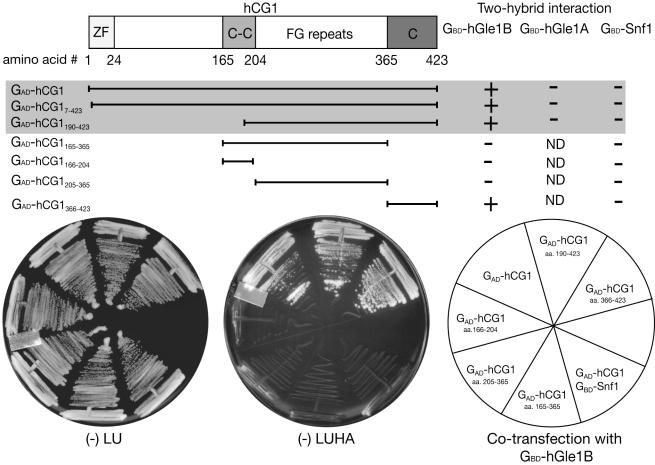
Figure 2.
hGle1B and hCG1 interact in the yeast two-hybrid assay. A schematic representation of hCG1 domain structure is shown. Amino acid (aa) residues 1-24 form a Zinc finger domain (ZF), aa 165-203 a predicted coiled-coil domain (C-C), aa 204-365 the FG-repeat domain (harboring phenylalanine (F)-glycine (G) repeats), and aa 366-423 the carboxy (C)-terminal domain. Three classes of GAD-hCG1 clones were isolated in the yeast two-hybrid screen and are highlighted in the shaded area. Interaction in the two-hybrid assay was detected by growth on media lacking leucine, uracil, histidine, and adenine (-LUHA) (for GBD-hGle1 and GBD-Snf1) or lacking leucine, uracil, histidine, and tryptophan (for GBD-hGle1A) (unpublished data). Growth was scored with (-) representing no growth and (+) representing growth. Each GAD fusion was tested for specificity by cotransformation with GBD-Snf1 and for self-activation (unpublished data).