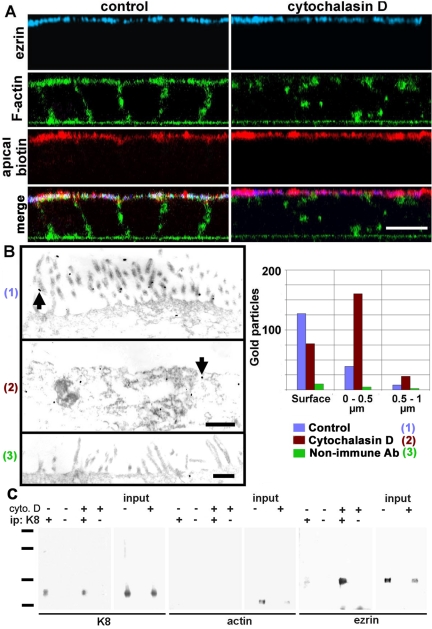
Figure 4.
Apical localization of ezrin is independent of F-actin and the membrane in cells treated with cytochalasin D. (A) CACO-2 cells were treated with or without (control) 2 μM cytochalasin D for 5 h, surface-biotinylated on the apical side, and fixed in formaldehyde. The cells were processed with antiezrin antibody (blue), fluorescent phalloidin (green, F-actin), and fluorescent streptavidin (red, apical biotin) and analyzed by confocal microscopy. The images are presented as XZ sections with the apical side up. (B) In similar experiments, the cells also were treated with cytochalasin D (2), processed with anti-ezrin antibody (1 and 2), or with nonimmune antibody (3) and processed with nanogold particles for EM. Arrows show examples of gold particles. Total gold particle counting over 30 μm of section in photographs from nonserial sections is shown for the surface (particles in contact with the plasma membrane including microvilli), a band of apical cytoplasm between 0 and 0.5 μm, or between 0.5 and 1 μm below the apical plasma membrane. Bars, 10 μm (A), 0.7 μm (B). (C) CACO-2 cells were incubated with (+) or without (–) cytochalasin D (cyto.D) as described above and extracted in TX-100 in the presence of antiproteases. The Triton-insoluble pellets from 1.5 × 107 cells were then fractionated by sonication, and the smallest multiprotein complexes were immunoprecipitated with anti-K8 antibody (ip +) or nonimmune IgG (ip –) and analyzed by immunoblot with anti-K8, antiactin, or anti-ezrin antibodies. Standards, 201, 127, 86, and 37 kDa.