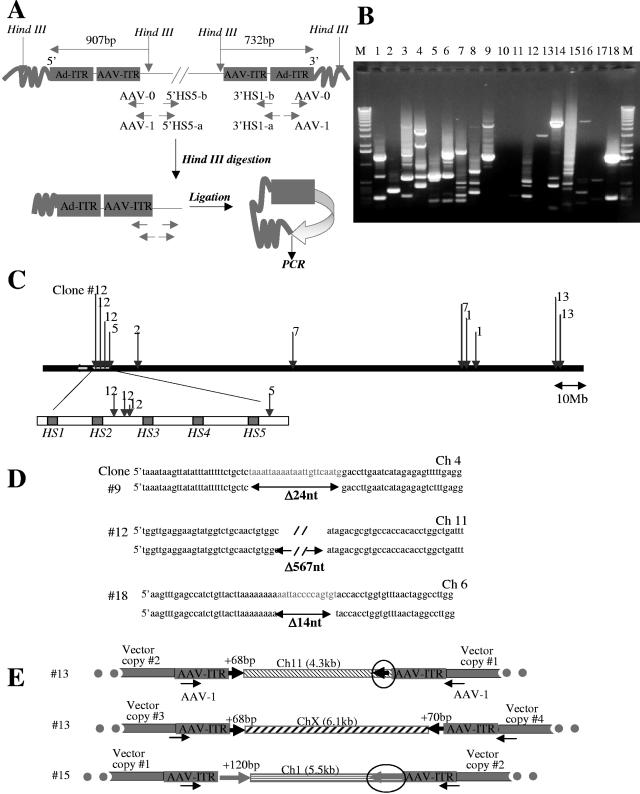
FIG. 4.
Analysis of integration junctions in MO7e clones by inverse PCR. (A) Schematic representation of inverse PCR. Five micrograms of genomic DNAs of 20 GFP-positive clones was digested with HindIII, relegated, and subjected to nested, inverse PCR with the indicated primers (see Materials and Methods). (B) 1% agarose gel showing inverse-PCR products from 18 clones. DNA bands were purified from the gel and cloned into pCR2.1 vector (Invitrogen) and transformed into the XL1-Blue strain, and junctions were sequenced. A sequence was considered to be from a genuine integration if it (i) contained both AAV ITR or Ad ITR sequence and the vector HindIII site, (ii) showed 95% or greater homology to the genomic sequence, and (iii) matched no more than one genomic locus with 95% or greater homology. (C) Schematic representation of integration sites found on chromosome 11. (D) Alignment of 5′ and 3′ junctions for three integration sites with corresponding genomic sequences found in GenBank (upper strand). Vector integration was associated with deletion of 24 bp, 567 bp, or 14 bp for the analyzed sites. (E) Schematic representation of transposition of genomic DNA fragments (circled) during vector integration (description in text).