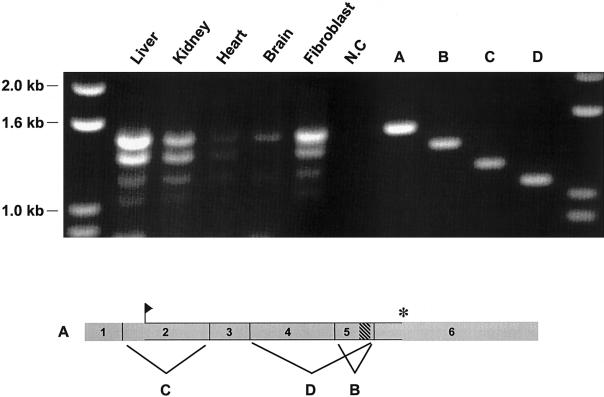
Figure 4.
PEX26, alternatively spliced in fibroblasts and human tissues. Top panel, The products of RT-PCR amplification of PEX26 transcripts. RT-PCR products with total RNA from human liver, kidney, heart, and brain, by use of primers complementary to the 5′ and 3′ ends of full-length PEX26 transcript (probes 26-15 and 26-16, respectively), analyzed by agarose-gel electrophoresis and ethidium-bromide staining. The source of the RNA is indicated above the five lanes on the left. On the right, we cloned the RT-PCR products (1,508, 1,361, 1,197, and 1,065 bps) from fibroblast RNA, and the inserts representing full-length PEX26 cDNA (A), PEX26-Δex5 (B),PEX26-Δex2 (C), and PEX26-Δex4+5 (D) splice forms are shown as size references. Lower panel, Full-length PEX26 transcript, except for exon 7, which encodes 3′ untranslated sequence and is not included in the RT-PCR amplicons. The segments contributed by each exon are numbered and shown to scale. The flag shows the translation start site, the cross-hatched rectangle indicates the segment of exon 5 encoding the transmembrane domain, and the asterisk (*) indicates the translation stop site. The letters indicate the exon deleted from the similarly lettered splice form shown in the top panel.