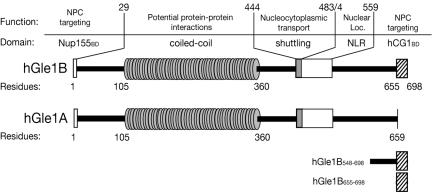
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of structural and functional features of hGle1B and hGle1A. Amino acid (aa) residues 1-29 delineate hNup155-binding domain (Nup155BD; Rayala et al., 2004), aa 105-360 the predicted coiled-coil domain, aa 444-483 the nucleocytoplasmic shuttling domain required for hGle1-mediated mRNA export (Kendirgi et al., 2003), aa 484-559 a novel nuclear localization region (NLR) with weak nuclear import activity (Kendirgi and Wente, unpublished results), and aa 655-698 the hCG1-binding domain (hCG1BD) which is absent from hGle1A (Kendirgi et al., 2003). The regions used in Figure 3B as His-tagged fusions (hGle1B548-698 and hGle1B655-698) are also shown.