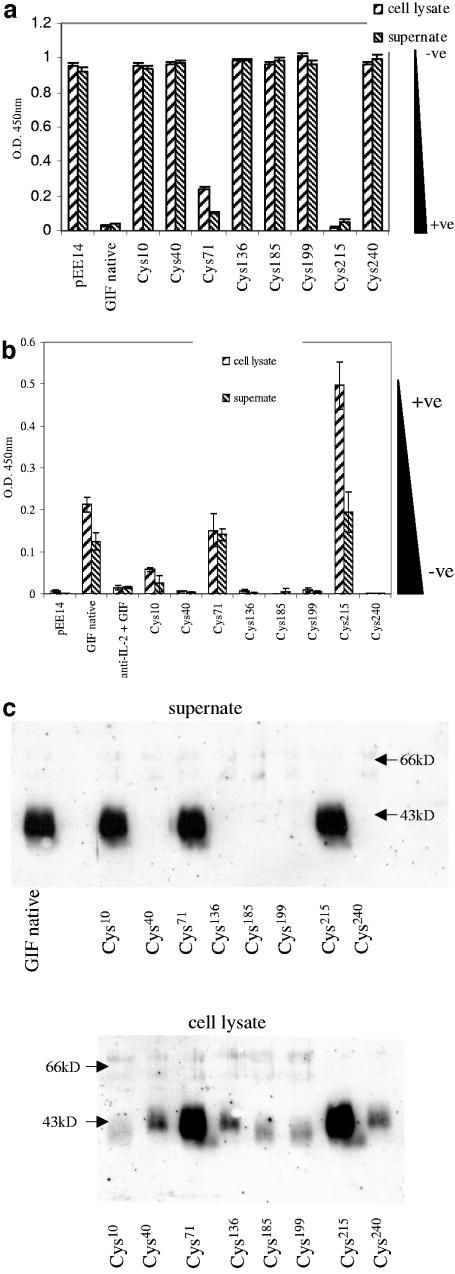
FIG. 2.
Cys-Ala substitution mutants of the GIF molecule were assessed, using the GM-CSF-specific ELISA, for the ability to bind native GM-CSF. Cell supernatants and cell lysates were collected from CHO cells transfected with various site-directed mutants of the GIFgene expressed from the mammalian expression vector pEE14. The pEE14 plasmid, containing no GIF insert, was included as a control. (a) Cys-Ala substitution mutants were tested for the ability to block detection of GM-CSF. Only GIF Cys71-Ala71 and GIF Cys215-Ala215 were able to do so. (b) Cys-Ala substitution mutants were tested for the ability to bind ovine IL-2 immobilized on an ELISA plate. GIF bound to IL-2 was detected with an anti-GIF antibody. Only GIF Cys71-Ala71 and GIF Cys215-Ala215 were able to bind to IL-2. The specificity of the interaction between GIF and IL-2 was verified by preincubating the IL-2-coated ELISA plate with an anti-ovine-IL-2 antibody (1B3) before incubating it with GIF. (c) Western blot of the cell supernatants and cell lysates from panel a. The error bars indicate standard errors of the mean. The +ve/−ve scale indicates binding of GIF to cytokine. O.D., optical density.