Abstract
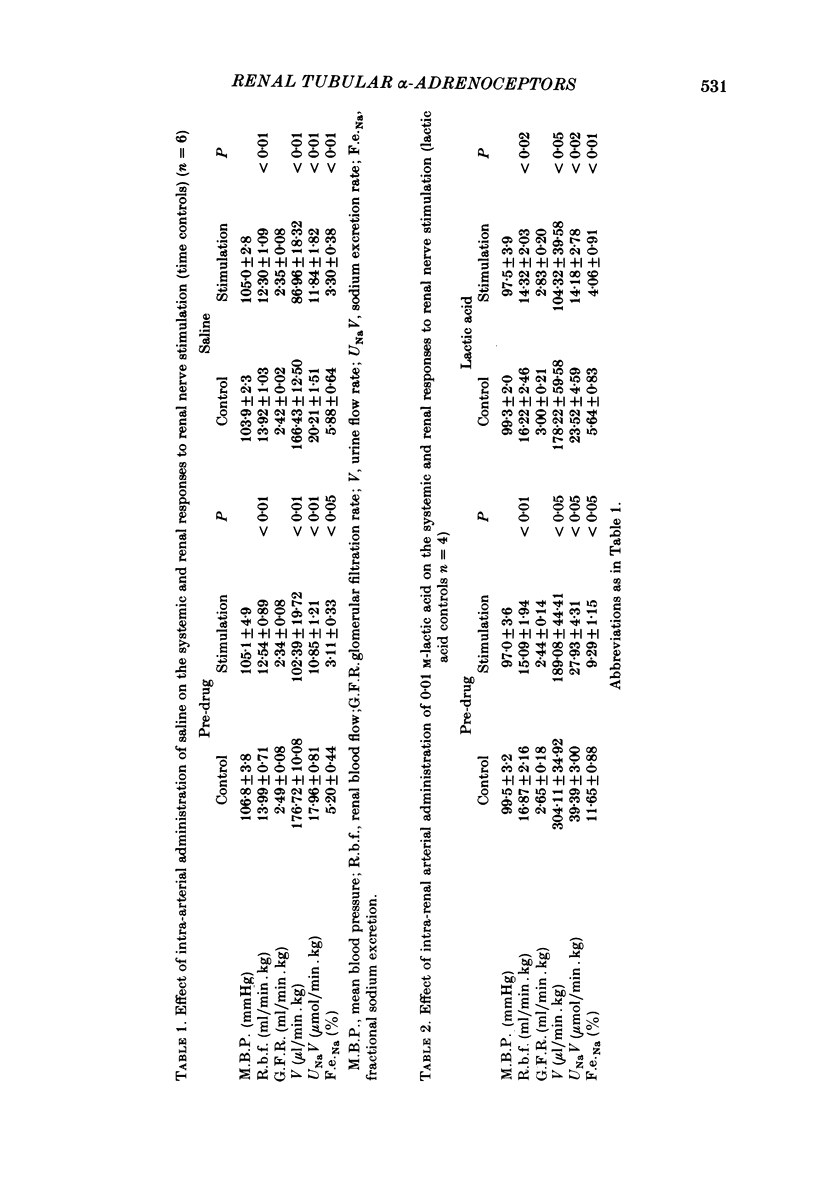
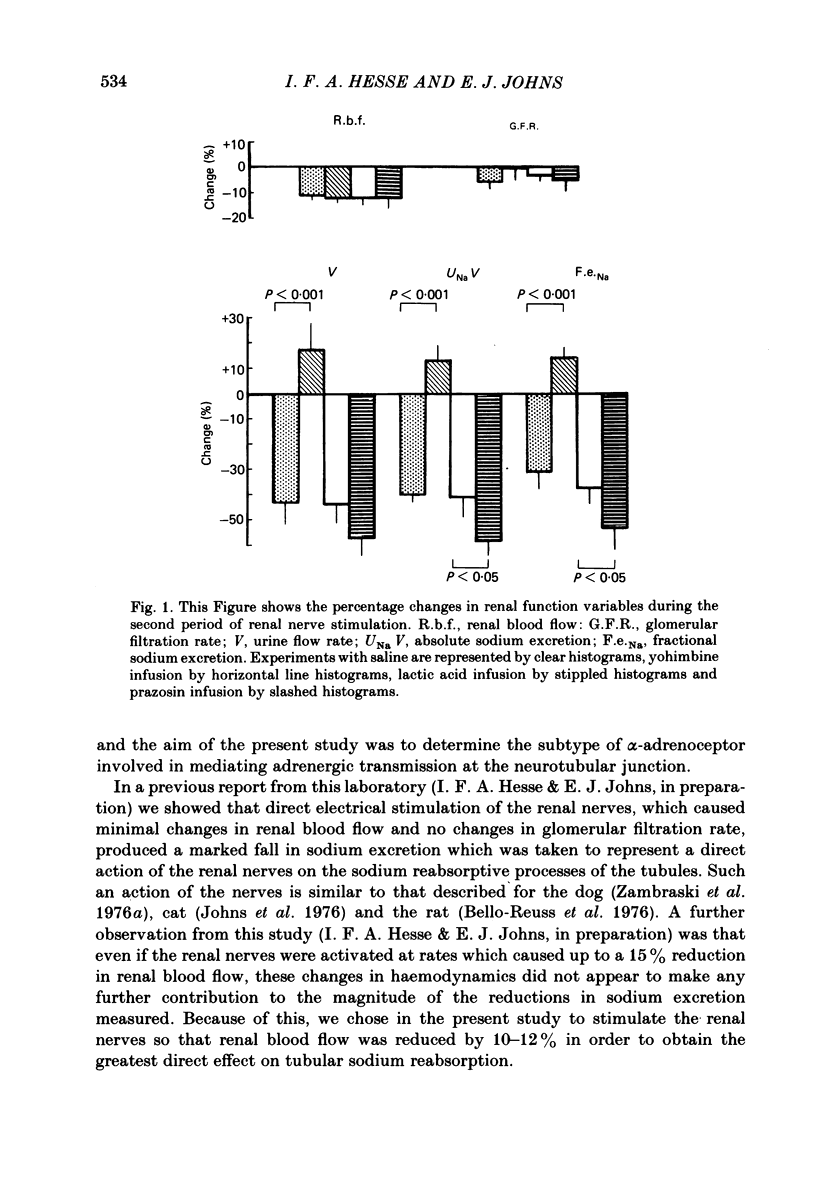
A study was undertaken in pentobarbitone anaesthetized rabbits, undergoing a saline diuresis, to determine the subtype of alpha-adrenoceptor mediating renal tubular sodium reabsorption. Stimulation of the renal nerves at low rates, to cause an 11% fall in renal blood flow, did not change glomerular filtration rate but significantly reduced urine flow rate, and absolute and fractional sodium excretions by approximately 40%. These responses were reproducible in different groups of animals and with time. Renal nerve stimulation during an intra-renal arterial infusion of prazosin, to block alpha 1-adrenoceptors, had no effect on the renal haemodynamic response but completely abolished the reductions in urine flow rate, and absolute and fractional sodium excretion. During intra-renal arterial infusion of yohimbine, to block renal alpha 2-adrenoceptors, stimulation of the renal nerves to cause similar renal haemodynamic changes resulted in significantly larger reductions in urine flow rate, and absolute and fractional sodium excretion of about 52-58%. These results indicate that in the rabbit alpha 1-adrenoceptors are present on the renal tubules, which mediate the increase in sodium reabsorption caused by renal nerve stimulation. They further suggest the presence of presynaptic alpha 2-adrenoceptors on those nerves innervating the renal tubules.
Full text
PDF









Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson R. J., Henrich W. L., Gross P. A., Dillingham M. A. Role of renal nerves, angiotensin II, and prostaglandins in the antinatriuretic response to acute hypercapnic acidosis in the dog. Circ Res. 1982 Feb;50(2):294–300. doi: 10.1161/01.res.50.2.294. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOJESEN E. A method for determination of inulin in plasma and urine. Acta Med Scand Suppl. 1952;266:275–282. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1952.tb13376.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barajas L. Innervation of the renal cortex. Fed Proc. 1978 Apr;37(5):1192–1201. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell-Reuss E., Trevino D. L., Gottschalk C. W. Effect of renal sympathetic nerve stimulation on proximal water and sodium reabsorption. J Clin Invest. 1976 Apr;57(4):1104–1107. doi: 10.1172/JCI108355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berry C. A. Heterogeneity of tubular transport processes in the nephron. Annu Rev Physiol. 1982;44:181–201. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.44.030182.001145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunton J., Parsons B. J., Poat J. A. Possible involvement of noradrenaline in the response of rat kidney cortex slices to angiotensin [proceedings]. J Physiol. 1978 Nov;284:73P–74P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiBona G. F., Johns E. J. A study of the role of renal nerves in the renal responses to 60 degree head-up tilt in the anaesthetized dog. J Physiol. 1980 Feb;299:117–126. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiBona G. F., Sawin L. L. Effect of renal nerve stimulation on NaCl and H2O transport in Henle's loop of the rat. Am J Physiol. 1982 Dec;243(6):F576–F580. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1982.243.6.F576. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johns E. J. A comparison of the ability of two angiotensin II receptor blocking drugs, 1-Sar; 8-Ala angiotensin II and 1-Sar, 8-Ile angiotensin II, to modify the regulation of glomerular filtration rate in the cat. Br J Pharmacol. 1980;71(2):499–506. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1980.tb10963.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johns E. J. Action of angiotensin I converting enzyme inhibitor on the control of renal function in the cat. Clin Sci (Lond) 1979 Apr;56(4):365–371. doi: 10.1042/cs0560365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johns E. J., Lewis B. A., Singer B. The sodium-retaining effect of renal nerve activity in the cat: role of angiotensin formation. Clin Sci Mol Med. 1976 Jul;51(1):93–102. doi: 10.1042/cs0510093. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessar P., Saggerson E. D. Evidence that catecholamines stimulate renal gluconeogenesis through an alpha 1-type of adrenoceptor. Biochem J. 1980 Jul 15;190(1):119–123. doi: 10.1042/bj1900119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lameire N. H., Lifschitz M. D., Stein J. H. Heterogeneity of nephron function. Annu Rev Physiol. 1977;39:159–184. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.39.030177.001111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langer S. Z. Sixth gaddum memorial lecture, National Institute for Medical Research, Mill Hill, January 1977. Presynaptic receptors and their role in the regulation of transmitter release. Br J Pharmacol. 1977 Aug;60(4):481–497. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1977.tb07526.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McPherson G. A., Summers R. J. A study of alpha 1-adrenoceptors in rat renal cortex: comparison of [3H]-prazosin binding with the alpha 1-adrenoceptor modulating gluconeogenesis under physiological conditions. Br J Pharmacol. 1982 Sep;77(1):177–184. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1982.tb09284.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McPherson G. A., Summers R. J. [3H]prazosin and [3H]clonidine binding to alpha-adrenoceptors in membranes prepared from regions of rat kidney. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1981 Mar;33(3):189–191. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1981.tb13752.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelayo J. C., Ziegler M. G., Jose P. A., Blantz R. C. Renal denervation in the rat: analysis of glomerular and proximal tubular function. Am J Physiol. 1983 Jan;244(1):F70–F77. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1983.244.1.F70. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saggerson E. D., Kessar P., Carpenter C. A. Regulation of renal gluconeogenesis by alpha-adrenergic action. Int J Biochem. 1980;12(1-2):107–111. doi: 10.1016/0020-711x(80)90051-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid H., Scholz M., Mall A., Schmidt U., Guder W. G., Dubach U. C. Carbohydrate metabolism in rat kidney: heterogeneous distribution of glycolytic and gluconeogenic key enzymes. Curr Probl Clin Biochem. 1977 Oct 23;8:282–289. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitz J. M., Graham R. M., Sagalowsky A., Pettinger W. A. Renal alpha-1 and alpha-2 adrenergic receptors: biochemical and pharmacological correlations. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1981 Nov;219(2):400–406. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slick G. L., Aguilera A. J., Zambraski E. J., DiBona G. F., Kaloyanides G. J. Renal neuroadrenergic transmission. Am J Physiol. 1975 Jul;229(1):60–65. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1975.229.1.60. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starke K. Alpha-adrenoceptor subclassification. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 1981;88:199–236. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starke K. Presynaptic receptors. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1981;21:7–30. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.21.040181.000255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker L. A., Valtin H. Biological importance of nephron heterogeneity. Annu Rev Physiol. 1982;44:203–219. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.44.030182.001223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zambraski E. J., DiBona G. F. Angiotensin II in antinatriuresis of low-level renal nerve stimulation. Am J Physiol. 1976 Oct;231(4):1105–1110. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1976.231.4.1105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zambraski E. J., DiBona G. F., Kaloyanides G. J. Specificity of neural effect on renal tubular sodium reabsorption. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1976 Mar;151(3):543–546. doi: 10.3181/00379727-151-39254. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zambraski E. J., Dibona G. F., Kaloyanides G. J. Effect of sympathetic blocking agents on the antinatriuresis of reflex renal nerve stimulation. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1976 Aug;198(2):464–472. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


