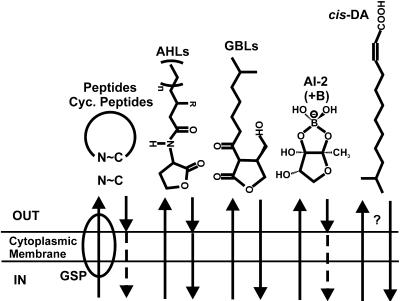
FIG. 1.
Examples of bacterial signal diversity. Several different signal types are depicted. N∼C indicates either linear or cyclized peptides, AHLs are acylated homoserine lactones, GBLs are γ-butyrolactones, AI-2 is the furanosyl borate diester, and cis-DA is cis-11-methyl-2-dodecenoic acid. Peptides may be externalized by the general secretion pathway (GSP) or through other more specific mechanisms. Arrows indicate transit of signals across the bacterial envelope. Arrowheads that contact the envelope indicate signals that are bound by membrane-associated receptors. Dashed arrows indicate active transport into cells. Peptides and AI-2 may be perceived externally but can also transported into the cell.