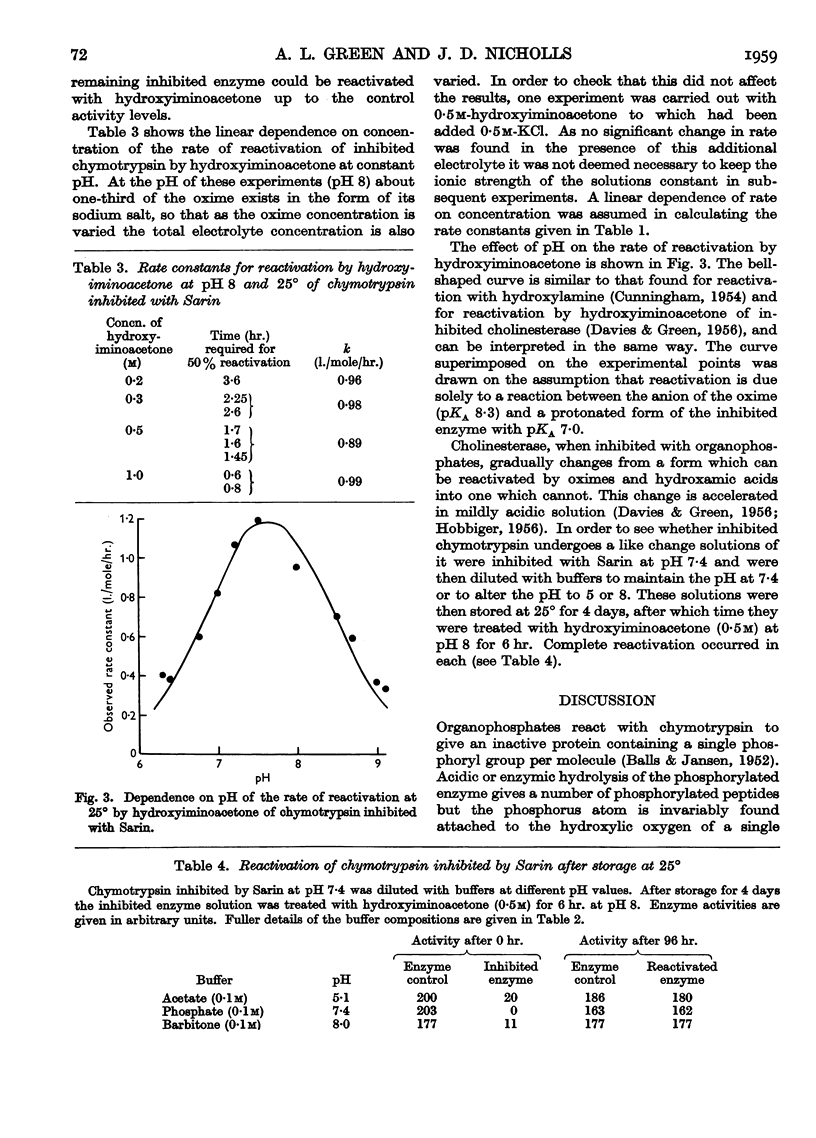
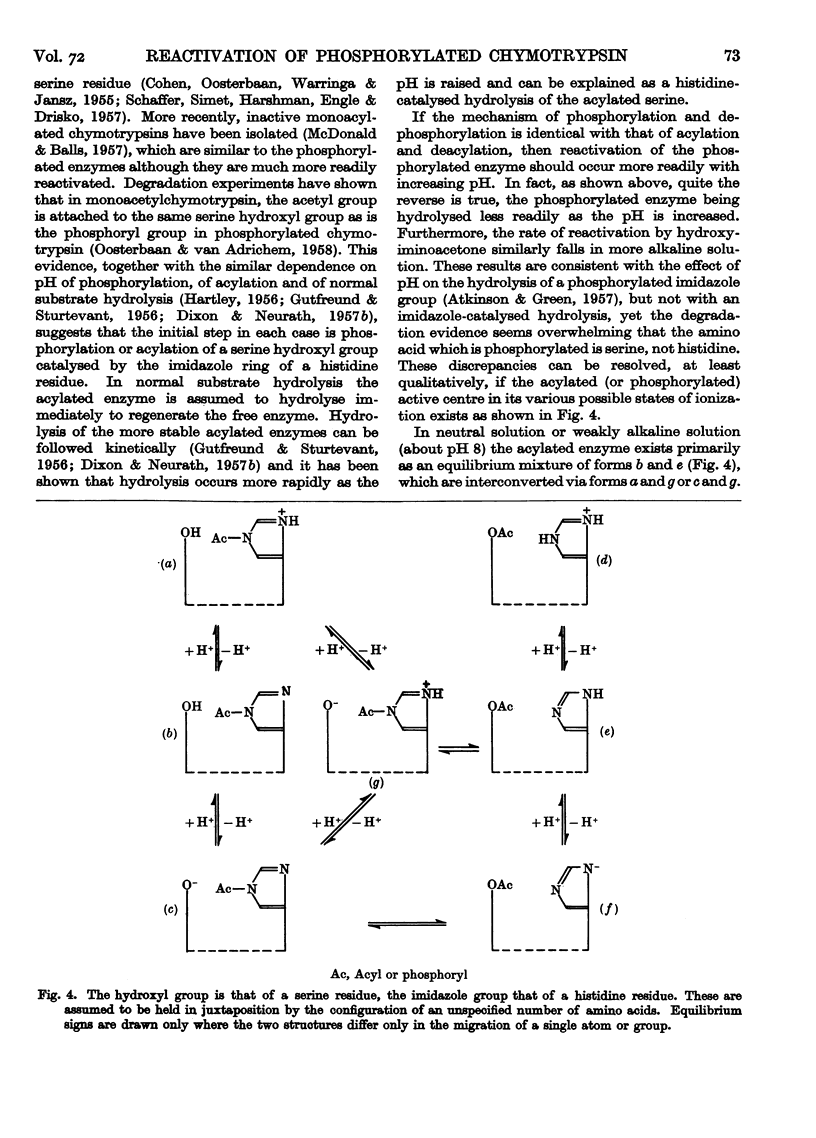
Full text
PDF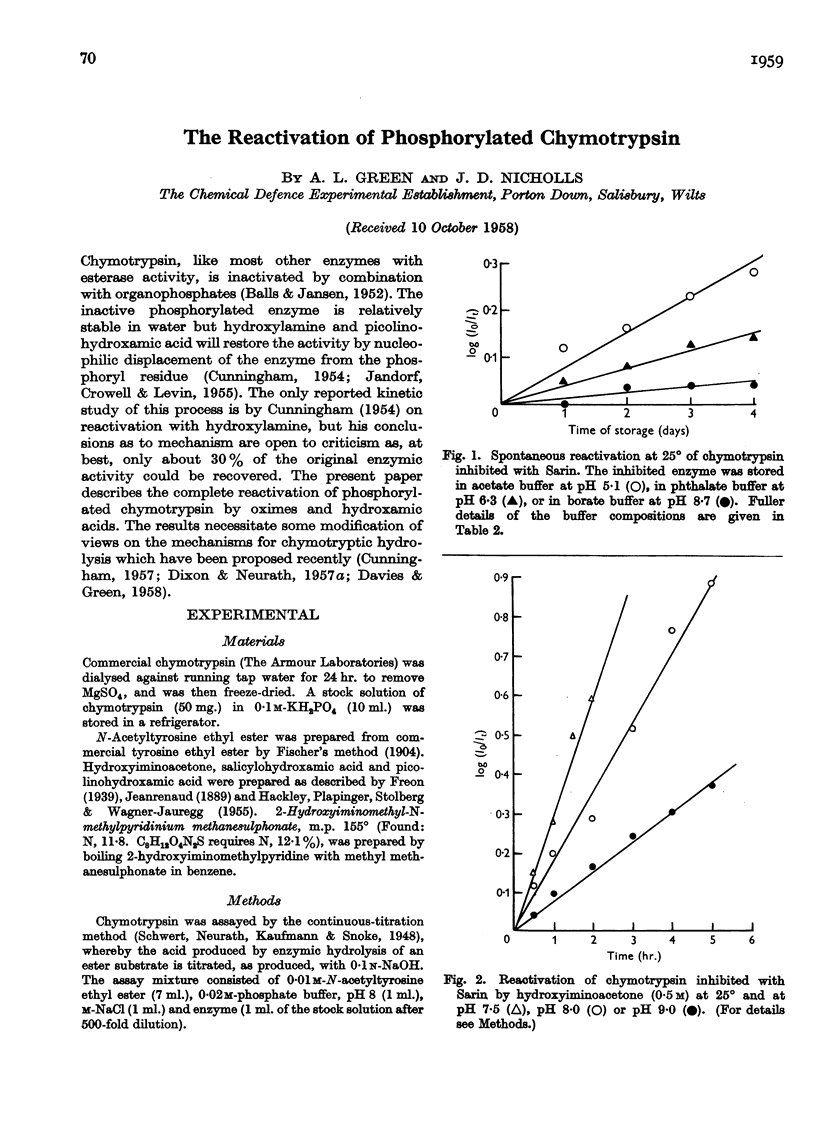



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BALLS A. K., JANSEN E. F. Stoichiometric inhibition of chymotrypsin. Adv Enzymol Relat Subj Biochem. 1952;13:321–343. doi: 10.1002/9780470122587.ch8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHILDS A. F., DAVIES D. R., GREEN A. L., RUTLAND J. P. The reactivation by oximes and hydroxamic acids of cholinesterase inhibited by organo-phosphorus compounds. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1955 Dec;10(4):462–465. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1955.tb00106.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CUNNINGHAM L. W., Jr Reactivation of diethyl p-nitrophenyl phosphate-inhibited alpha-chymotrypsin by hydroxylamine. J Biol Chem. 1954 Mar;207(1):443–458. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CUNNINGHAM L. W. Proposed mechanism of action of hydrolytic enzymes. Science. 1957 Jun 7;125(3258):1145–1146. doi: 10.1126/science.125.3258.1145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIES D. R., GREEN A. L. The kinetics of reactivation, by oximes, of cholinesterase inhibited by organophosphorus compounds. Biochem J. 1956 Aug;63(4):529–535. doi: 10.1042/bj0630529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIES D. R., GREEN A. L. The mechanism of hydrolysis by cholinesterase and related enzymes. Adv Enzymol Relat Subj Biochem. 1958;20:283–318. doi: 10.1002/9780470122655.ch9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DIXON G. H., NEURATH H. Acylation of the enzymatic site of delta-chymotrypsin by esters, acid anhydrides, and acid chlorides. J Biol Chem. 1957 Apr;225(2):1049–1059. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutfreund H., Sturtevant J. M. THE MECHANISM OF CHYMOTRYPSIN-CATALYZED REACTIONS. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1956 Oct;42(10):719–728. doi: 10.1073/pnas.42.10.719. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOBBIGER F. Chemical reactivation of phosphorylated human and bovine true cholinesterases. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1956 Sep;11(3):295–303. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1956.tb01069.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOUNTER L. A., ALEXANDER H. C., 3rd, TUCK K. D., DIEN L. T. The pH dependence and dissociation constants of esterases and proteases treated with diisopropyl fluorophosphate. J Biol Chem. 1957 Jun;226(2):867–872. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDONALD C. E., BALLS A. K. Analogues of acetyl chymotrypsin. J Biol Chem. 1957 Aug;227(2):727–736. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OOSTERBAAN R. A., VAN ADRICHEM M. E. Isolation of acetyl peptides from acetylchymotrypsin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1958 Feb;27(2):423–425. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(58)90359-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHAFFER N. K., SIMET L., HARSHMAN S., ENGLE R. R., DRISKO R. W. Phosphopeptides from acid-hydrolyzed P32-labeled diisopropylphosphoryl chymotrypsin. J Biol Chem. 1957 Mar;225(1):197–206. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


