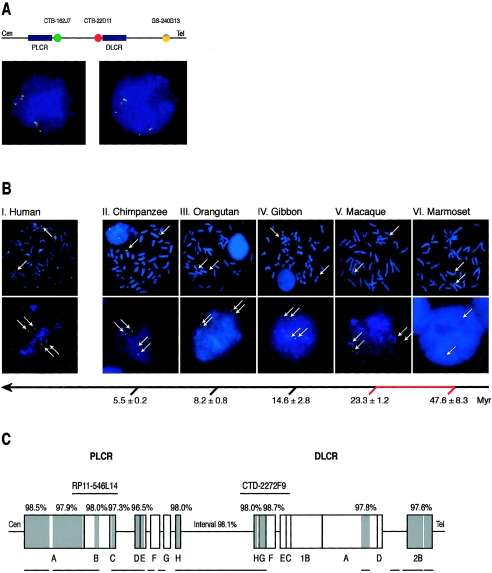
Figure 3.
A, Three-color FISH analysis for confirmation of the inversion polymorphism of the 1.3-Mb interval between the LCRs. Clones CTB-162J7 and CTB-22D11 were located in the interval, and GS-240G13 was located at the 5q subtelomeric region, as shown above the interphase FISH photographs. CTB-162J7, CTB-22D11, and GS-240G13 were labeled with SpectrumGreen (green), SpectrumOrange (red), and a 50-50 combination of SpectrumGreen and SpectrumOrange (yellow), respectively. The left photograph indicates a normal homozygous state (green-red-yellow) of the interval in both chromosomes. The right photograph shows a heterozygous inversion pattern (red-green-yellow) in one chromosome and a normal pattern (green-red-yellow) in the other. B, FISH signals (arrows) of BAC clone CTD-2272F9 (SpectrumGreen-11-dUTP) on metaphase (upper row) and interphase (lower row) cells from human (Homo sapiens) (I), chimpanzee (Pan troglodytes) (II), orangutan (Pongo pygmaeus) (III), gibbon (Hylobates lar) (IV), Old World monkey (Macaca fuscata) (V), and the New World monkey marmoset (Callithrix jacchus) (VI). The BAC clone represents the region of DLCR between DLCR-C and DLCR-H (see panel C). Duplicated signals are observed in interphase cells in photographs I–V; a single signal is seen in VI. The arrow with horizontal branches indicates the molecular timescale, as described elsewhere (Kumar and Hedges 1998), with estimated time (±1 SE) showing the divergence of the human and other species. The red portion of the branched arrow shows the introduction of the SoS LCR duplication in the primate/monkey evolution. Myr = million years ago. C, Schematic presentation of the human LCRs (blocks) and intervals (lines) and their orthologous chimpanzee genome sequences. Gray blocks indicate regions homologous to the chimpanzee sequence. The similarity percentages of these regions (i.e., similarity between the human and chimpanzee sequence) are shown above the blocks. Lines below the LCRs depict the available chimpanzee sequences, and interruptions in lines indicate gaps (>5 kb) in the present NCBI build 1 (November 2003) UCSC Chimp Genome Browser. RP11-546L14 and CTD-2272F9 show the position of the FISH probes, as used in the evolutionary study (see panel B).