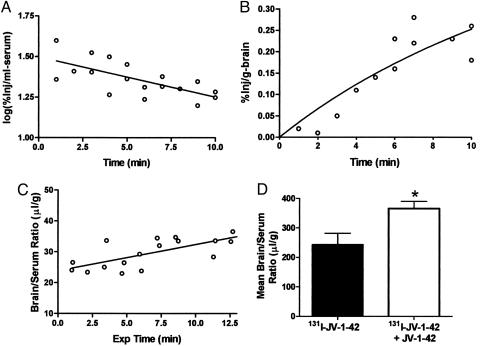
Fig. 1.
Kinetics of blood-to-brain transport of 131I-JV-1-42 after i.v. administration. (A) The initial phase of clearance from serum follows first-order kinetics. 131I-JV-1-42 has a serum half-life of 12.2 min. (B) 131I-JV-1-42 readily entered the brain tissue. The maximal percent of the injected dose taken up by each gram of brain was 0.41%, indicating that brain uptake was high. (C) Brain uptake values were corrected for exposure time and plotted against their respective brain/serum ratios. The slope of the resulting graph revealed that 131I-JV-1-42 enters the brain at a rate of 0.8514 μl/g per min (n = 1-2 per time point for B and C). (D) Coinjection of 131I-JV-1-42 with unlabeled JV-1-42 did not saturate blood-to-brain transport of 131I-JV-1-42. Instead, it produced a paradoxical increase in the amount of 131I-JV-1-42 detected in the brain (t = 10 min after i.v. injection; n = 6 per group; *, P < 0.05).