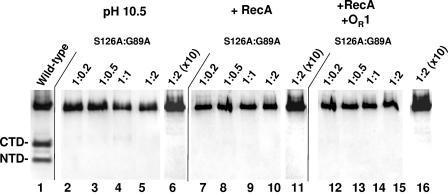
FIG. 4.
pH- and RecA-stimulated cleavage of mixtures of cleavage site (G89A) and active site (S126A) mutant 434 repressors. The wild-type repressor (200 ng) was incubated with active RecA for 4 h (lane 1) as a control. The cleavage site (G89A) and active site (S126A) mutant 434 repressors were mixed in various ratios (lanes 2 to 5, 7 to 10, and 12 to 15 contained 200 ng of 434S126A plus [434G89A; lanes 6, 11, and 16 contained 2,000 ng of 434S126A plus 434G89A) and were incubated at pH 10.5 for 24 h (lanes 2 to 6), in the presence of RecA for 4 h (lanes 7 to 11), or in the presence of RecA and a twofold molar excess of 434 OR1 for 4 h (lanes 12 to 16). Intact repressors and the cleavage products were fractionated on 15% Tris/Tricine gels and visualized by Western blotting using anti-434 repressor antibodies. The positions of the intact repressor and the N- and C-terminal cleavage products are indicated on the left. CTD, C-terminal domain; NTD, N-terminal domain.