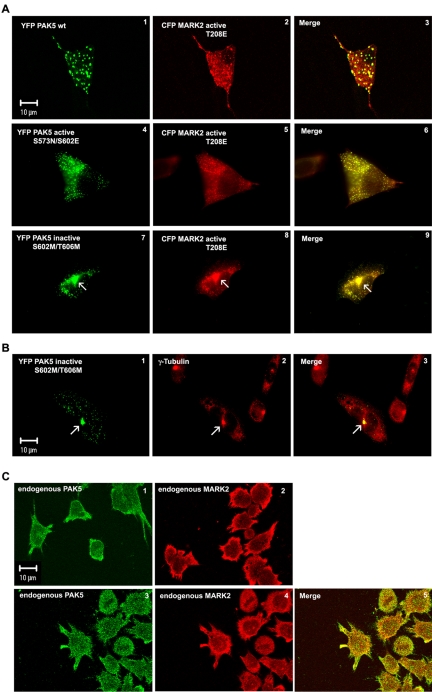
Figure 5.
Subcellular localization of MARK2 and PAK5. (A) Colocalization of different YFP-PAK5 constructs with transfected CFP-MARK2 (red). (A1-3) Cotransfection of PAK5wt and active MARK2E shows colocalization of both kinases on vesicles and a diffuse background of MARK2E. (A4-6) Cotransfection of active PAK5NE and active MARK2E shows colocalization on vesicles and a diffuse background of both kinases. (A7-9) Cotransfection of inactive PAK5MM and active MARK2E shows colocalization on vesicles and accumulation of both kinases around the centrosome (arrow). (B) Colocalization of transfected inactive YFP-PAK5MM (green) with centrosomes, visualized by fixation and labeling with an antibody against γ-tubulin (red). The merge (yellow, B3) confirms that inactive PAK5 preferentially localizes on the centrosome (arrow). (C) Localization of endogenous PAK5 (C1) or endogenous MARK2 (C2) stained with specific PAK5 or MARK2 antibodies, and TRITC secondary antibody in differentiated LAN5 cells. Colocalization of endogenous PAK5 (C3, green) visualized by first staining with a PAK5-specific antibody plus Cy5 secondary antibody and then staining endogenous MARK2 in differentiated LAN5 cells (C4, red) with a MARK2 antibody (SA 2117) directly coupled to Alexa 488.