Abstract
Experiments were performed to ascertain whether the monotonic (q beta) and delayed (q gamma) components of non-linear charge in skeletal muscle membranes form a sequential system, or are the result of separate, independent processes. The non-linear capacitance studied in a large number of fibres increased with fibre diameter. This dependence was attributable to tetracaine-sensitive (q gamma) but not to tetracaine-resistant (q beta and q alpha) charge. The kinetics and total quantity of q gamma charge moving in response to voltage steps from varying pre-pulse potentials to a fixed probe potential remained constant despite variations in the size of the early q beta decay. The kinetics of the delayed (q gamma) charging current obtained from a single 20 mV depolarizing step were compared with the sum of the responses to two 10 mV steps adding to the same voltage excursion. The respective transients superimposed only if one of the 10 mV steps did not reach the voltage at which q gamma first appears. In the two preceding experiments, total charge was conserved. These results are consistent with separate and functionally independent q beta and q gamma systems of potential-dependent charge, with q gamma residing in the transverse tubules and q beta on surface membrane. The findings can be discussed in terms of a contractile 'activator' with a steep sensitivity to voltage that begins only with depolarization beyond a level close to the actual mechanical threshold.
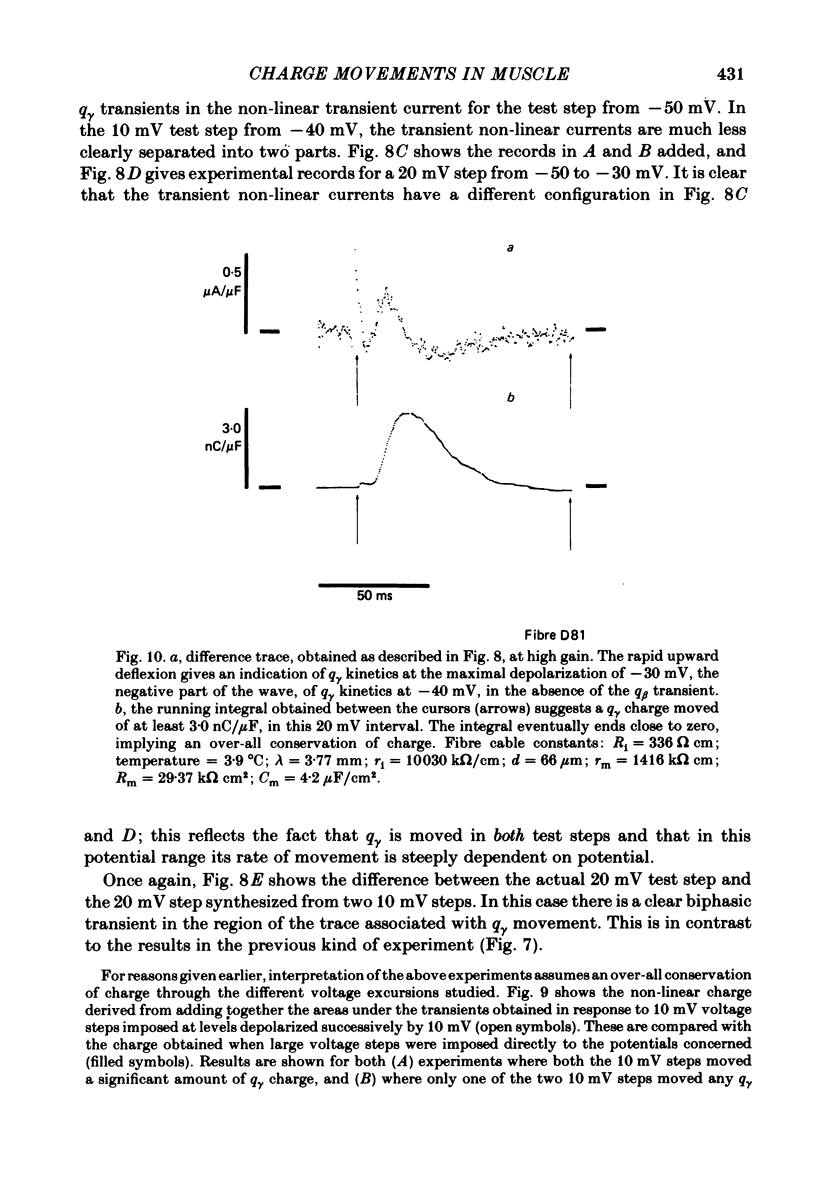
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adrian R. H., Almers W. Charge movement in the membrane of striated muscle. J Physiol. 1976 Jan;254(2):339–360. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adrian R. H., Almers W. Membrane capacity measurements on frog skeletal muscle in media of low ion content. J Physiol. 1974 Mar;237(3):573–605. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adrian R. H., Chandler W. K., Hodgkin A. L. The kinetics of mechanical activation in frog muscle. J Physiol. 1969 Sep;204(1):207–230. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008909. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adrian R. H., Huang C. L. Charge movements near the mechanical threshold in skeletal muscle of Rana temporaria. J Physiol. 1984 Apr;349:483–500. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adrian R. H., Peres A. Charge movement and membrane capacity in frog muscle. J Physiol. 1979 Apr;289:83–97. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012726. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adrian R. H., Rakowski R. F. Reactivation of membrane charge movement and delayed potassium conductance in skeletal muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1978 May;278:533–557. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson W. P., Korner P. I. The importance of renal vascular tone in determining the severity of renal artery stenosis in dogs. J Physiol. 1980 Aug;305:31–41. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caputo C., Fernandez de Bolaños P. Membrane potential, contractile activation and relaxation rates in voltage clamped short muscle fibres of the frog. J Physiol. 1979 Apr;289:175–189. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandler W. K., Rakowski R. F., Schneider M. F. A non-linear voltage dependent charge movement in frog skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1976 Jan;254(2):245–283. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011232. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duane S., Huang C. L. A quantitative description of the voltage-dependent capacitance in frog skeletal muscle in terms of equilibrium statistical mechanics. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1982 Apr 22;215(1198):75–94. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1982.0029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
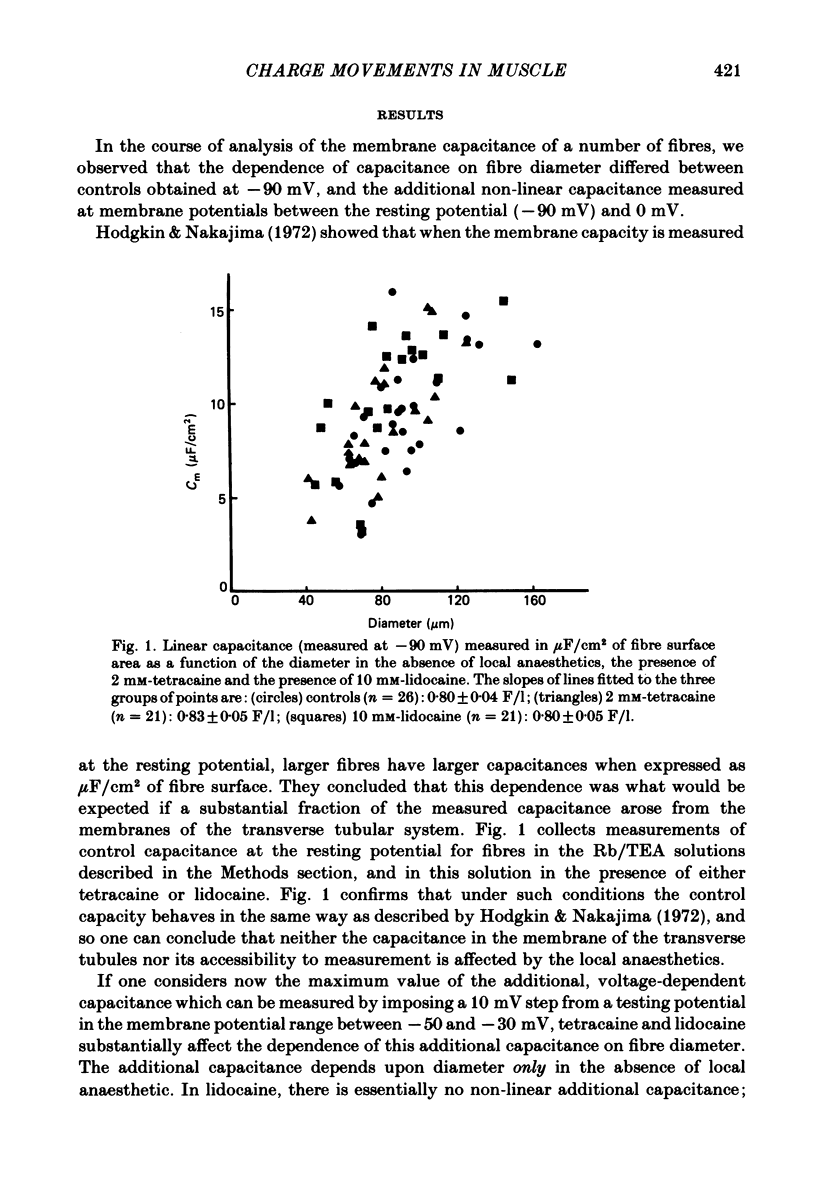
- Hodgkin A. L., Nakajima S. The effect of diameter on the electrical constants of frog skeletal muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1972 Feb;221(1):105–120. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009742. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horowicz P., Schneider M. F. Membrane charge movement in contracting and non-contracting skeletal muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1981 May;314:565–593. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang C. L. Dielectric components of charge movements in skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1981;313:187–205. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013658. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang C. L. Experimental analysis of alternative models of charge movement in frog skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1983 Mar;336:527–543. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014596. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
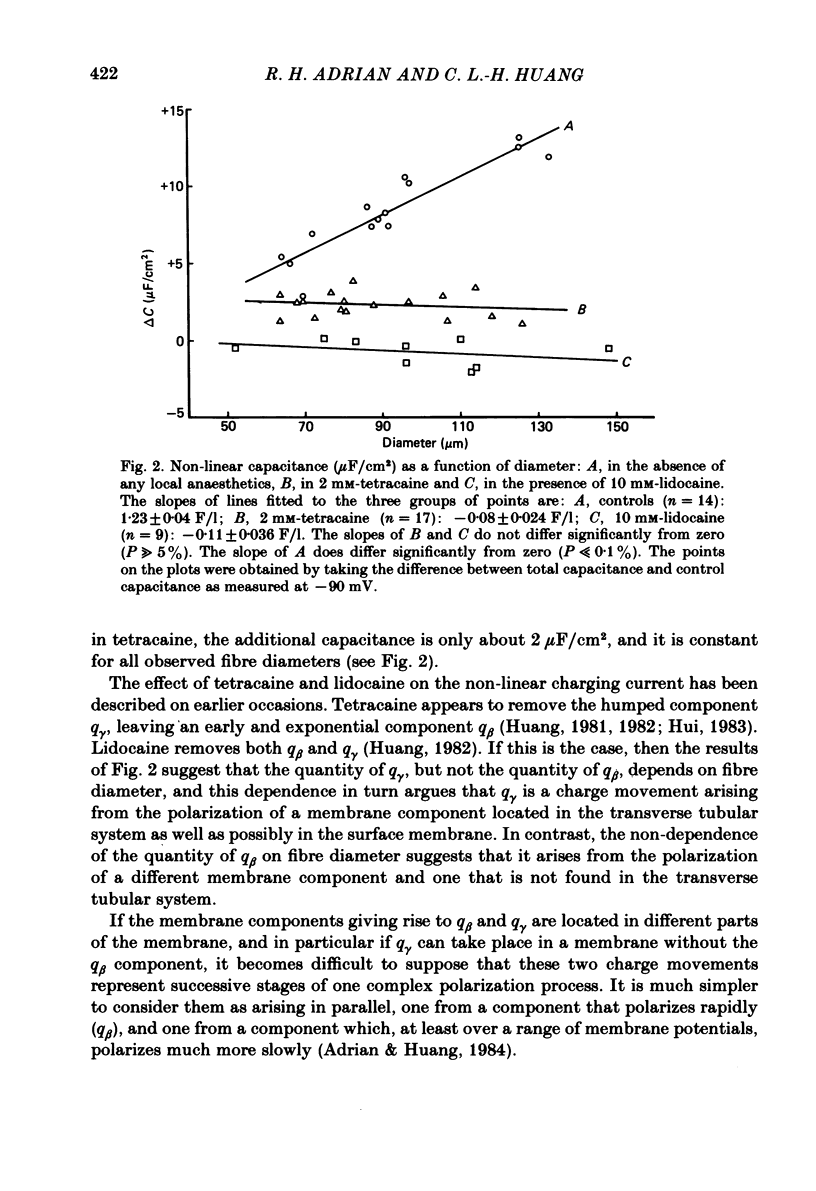
- Huang C. L. Pharmacological separation of charge movement components in frog skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1982 Mar;324:375–387. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang C. L. Time domain spectroscopy of the membrane capacitance in frog skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1983 Aug;341:1–24. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hui C. S. Pharmacological studies of charge movement in frog skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1983 Apr;337:509–529. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider M. F., Chandler W. K. Voltage dependent charge movement of skeletal muscle: a possible step in excitation-contraction coupling. Nature. 1973 Mar 23;242(5395):244–246. doi: 10.1038/242244a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vergara J., Caputo C. Effects of tetracaine on charge movements and calcium signals in frog skeletal muscle fibers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(5):1477–1481. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.5.1477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


