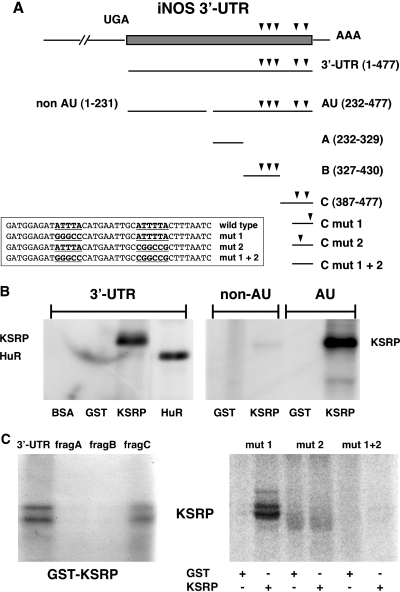
Figure 8.
Analysis of the KSRP binding site in the human iNOS 3′-UTR RNA. Purified BSA, glutathione-S-transferase (GST), and GST-KSRP or GST-HuR fusion proteins were incubated with different radiolabeled RNAs generated by in vitro transcription using the different iNOS 3′-UTR fragments shown in Figure A. After binding, proteins were UV crosslinked to the RNA and the complexes were digested with RNase. RNA–protein complexes were separated on SDS–polyacrylamide gels. (A) Structure of the human iNOS 3′-UTR mRNA and fragments used in RNA binding studies. Scheme of the human iNOS 3′-UTR mRNA (477 nt) and transcripts used in RNA binding studies. The initial UGA nucleotide sequence (−3 to −1) corresponds to the translation termination codon. AUUUA and AUUUUA repeats are indicated by arrowheads. The sequences of different mutations in fragment C are shown. (B) KSRP binds to the AU-fragment of the human iNOS 3′-UTR. 32P-radiolabeled RNA transcripts [3′-UTR; non-AU; AU; see (A)] were incubated with BSA, GST, GST-KSRP fusion protein (KSRP) or GST-HuR fusion protein (HuR). The positions of RNA–protein complexes are indicated. (C) KSRP binds to the most 3′-located ARE in the human iNOS 3′-UTR. 32P-radiolabeled 3′-UTR, subfragment A (232–319, frag A), subfragment B (317–420; frag B) or subfragment C (387–477; frag C) were incubated with GST-KSRP (GST-KSRP) protein. The positions of RNA–protein complexes are indicated (left side). 32P-radiolabeled RNA transcripts (5′-ARE mutated: mut 1; 3′-ARE mutated: mut 2; both AREs mutated: mut 1 + 2) were incubated with either GST or GST-KSRP fusion protein (KSRP). The positions of RNA–protein complexes are indicated (right side).