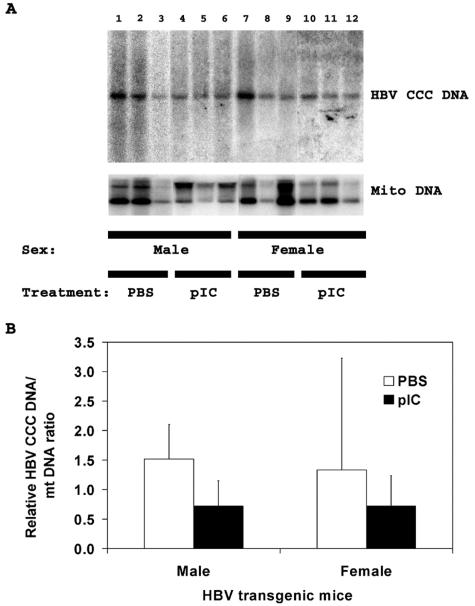
FIG. 5.
DNA (Southern) filter hybridization analysis of HBV CCC DNA replication intermediates and mitochondrial DNA in the livers of HNF1α-null HBV transgenic mice. (A) Groups of three representative mice of each sex are shown. The mitochondrial DNA was used as an internal control for the quantitation of the HBV CCC DNA. The probe used was HBVayw genomic DNA and a mouse mitochondrial DNA fragment. HBV CCC DNA, HBV covalently closed circular DNA; Mito DNA, mouse mitochondrial DNA. Mice were injected with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) or poly(I-C) (pIC). (B) Quantitative analysis of the HBV CCC DNA replication intermediate levels in HNF1α-null HBV transgenic mice. The mean HBV CCC DNA replication intermediate levels plus standard deviations derived from four male HNF1α−/− HBV transgenic mice injected with phosphate-buffered saline, eight male HNF1α−/− HBV transgenic mice injected with poly(I-C), eight female HNF1α−/− HBV transgenic mice injected with phosphate-buffered saline, and nine female HNF1α−/− HBV transgenic mice injected with poly(I-C) are shown. The lower levels of the HBV CCC DNA replication intermediates in the poly(I-C)-injected male but not the female HNF1α-null HBV transgenic mice are statistically significantly different from the levels in the control phosphate-buffered saline-injected HNF1α-null HBV transgenic mice as determined by a Student t test (P < 0.05).