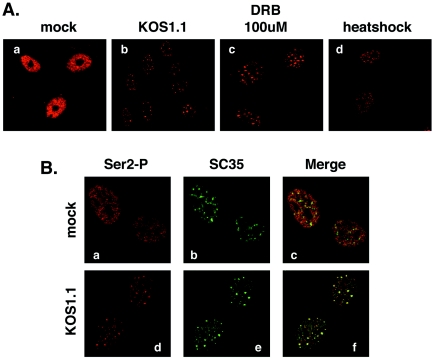
FIG. 7.
Both HSV-1 infection and RNAP II transcription inhibitors cause Ser-2-phosphorylated RNAP II to relocalize to splicing antigen-rich nuclear speckles. (A) Localization of Ser-2-phosphorylated RNAP II after HSV-1 infection or treatments which lead to transcriptional inhibition. Vero cells were mock-infected (a) or infected with HSV-1 KOS1.1 (b) for 6 h. Replicate uninfected cultures were treated with 100 μM DRB for 2 h (c) or subjected to heat shock for 1 h at 45° (d). All samples were processed for immunofluorescence and stained with MAb H5. (B) Foci containing Ser-2-phosphorylated RNAP II after HSV-1 infection correspond to splicing antigen-rich nuclear speckles. Vero cells were mock infected (a to c) or infected for with HSV-1 KOS1.1 for 6 h (d to f). Cells were processed for immunofluorescence with H5 and an antibody specific for splicing factor SC35.