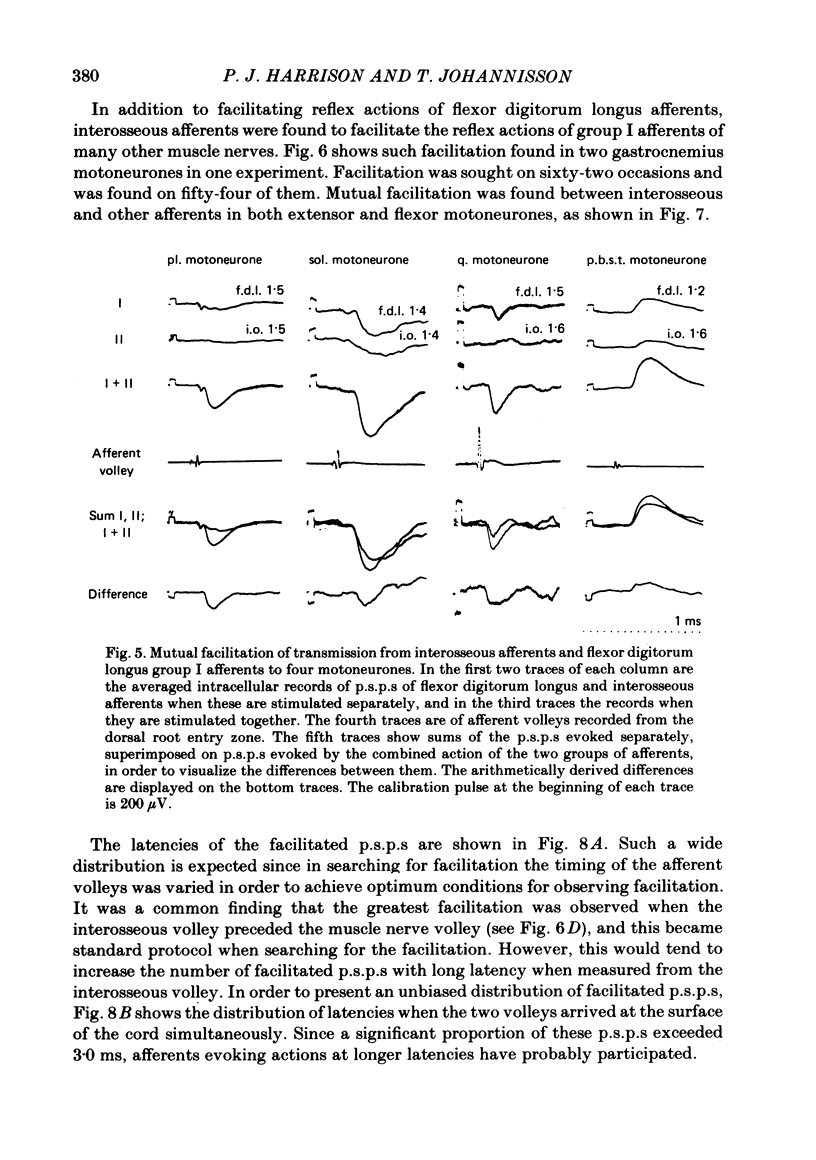
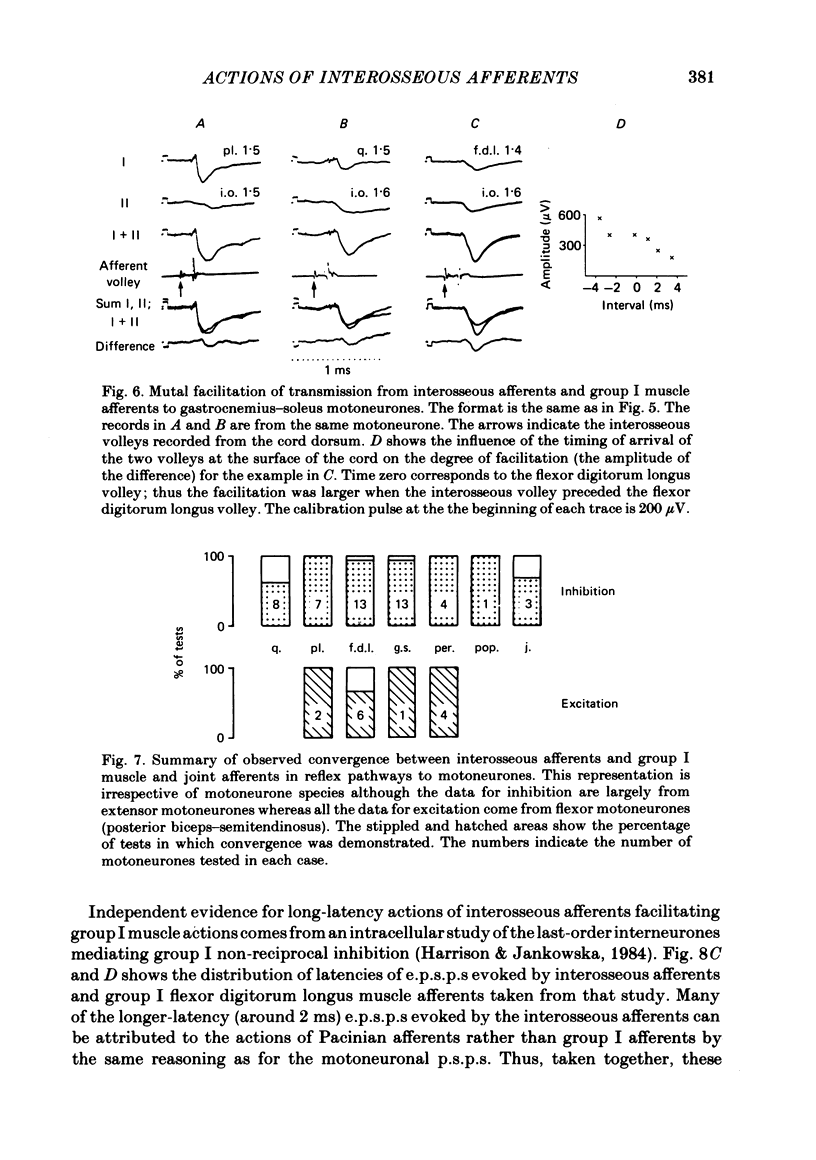
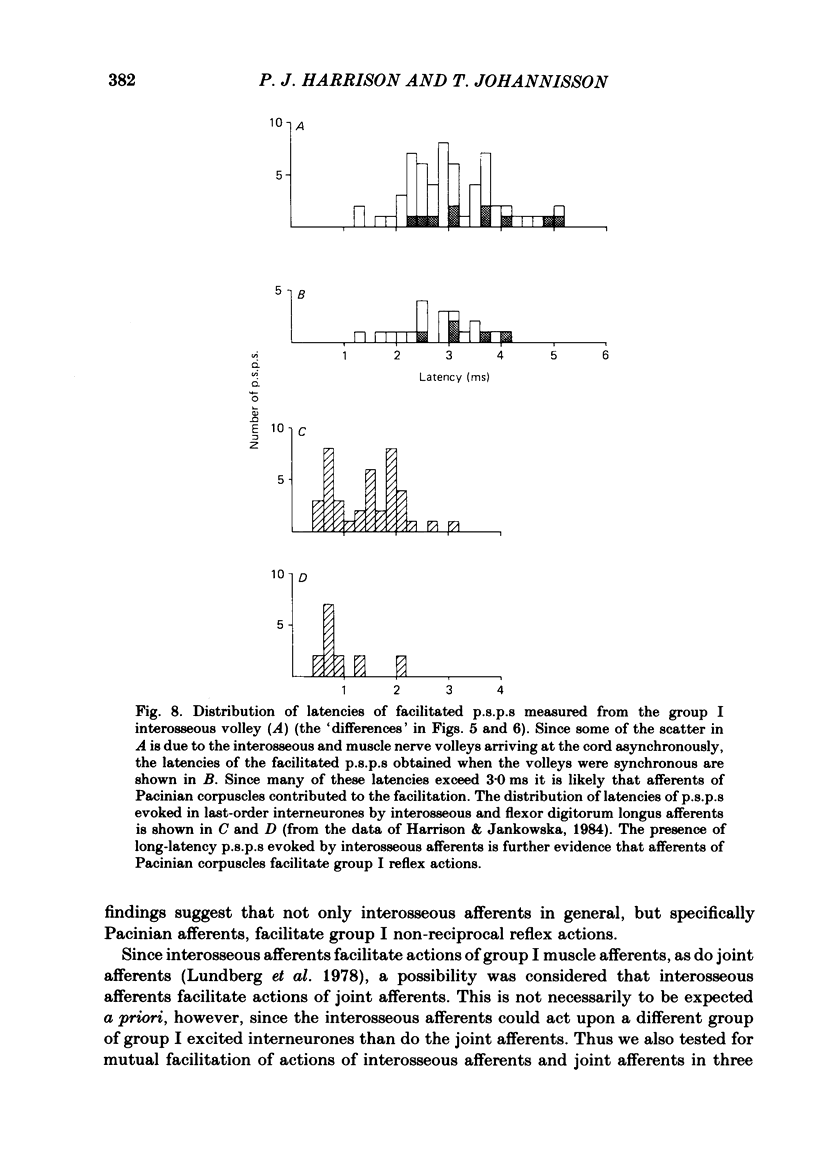
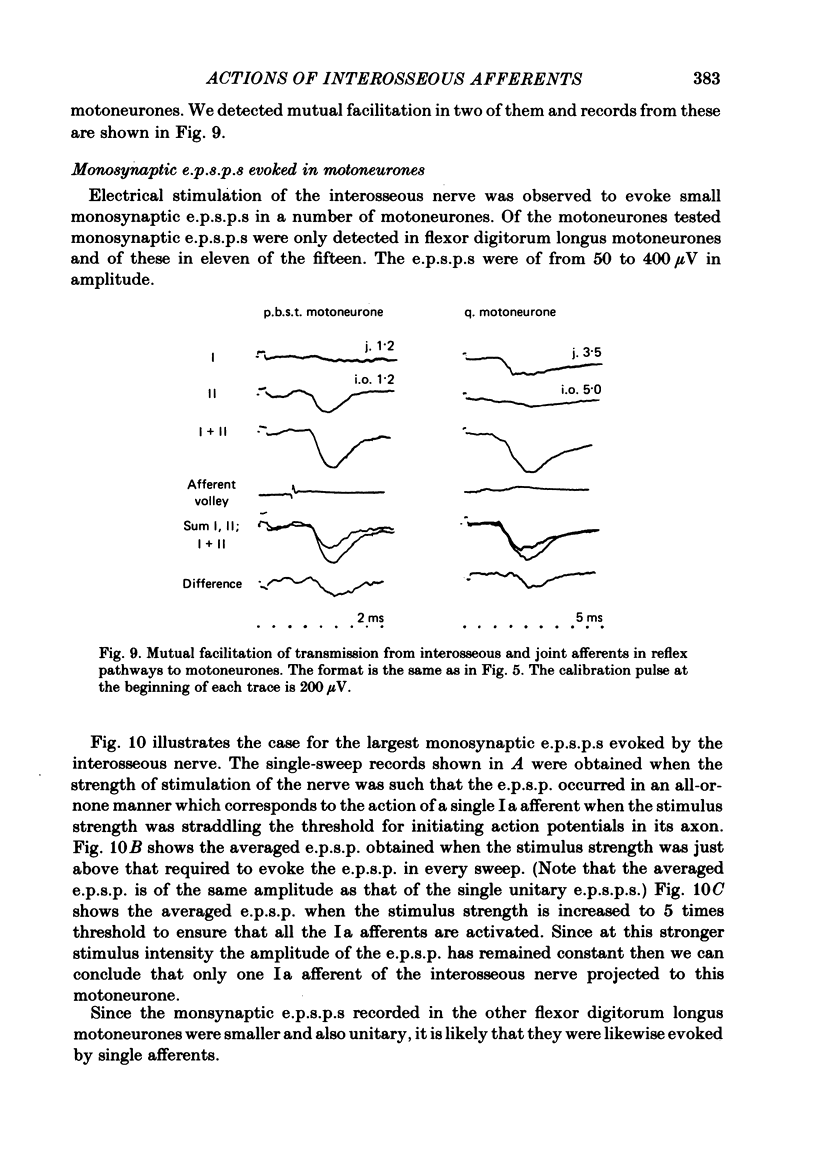
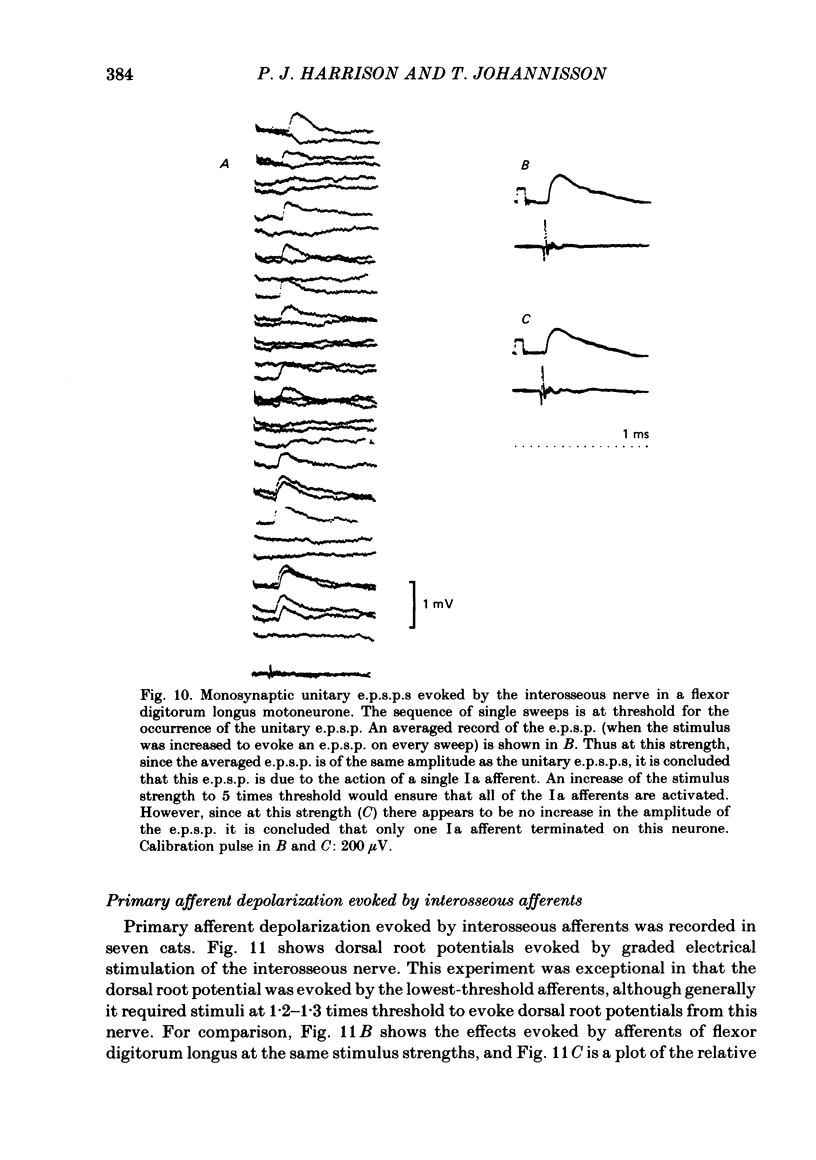
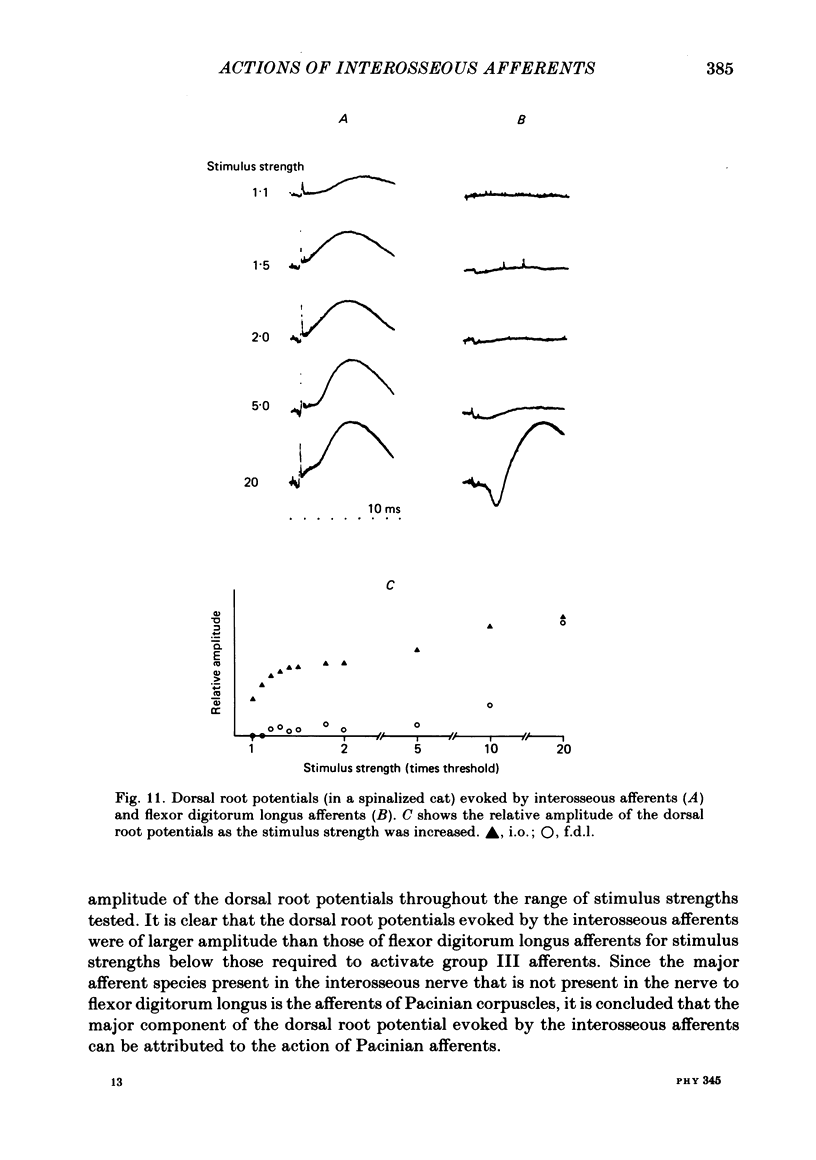
Abstract
Electrical stimulation of the interosseous nerve evokes oligosynaptic inhibition of extensor motoneurones and excitation of flexor motoneurones. Lowest-threshold, shortest-latency post-synaptic potentials evoked at group I strength are attributed to the action of group Ib afferents. Post-synaptic potentials evoked at slightly higher stimulus strengths (within the higher group I and the group II range) and at longer latency are attributed to the action of afferents of Pacinian corpuscles. Facilitation of post-synaptic potentials evoked from afferents in the interosseous nerve by group I muscle afferents and by joint afferents is taken to indicate convergence of these afferents onto common interneurones in reflex pathways to motoneurones. Evidence is presented that afferents of Pacinian corpuscles project to the interneurones mediating group I (non-reciprocal) reflex actions to motoneurones. Unitary monosynaptic excitatory post-synaptic potentials (e.p.s.p.s) evoked from the interosseous nerve are taken to indicate that only a very small number of muscle spindle Ia afferents course through the interosseous nerve. Dorsal root potentials evoked by low-strength electrical stimulation of the interosseous nerve are largely attributable to the action of afferents of Pacinian corpuscles.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ECCLES J. C., ECCLES R. M., LUNDBERG A. The convergence of monosynaptic excitatory afferents on to many different species of alpha motoneurones. J Physiol. 1957 Jun 18;137(1):22–50. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005794. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellaway P. H., Murphy P. R. Lack of segmental reflex action from Pacinian corpuscle afferents on gamma motoneurones in the cat and rabbit [proceedings]. J Physiol. 1978 Dec;285:60P–60P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUNT C. C., McINTYRE A. K. Characteristics of responses from receptors from the flexor longus digitorum muscle and the adjoining interosseous region of the cat. J Physiol. 1960 Aug;153:74–87. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1960.sp006519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUNT C. C. On the nature of vibration receptors in the hind limb of the cat. J Physiol. 1961 Jan;155:175–186. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1961.sp006621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison P. J., Jankowska E., Johannisson T. Shared reflex pathways of group I afferents of different cat hind-limb muscles. J Physiol. 1983 May;338:113–128. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014664. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hongo T., Jankowska E., Lundberg A. The rubrospinal tract. II. Facilitation of interneuronal transmission in reflex paths to motoneurones. Exp Brain Res. 1969;7(4):365–391. doi: 10.1007/BF00237321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jankowska E., McCrea D. A. Shared reflex pathways from Ib tendon organ afferents and Ia muscle spindle afferents in the cat. J Physiol. 1983 May;338:99–111. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jankowska E., McCrea D., Mackel R. Pattern of 'non-reciprocal' inhibition of motoneurones by impulses in group Ia muscle spindle afferents in the cat. J Physiol. 1981 Jul;316:393–409. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013796. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jänig W., Schmidt R. F., Zimmermann M. Two specific feedback pathways to the central afferent terminals of phasic and tonic mechanoreceptors. Exp Brain Res. 1968;6(2):116–129. doi: 10.1007/BF00239166. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LUNDBERG A., VOORHOEVE P. Effects from the pyramidal tract on spinal reflex arcs. Acta Physiol Scand. 1962 Nov-Dec;56:201–219. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1962.tb02498.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg A., Malmgren K., Schomburg E. D. Convergence from Lb, cutaneous and joint afferents in reflex pathways to motoneurones. Brain Res. 1975 Apr 4;87(1):81–84. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(75)90783-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg A., Malmgren K., Schomburg E. D. Cutaneous facilitation of transmission in reflex pathways from Ib afferents to motoneurones. J Physiol. 1977 Mar;265(3):763–780. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011742. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg A., Malmgren K., Schomburg E. D. Role of joint afferents in motor control exemplified by effects on reflex pathways from Ib afferents. J Physiol. 1978 Nov;284:327–343. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIntyre A. K. Cortical projection of impulses in the interosseous nerve of the cat's hind limb. J Physiol. 1962 Aug;163(1):46–60. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1962.sp006958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIntyre A. K., Holman M. E., Veale J. L. Cortical responses to impulses from single Pacinian corpuscles in the cat's hind limb. Exp Brain Res. 1967;4(3):243–255. doi: 10.1007/BF00248025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendell L. M., Henneman E. Terminals of single Ia fibers: location, density, and distribution within a pool of 300 homonymous motoneurons. J Neurophysiol. 1971 Jan;34(1):171–187. doi: 10.1152/jn.1971.34.1.171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norrsell U., Wolpow E. R. An evoked potential study of different pathways from the hindlimb to the somatosensory areas in the cat. Acta Physiol Scand. 1966 Jan-Feb;66(1):19–33. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1966.tb03164.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt R. F. Presynaptic inhibition in the vertebrate central nervous system. Ergeb Physiol. 1971;63:20–101. doi: 10.1007/BFb0047741. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silfvenius H. Characteristics of receptors and afferent fibers of the forelimb interosseous nerve of the cat. Acta Physiol Scand. 1970 May;79(1):6–23. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1970.tb04697.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silfvenius H. Projections to the cerebral cortex from afferents of the interosseous nerves of the cat. Acta Physiol Scand. 1970 Oct;80(2):196–214. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1970.tb04784.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


