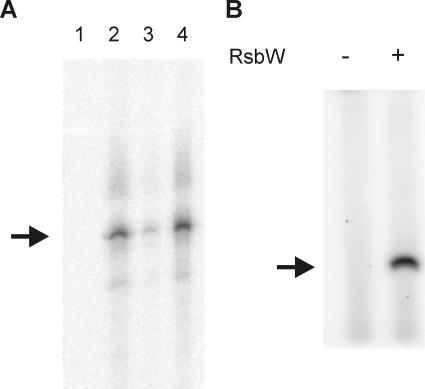
FIG. 1.
Functional analysis of RsbV and RsbW of B. cereus. (A) In vitro transcription assays for the determination of the function of RsbV and RsbW. A PCR template containing the σB-dependent promoter site 5′ of orf4 was used in the in vitro transcription reactions including B. cereus core RNAP (lane 1); core RNAP and σB (lane 2); core RNAP, σB, and RsbW (lane 3); and core RNAP, σB, RsbW, and RsbV (lane 4). After electrophoresis, runoff transcription products were visualized by autoradiography. The size of the σB-dependent transcription product is indicated with the arrow. (B) Phosphorylation of RsbV by RsbW. The phosphorylation reaction mixture contained 40 μCi [γ-32P]ATP (3,000 Ci/mmol), 1 μM RsbV, and where indicated, 1 μM RsbW. Non-radioactively labeled ATP was added at a concentration of 20 μM. Proteins were separated on an 18% SDS-PAGE gel, and phosphorylated proteins were visualized by autoradiography. The position of RsbV (determined by running a sample of purified RsbV in parallel to the phosphorylation reaction mixtures) is indicated by the arrow.