packing is disrupted. Frequently, N-cadherin-positive and -negative cone cells separate from each other (arrows). (A and B) In contrast, cone cell arrangements and N-Cadherin staining in clones of N-cad18Astop (B) were indistinguishable from wild type (A).