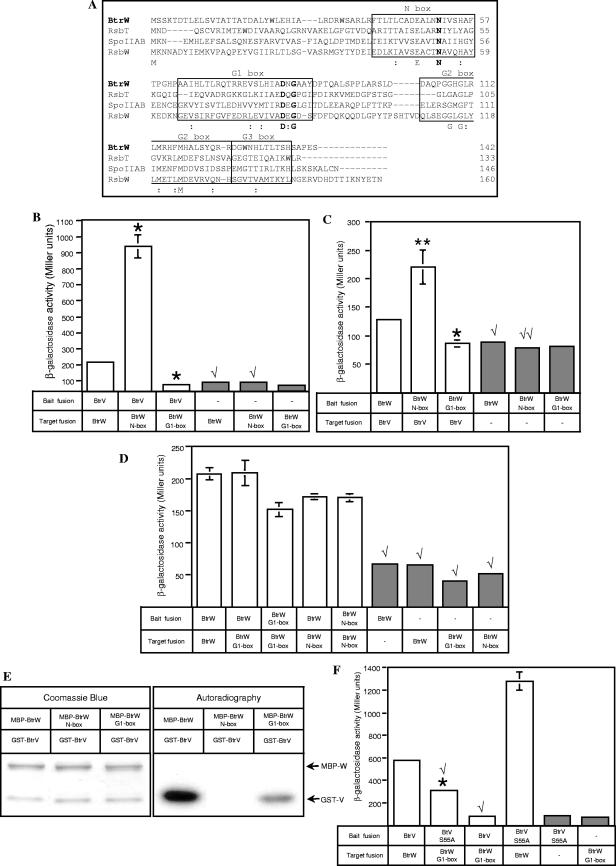
FIG.5.
BtrW N-box mutant binds but cannot phosphorylate BtrV, whereas BtrW G1-box mutant preserves its serine kinase activity despite its low affinity for BtrV. (A) Multiple sequence alignment between B. bronchiseptica and B. subtilis anti-sigma factors/serine kinase orthologs. CLUSTAL_X was used to align the DNA-derived amino acid sequence of BtrW (GenBank accession number NP_888190) with the sequences of B. subtilis RsbW, RsbT, and SpoIIAB (GenBank accession numbers P17904, P42411, and P10728, respectively). The conserved N, G1, G2, and G3 boxes of the Bergerat fold are outlined. The sequences of the conserved motifs were identified based on the alignment of the B. bronchiseptica BtrW and B. subtilis RsbW, RsbT, and SpoIIAB sequences with B. stearothermophilus SpoIIAB (GenBank accession number 1L0OB) (5). Identical residues are shown below the alignment in one-letter amino acid code, and “:” indicates the positions of strongly conserved residues. The conserved arginine residue corresponding to N51 of BtrW within the N box and the conserved aspartate and glycine residues corresponding to D82 and D84, respectively, of BtrW within the G1 box are shown in boldface. (B and C) Bacterial two-hybrid analysis of interactions between wild-type BtrV and BtrW N- and G1-box mutants. The BacterioMatch reporter strain was cotransformed with bait and target vectors carrying fusions of wild-type BtrV and wild-type BtrW, the BtrW N-box mutant, or the BtrW G1-box mutant. For the negative controls, the reporter strain was cotransformed with one vector carrying fusions to wild-type or mutant BtrW and another empty vector. The unpaired t test was used to compare differences between the activities of strains carrying BtrV-BtrW(N51A) and BtrV-BtrW(D82G84) pairs versus that of the strain with the wild-type BtrV-BtrW pair. *, P < 0.005; **, P < 0.05. The unpaired t test was also used to compare differences between the activity of the negative controls carrying a single fusion of wild-type or mutant BtrW (gray bars) versus that of the reporter strains carrying that BtrW fusion together with the BtrV fusion (white bars). √, P < 0.005; √√, P < 0.05. Note the differences in scales of β-galactosidase activity for panels B and C. In some cases, the error bars (standard errors) are too small to be seen. (B) β-Galactosidase activities of the reporter strains cotransformed with bait vectors carrying the BtrV fusions and target vectors carrying BtrW fusions. (C) β-Galactosidase activities of the reporter strains containing the reciprocal arrangement of BtrV and BtrW fusions compared to panel B. (D) Test for the ability of BtrW N-box and G1-box mutants to form homodimers. The reporter strain was cotransformed with bait and target plasmids carrying fusions of wild-type BtrW or BtrW N-box or BtrW G1-box mutants, and the β-galactosidase activities of the transformed strains were measured. The unpaired t tests to compare differences between the activity of the reporter strains carrying BtrW mutant-BtrW wild-type or double-BtrW mutant pairs versus the activity of the strain carrying a double-wild-type BtrW pair indicate that the activity levels are comparable. The unpaired t test was used to compare differences between the activities of the negative controls (gray bars) versus the strains carrying fusions on both bait and target vectors (white bars); √, P < 0.005. In some cases, the error bars are too small to be seen. (E) In vitro phosphorylation assay to assess serine kinase activities of MBP-BtrW N-box and MBP-BtrW G1-box mutants. Affinity-purified MBP-BtrW(N51A) and MBP-BtrW(D82AG84A) proteins were tested for the ability to phosphorylate GST-BtrV upon incubation with [γ-32P]ATP. The 32P-labeled bands were detected by autoradiography (right). The same amounts of the purified fusion proteins as were used in the kinase reactions were mixed and separated by SDS-PAGE, followed by Coomassie blue staining (left). The Coomassie blue staining indicated that 32P-labeled bands corresponded to GST-BtrV. The MBP-BtrW G1-box mutant can phosphorylate GST-BtrV, albeit more weakly than the MBP-BtrW wild type. (F) Assay for the ability of BtrV(S55A) to interact stably with the BtrW G1-box mutant in the bacterial two-hybrid system. β-Galactosidase activity was measured in the reporter strain cotransformed with bait vectors carrying the wild type or the S55A mutant of BtrV and the target vector carrying the wild type or the G1-box mutant of BtrW. Negative controls are in gray. The unpaired t test was used to compare the differences between the activity of the strain containing the BtrV(S55A)-BtrW G1-box mutant pair versus the strain containing the BtrV wild type-BtrW G1-box mutant pair; *, P < 0.005. In addition, an unpaired t test was conducted to evaluate the differences between the activities of the strains used in the test described above versus the reporter strain with wild-type BtrV and BtrW fusions; √, P < 0.005. In some cases, the error bars are too small to be seen.