Abstract
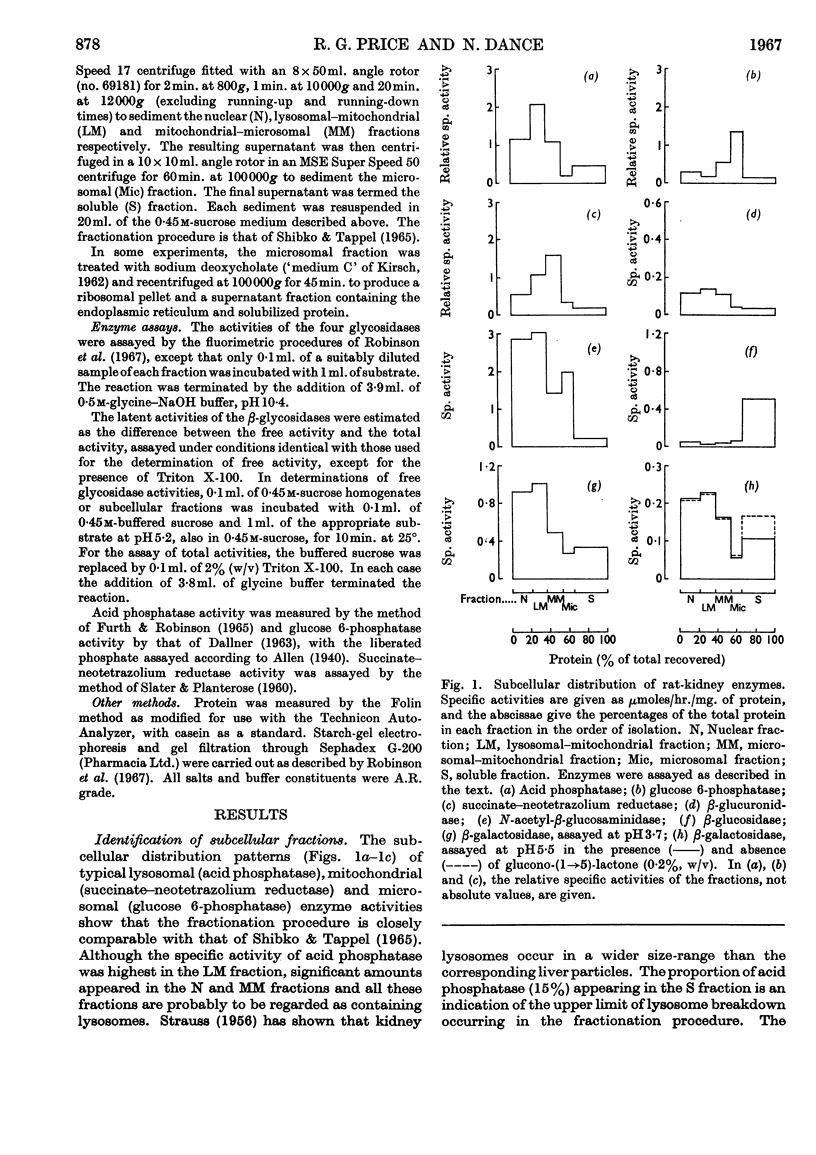
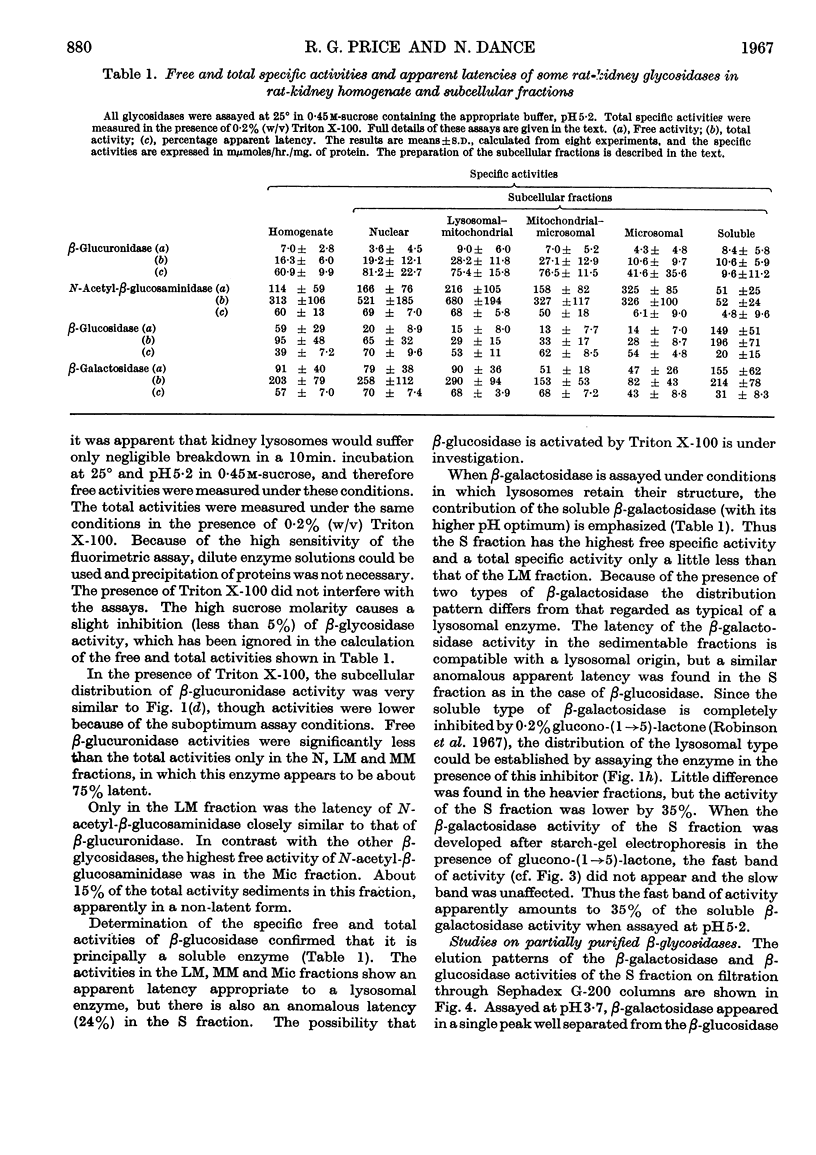
1. Free and total activities of β-glucosidase, β-galactosidase, N-acetyl-β-glucosaminidase and β-glucuronidase have been determined fluorimetrically in five subcellular fractions of rat kidney. 2. The β-glucosidase activity appeared in the soluble fraction, β-glucuronidase had the distribution pattern of a lysosomal enzyme, and both β-galactosidase and N-acetyl-β-glucosaminidase had bimodal distributions. 3. Two types of β-galactosidase activity were found: a sedimentable type, having optimum pH3·7, mol.wt. about 80000 and slow electrophoretic mobility at pH7·0 in starch gel; and a soluble type of much faster mobility, having optimum pH5·5–6·5 and mol.wt. about 40000. 4. Evidence is presented that the β-glucosidase and the soluble type of β-galactosidase are the same enzyme. 5. Most of the N-acetyl-β-glucosaminidase activity was in the lysosome-rich fractions, but a significant proportion occurred in the microsomal fraction in a non-latent form. 6. The use of β-galactosidase and N-acetyl-β-glucosaminidase as lysosomal marker enzymes is complicated by the possible presence of multiple forms, but this limitation does not apply to β-glucuronidase in the rat kidney.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen R. J. The estimation of phosphorus. Biochem J. 1940 Jun;34(6):858–865. doi: 10.1042/bj0340858. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CONCHIE J., HAY A. J. Mammalian glycosidases. 4. The intracellular localization of beta-galactosidase, alpha-mannosidase, beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase and alpha-L-fucosidase in mammalian tissues. Biochem J. 1963 May;87:354–361. doi: 10.1042/bj0870354. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chytil F. Mammalian beta-galactosidases. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1965 May 18;19(5):630–636. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(65)90386-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fishman W. H., Goldman S. S., DeLellis R. Dual localization of beta-glucuronidase in endoplasmic reticulum and in lysosomes. Nature. 1967 Feb 4;213(5075):457–460. doi: 10.1038/213457a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furth A. J., Robinson D. Specificity and multiple forms of beta-galactosidase in the rat. Biochem J. 1965 Oct;97(1):59–66. doi: 10.1042/bj0970059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEVVY G. A., McALLAN A., HAY A. J. Inhibition of glycosidases by aldonolactones of corresponding configuration. 3. Inhibitors of beta-D-galactosidase. Biochem J. 1962 Feb;82:225–232. doi: 10.1042/bj0820225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RUTENBURG A. M., RUTENBURG S. H., MONIS B., TEAGUE R., SELIGMAN A. M. Histochemical demonstration of beta-D-galactosidase in the rat. J Histochem Cytochem. 1958 Mar;6(2):122–129. doi: 10.1177/6.2.122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson D., Abrahams H. E. Beta-D-xylosidase in pig kidney. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Jan 11;132(1):212–214. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(67)90215-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson D., Price R. G., Dance N. Separation and properties of beta-galactosidase, beta-glucosidase, beta-glucuronidase and N-acetyl-beta-glucosaminidase from rat kidney. Biochem J. 1967 Feb;102(2):525–532. doi: 10.1042/bj1020525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SELLINGER O. Z., BEAUFAY H., JACQUES P., DOYEN A., DE DUVE C. Tissue fractionation studies. 15. Intracellular distribution and properties of beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase and beta-galactosidase in rat liver. Biochem J. 1960 Mar;74:450–456. doi: 10.1042/bj0740450. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHIBKO S., TAPPEL A. L. RAT-KIDNEY LYSOSOMES: ISOLATION AND PROPERTIES. Biochem J. 1965 Jun;95:731–741. doi: 10.1042/bj0950731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SLATER T. F., PLANTEROSE D. N. Studies on the particulate components of rat mammary gland. 5. Comparison of large particles from liver and mammary gland. Biochem J. 1960 Mar;74:584–591. doi: 10.1042/bj0740584. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STELLWAGEN E., SCHACHMAN H. K. The dissociation and reconstitution of aldolase. Biochemistry. 1962 Nov;1:1056–1069. doi: 10.1021/bi00912a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STRAUS W. Concentration of acid phosphatase, ribonuclease, desoxyribonuclease, beta-glucuronidase, and cathepsin in droplets isolated from the kidney cells of normal rats. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1956 Sep 25;2(5):513–521. doi: 10.1083/jcb.2.5.513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VANLANCKER J. L. LYSOSOMES. CONCLUDING REMARKS. Fed Proc. 1964 Sep-Oct;23:1050–1052. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wattiaux-De Coninck S., Rutgeerts M. J., Wattiaux R. Lysosomes in rat-kidney tissue. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Sep 20;105(3):446–459. doi: 10.1016/s0926-6593(65)80230-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




