Figure 1.
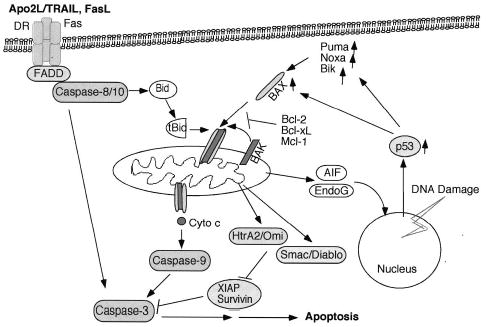
Apoptotic pathways. The death receptor (DR) pathway is activated by ligation of the death ligands (eg, Apo2L/TRAIL [tumor necrosis factor–related apoptosis-inducing factor ligand] and FasL) to their cognate receptors on the cell surface. This process results in sequential binding of Fas-associated death domain (FADD) and pro–caspase 8. Active caspase 8 cleaves and activates caspase 3. In addition, caspase 8 cleaves Bid, and truncated Bid translocates to the mitochondria to promote the release of cytochrome c (Cyto c). The mitochondrial pathway is activated by a number of stimuli, including chemotherapeutic drugs and ionizing radiation (IR). All these stimuli result in activation and oligomerization of Bax and Bak. These changes contribute to pore formation in the outer mitochondrial membrane and the release of cyto c and other apoptogenic factors. Cyto c promotes activation of caspase 9 and of the effector caspases. DNA-damaging agents such as IR induce activation of the p53 that promotes transcription of proapoptotic Bcl-2 family members such as the multidomain Bax and the Bcl-2 homology 3 (BH3)-only proteins Puma, Noxa, and Bik. Activation of the BH3-only molecules either directly or indirectly results in activation of Bax and Bak. AIF indicates apoptosis-inducing factor.
