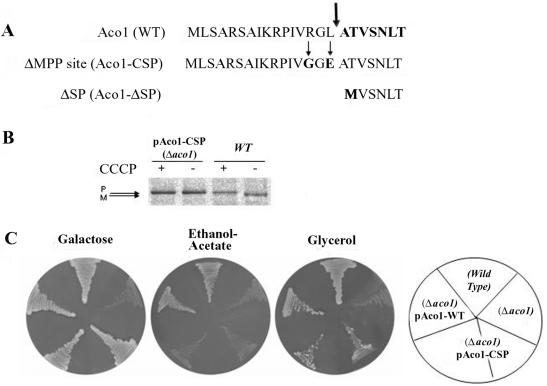
Figure 6.
(A) Amino terminus of aconitase. Sequences of the amino termini of wild-type aconitase, aconitase with a mutated MPP cleavage site (Aco1-CSP), and aconitase lacking the mitochondrial targeting sequence (Aco1-ΔSP). The thick arrow indicates the position of the MPP cleavage site determined by Edman degradation. The thin arrows indicate amino acids changes in the MPP cleavage site mutant. (B) Aconitase's MPP cleavage site mutant is not processed. Aconitase processing was blocked by inhibiting import into mitochondria with CCCP. Wild-type or Δaco1 yeast cells induced in galactose medium for the expression of the Aco1 MPP cleavage site mutants (Aco1-CSP) were labeled with [35S]methionine for 30 min, either in the absence (-) or presence (+) of CCCP. Total cell extracts were prepared, immunoprecipitated with aconitase antiserum and analyzed by SDS-PAGE. Dual arrows show positions of the precursor (P) and mature (M) proteins. (C) pAco1-CSP encoding an unprocessable Aco1 does not complement cells for growth on ethanol-acetate. Cells expressing an unprocessed aconitase were examined for growth on ethanol-acetate as the carbon source. Wild-type and Δaco1 harboring the indicated plasmids were grown on galactose, ethanol-acetate, or glycerol medium agar plates.