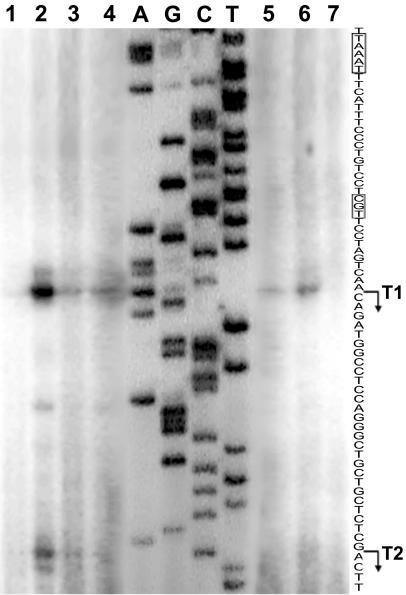
FIG. 3.
Effect of the algQ mutation on the initiation pattern of pvdA transcripts in P. aeruginosa PAO1 algQ-proficient and -defective backgrounds and in the heterologous host E. coli. The primer extension reaction was carried out with the 5′-end-labeled oligonucleotide RVPpa and equal amounts of total RNA isolated from P. aeruginosa and E. coli cells grown in DCAA and M9 medium, respectively. The single-stranded pvdA promoter sequence is shown on the right, and consensus motifs recognized by PvdS are enclosed in boxes. The previously identified 5′ ends of T1 and T2 transcripts (29) and the direction of transcription are indicated by bent arrows. Lanes A, G, C, and T, pvdA sequencing ladder generated from pPV226 with the same oligonucleotide (RVPpa): lane 1, primer extension analysis of total RNA extracted from P. aeruginosa PAO1(pUCP19) iron-rich cultures (DCAA plus 100 μM FeCl3); lanes 2 to 4, primer extension analysis with total RNA from P. aeruginosa PAO1(pUCP19) (lane 2), PAO1ΔalgQ(pUCP19) (lane 3), and PAO1ΔalgQ(pUCPalgQ) (lane 4); lanes 5 to 7, primer extension analysis with total RNA from E. coli MC4100(PpvdA::lacZ; pBRXB) carrying pACYCalgQ (lane 5), pACYCpfrA (lane 6), and pACYC184 (lane 7). Lane cutting and pasting were needed to visualize the sequencing ladder and primer extension products, which required different exposure times.