Abstract
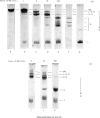
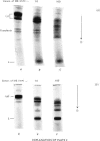
The relative lability of the interchain disulphide bonds of mouse G2a-myeloma protein 5563 was studied as a function of 2-mercaptoethanol concentration. Analysis of partial-reduction mixtures by polyacrylamide-gel electrophoresis and microdensitometry showed that the disulphide bonds between light and heavy chains are much more susceptible to reduction than the bonds between heavy chains. At a low concentration of 2-mercaptoethanol (10mm) the major dissociable products of mouse immunoglobulin G are heavy-chain dimers and free light chains. These findings contrast with the reported behaviour of rabbit immunoglobulin G, for which the lability of inter-heavy-chain bonds was found to exceed that of the bonds linking light and heavy chains (Hong & Nisonoff, 1965); the relative stability of rabbit immunoglobulin G interchain bonds was confirmed in the present study. Examination of human immunoglobulin G and an immunoglobulin G (γ2) of guinea pig showed that at least in the majority of molecules, as with mouse immunoglobulin G, the disulphide bonds between light and heavy chains are more susceptible to reduction than the inter-heavy-chain bonds.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ASKONAS B. A. A study on globulin formation by plasma-cell neoplasm (5563) transplantable in mice. Biochem J. 1961 Apr;79:33–43. doi: 10.1042/bj0790033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Askonas B. A., White R. G., Wilkinson P. C. Production of gamma-1- and gamma-2-antiovalbumin by various lymphoid tissues of the guinea pig. Immunochemistry. 1965 Dec;2(4):329–336. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(65)90033-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S., Gordon S. Dissociation of kappa- and lambda-chains from reduced human immunoglobulins. Biochem J. 1965 Nov;97(2):460–465. doi: 10.1042/bj0970460. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EDELMAN G. M., POULIK M. D. Studies on structural units of the gamma-globulins. J Exp Med. 1961 May 1;113:861–884. doi: 10.1084/jem.113.5.861. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FAHEY J. L., ASKONAS B. A. Enzymatically produced subunits of proteins formed by plasma cells in mice. I. gamma-Globulin and gamma-myeloma proteins. J Exp Med. 1962 Mar 1;115:623–639. doi: 10.1084/jem.115.3.623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FLEISCHMAN J. B., PAIN R. H., PORTER R. R. Reduction of gamma-globulins. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1962 Sep;Suppl 1:174–180. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hong R., Nisonoff A. Relative labilities of the two types of interchain disulfide bond of rabbit gamma G-immunoglobulin. J Biol Chem. 1965 Oct;240(10):3883–3891. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NISONOFF A., DIXON D. J. EVIDENCE FOR LINKAGE OF UNIVALENT FRAGMENTS OR HALF-MOLECULES OF RABBIT GAMMA-GLOBULIN BY THE SAME DISULFIDE BOND. Biochemistry. 1964 Sep;3:1338–1342. doi: 10.1021/bi00897a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PALMER J. L., NISONOFF A. DISSOCIATION OF RABBIT GAMMA-GLOBULIN INTO HALF-MOLECULES AFTER REDUCTION OF ONE LABILE DISULFIDE BOND. Biochemistry. 1964 Jun;3:863–869. doi: 10.1021/bi00894a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PALMER J. L., NISONOFF A., VANHOLDE K. E. DISSOCIATION OF RABBIT GAMMA GLOBULIN INTO SUBUNITS BY REDUCTION AND ACIDIFICATION. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1963 Aug;50:314–321. doi: 10.1073/pnas.50.2.314. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POTTER M., KUFF E. L. DISORDERS IN THE DIFFERENTIATON OF PROTEIN SECRETION IN NEOPLASTIC PLASMA CELLS. J Mol Biol. 1964 Aug;9:537–544. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(64)80225-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter M., Appella E., Geisser S. Variations in the heavy polypeptide chain structure of gamma myeloma immunoglobulins from an inbred strain of mice and a hypothesis as to their origin. J Mol Biol. 1965 Dec;14(2):361–372. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80187-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summers D. F., Maizel J. V., Jr, Darnell J. E., Jr Evidence for virus-specific noncapsid proteins in poliovirus-infected HeLa cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Aug;54(2):505–513. doi: 10.1073/pnas.54.2.505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]