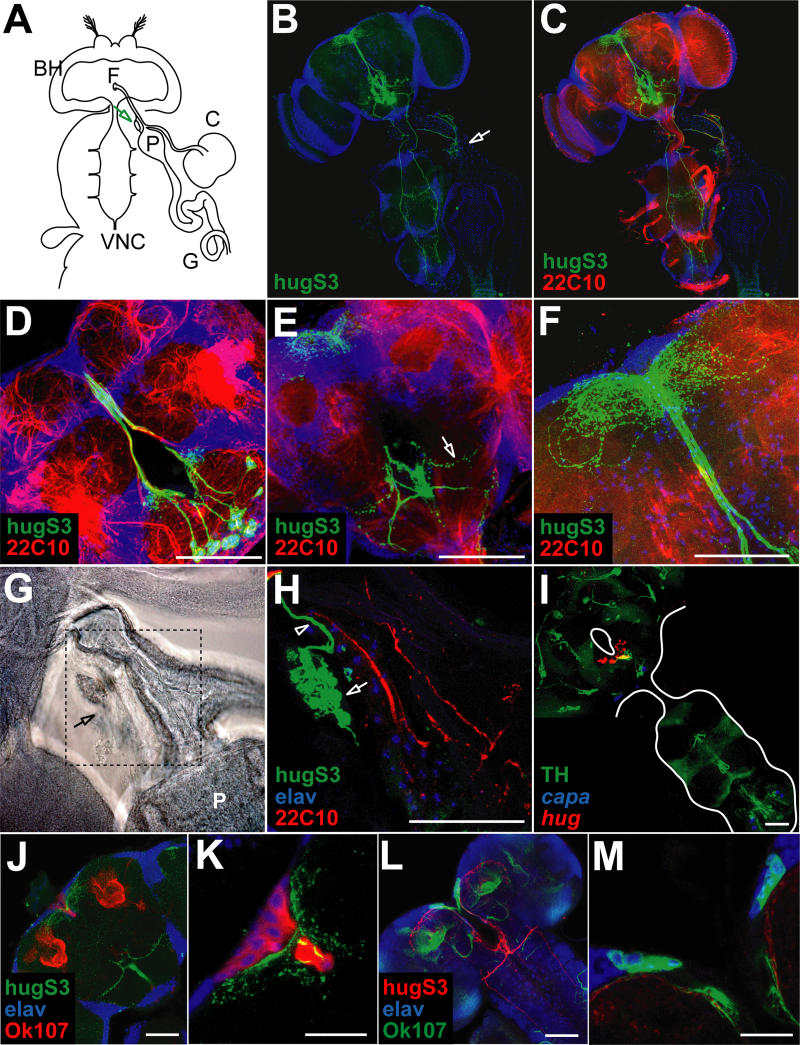
Figure 5. Neuroanatomical Analysis of hug Interneurons in Adults.
(A) Relative positions of adult CNS composed of brain hemispheres (BH) and VNC, as well as esophagus passing the brain through the foramen (F), proventriculus (P), crop (C), and gut (G) are depicted schematically. The neuroendocrine CC/CA complex is located on top of the proventriculus (arrow).
(B) Localization of hug neurons and projections in adult CNS relative to nuclear marker. Note projections to the protocerebrum (top of the head), VNC, and CC/CA (arrow).
(C) hug neuronal projections relative to general neuropil marker (22c10, shown in red).
(D–F) Close-ups of different optical sections (composed of confocal 1- to 2.5-μm sections) show spherical hug arborizations in median SOG region (green in [D]), arborizations in lateral SOG region (green in [E], arrow) and in protocerebrum (green in [F]).
(G) Transmission light image of CC/CA complex (arrow) on top of proventriculus (P).
(H) Immunofluorescent close-up of the area boxed in (G). Nuclei of elav positive CC cells (blue) and of CA (green, see arrow), hug axon terminals (green, see arrowhead).
(I) TH positive SOG neurons (green) co-express hug (red); capa staining serves as morphological landmark.
(J and K) Different optical sections (composed of confocal 1- to 2.5-mm sections) show hug (green) projections above the mushroom bodies and adjacent to the median neurosecretory cells marked by OK107 (mushroom body and median neurosecretory cell marker, red); elav marker, blue. (K) Close-up of the region in (J), showing the medial neurosecretory cells. Scale bars equal 20 μ.
(L and M) Different optical sections (composed of confocal 1-to 2.5-mm sections) showing OK107 (green) and hug (red) in larva. (M) Close-up of the median neurosecretory cell region. Scale bars equal 20 μ.