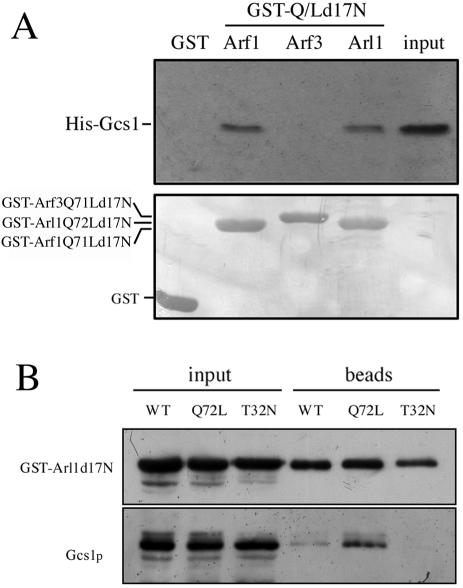
Figure 2.
Arl1Q72Ld17N interacts with Gcs1p in vitro and in vivo. (A) In vitro interaction of His-Gcs1 with GST-Arl1Q72Ld17N, GST-Arf1Q71Ld17N, or GST-Arf3Q71Ld17N constructs. Purified recombinant His-Gcs1 (2 μg) was mixed with 2 μg of purified recombinant GST, GST-Arl1Q72Ld17N, GST-Arf1Q71Ld17N, or GST-Arf3Q71Ld17N immobilized on glutathione-Sepharose beads and incubated at 4°C for 1 h. After three times wash, bound proteins were eluted by boiling in 20 μl of 2× sample buffer, and separated by SDS-PAGE in a 12% gel. Input lane contained 1% of the amount added to beads. Proteins were stained with Coomassie Blue (bottom) to assess equal loading, and bound proteins were visualized by Western blotting with anti-Gcs1p antibody (top). (B) In vivo interaction of Arl1Q72Ld17N with endogenous Gcs1p in a GTP-dependent manner. Expression of GST-fused Arl1d17N (WT), Arl1Q72Ld17N (Q72L), or Arl1T32Nd17N (T32N) from pYEX-4T-1 was induced, and yeast were lysed with glass beads. After centrifugation, the cleared lysates were incubated with glutathione-Sepharose beads at 4°C overnight and then washed three times with binding buffer before analysis of bound proteins as described in A. Antibodies used are indicated to the left of the panel.