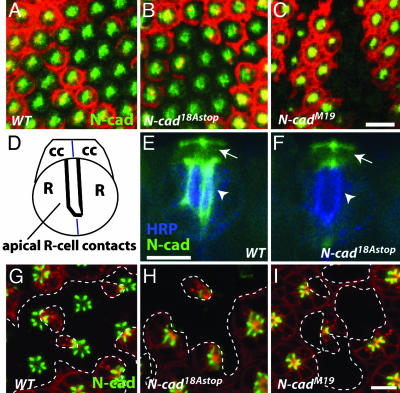
Fig. 6.
N-cadherin isoform expression changes during pupal development. Anti-N-cadherin staining (green) was examined in retinal clones [marked by loss of RFP (red)] homozygous for the indicated mutations. (A-C) Horizontal confocal sections through the apical region of early pupal eye discs (≈20%APF) show N-cadherin staining in wild-type (A) and N-cad18AStop (B), but not in N-cadM19 (C) clones. (Scale bars, 10 μm.) (D) Schematic of R cells (R) and cone cells (cc) in midpupal retina (side view). (E and F) At this stage (≈45% APF) N-cadherin is concentrated at apical R cell junctions (now oriented perpendicular to the eye surface along the developing rhabdomere as in D) (arrow-heads). N-cadherin also is localized to cone cells with strong staining at cone cell contacts (arrow). Comparison of N-cad18AStop (F) to wild-type (FRT40) control (E) clones shows a marked reduction of N-cadherin on R cells but not on cone cells. Anti-horseradish peroxidase staining (blue) in (E and F) labels all R cells. (G-I) Horizontal confocal sections of older eye discs (≈45% APF) at the R cell level shows N-cadherin enriched at the apical contacts of neighboring R cells. R8 cells are in a different focal plane and are not shown. Apical N-cadherin staining in N-cad18AStop R cells (H) is strongly reduced, indicating a loss of 18B isoform expression at this stage in development. (I) Control N-cadM19 clones also show no apical N-cadherin. Clone boundaries are marked by dashed lines. (Scale bar, 5 μm.).