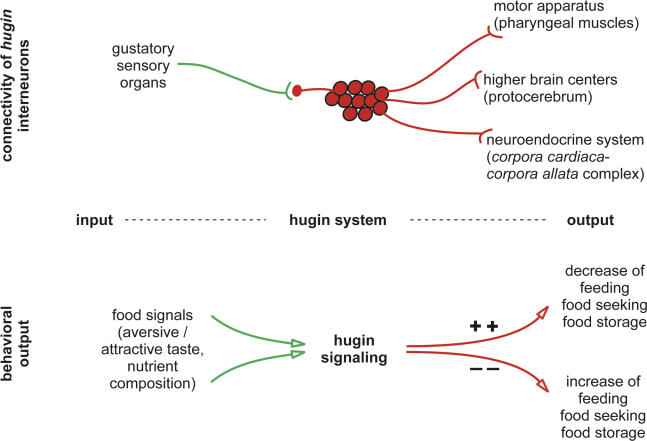
Figure 7. Model of hug as Modulator of Feeding Behavior.
The hug neurons, which express the neuropeptide gene hug and which interconnect gustatory sensillae via the SOG to the pharyngeal muscles, the protocerebrum, and the neuroendocrine organ, modulate chemosensory dependent feeding behavior. Increased hug signaling correlates with decreased feeding, whereas decreased hug signaling correlates with increased feeding (see Discussion section for details).