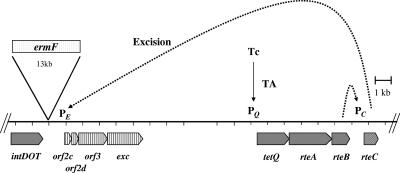
FIG. 1.
Model for the regulation of the excision of CTnDOT. The genes important for the excision of CTnDOT are shown. The 13-kbp ermF region present in CTnDOT is indicated by the bar labeled ermF. The dashed lines indicate the hypothetical regulatory steps that are proven in this study. The intDOT gene, which is required both for integration and excision, is expressed constitutively, but expression of the orf2c-2d-orf3-exc operon is regulated. Growth of the cells in tetracycline stimulates the production of TetQ and RteA-RteB, a process that is regulated by translational attenuation (TA) (37), shown by the solid arrow. RteB activates the transcription of rteC, and the RteC protein then activates the transcription of the orf2c operon. IntDOT plus products from the orf2c operon interact to cause the excision of the CTn.