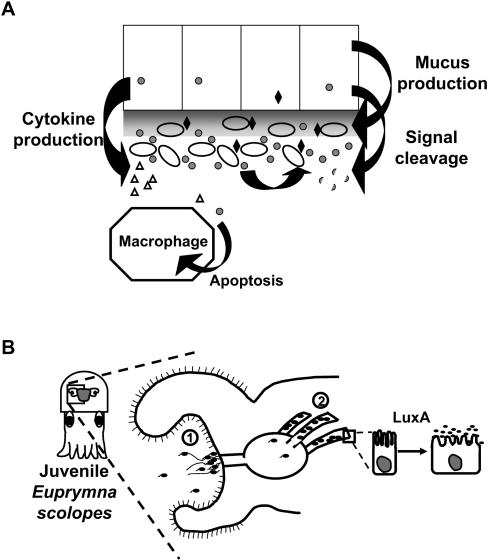
FIG. 4.
Diffusible signaling in bacteria-host associations. (A) Not only do bacteria recognize their own secreted signals (gray circles) to coordinate a response (black diamonds), but eukaryotic cells in the vicinity may also recognize these signals and produce a response. Some of the potential interactions are diagrammed. Various host cells may alter cytokine production (open triangles), mucus production (shaded gray), or other developmental events, such as apoptosis, in response to either the signal itself or the bacterial product of the signal transduction pathway. Hosts may also induce or constitutively synthesize signal-degrading enzymes. (B) Symbiotic Euprymna scolopes-V. fischeri interaction during light organ colonization. LuxA activity is dependent on AHL quorum sensing. The locations at which bacterial cell-cell signaling likely occurs are labeled as 1 and 2. Region 1 is the site of the initial attachment, or aggregation, by bacteria on the surface of the light organ. Region 2 is the site of colonization inside, where the bacteria multiply to high cell density and induce developmental changes, such as the AHL-dependent LuxA activity that is required for host epithelial cell swelling.