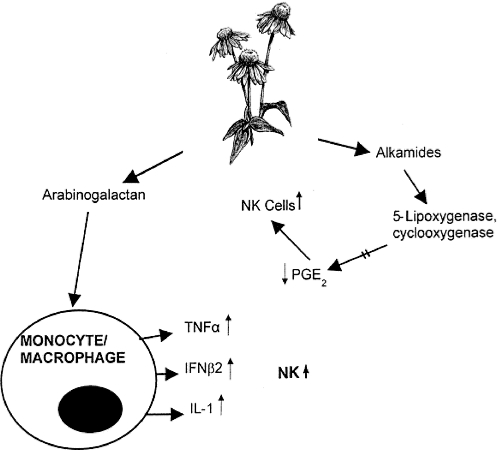
Figure 1.
Contained within Echinacea root extract is a family of complex polysaccharides known as arabinogalactans. These sugars directly stimulate macrophages to produce three cytokines that, in turn, directly stimulate NK cells. The latter respond by means of new NK cell production/numbers and/or increased lytic functional capacity. On the other hand, contained also within Echinacea root extract are a group of molecules known as the alkamides, some of which interact with two key enzymes essential to the production of prostaglandin E2 (PGE2). Normally, PGE2 is suppressive to NK cells. Consequently, when the fundamental enzymes are blocked, PGE2 levels are negligible and NK cells, now free of their suppressors, become increased in numbers and function. Thus, via these two different avenues, i.e. stimulation indirectly through macrophages, and release from suppressor factors (PGE2), whole Echinacea is a powerful NK cell stimulant. The diagram of the Echinacea plant is reproduced with permission from The Herbal Drugstore, LB White & S Foster, Rodale Inc., 2000.