Abstract
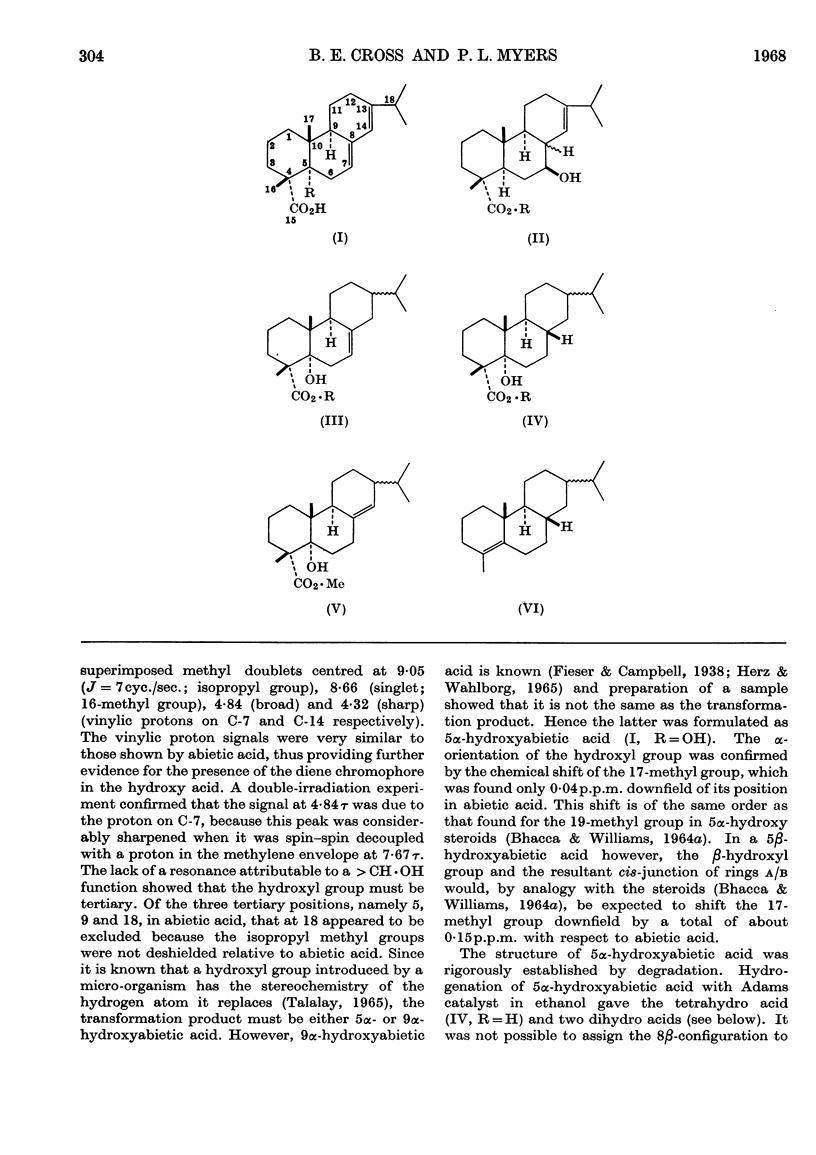
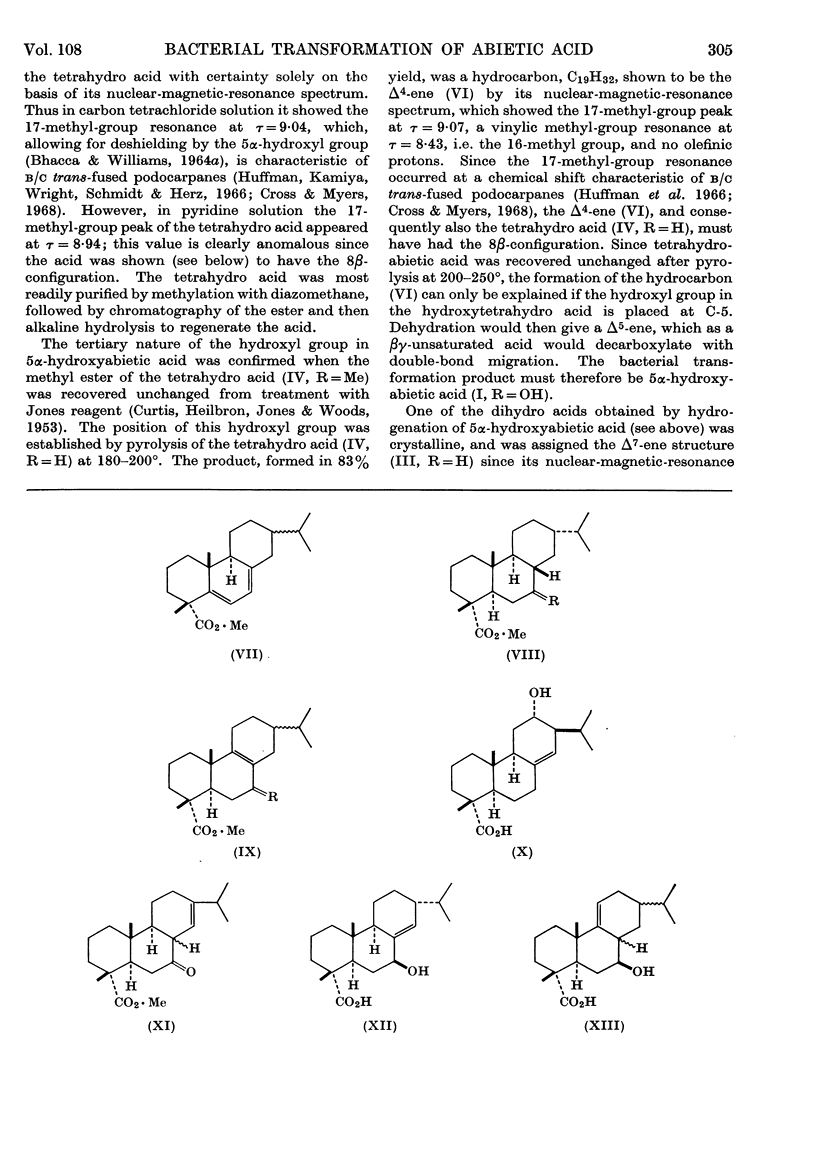
An Alcaligenes species, which was isolated from soil, can utilize abietic acid as its sole carbon source. During growth, the bacterium transforms abietic acid into 5α-hydroxyabietic acid (I, R=OH), a product considered to be 7β-hydroxy-13-isopropyl-8ξ-podocarp-13-en-15-oic acid (II, R=H) and a compound, C20H28O3, which is believed to be an epoxy-γ-lactone.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CHAPMAN P. J., MEERMAN G., GUNSALUS I. C. THE MICROBIOLOGICAL TRANSFORMATION OF FENCHONE. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1965 Jun 18;20:104–108. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(65)90955-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CONRAD H. E., DUBUS R., NAMTVEDT M. J., GUNSALUS I. C. MIXED FUNCTION OXIDATION. II. SEPARATION AND PROPERTIES OF THE ENZYMES CATALYZING CAMPHOR LACTONIZATION. J Biol Chem. 1965 Jan;240:495–503. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DASTE P. Sur l'utilisation de résinates métalliques comme source de carbone par le Flavobacterium resinovorum Delaporte et Daste. C R Hebd Seances Acad Sci. 1958 May 19;246(20):2953–2955. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson D. T., Wang K. C., Sih C. J., Whitlock H., Jr Mechanisms of steroid oxidation by microorganisms. IX. On the mechanism of ring A cleavage in the degradation of 9,10-seco steroids by microorganisms. J Biol Chem. 1966 Feb 10;241(3):551–559. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sih C. J., Lee S. S., Tsong Y. Y., Wang K. C. Mechanisms of steroid oxidation by microorganisms. 8. 3,4-Dihydroxy-9,10-secoandrosta-1,3,5(10)-triene-9,17-dione, an intermediate in the microbiological degradation of ring A of androst-4-ene-3,17-dione. J Biol Chem. 1966 Feb 10;241(3):540–550. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TALALAY P. ENZYMATIC MECHANISMS IN STEROID BIOCHEMISTRY. Annu Rev Biochem. 1965;34:347–380. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.34.070165.002023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WANG K. C., SIH C. J. MECHANISMS OF STEROID OXIDATION BY MICROORGANISMS. IV. SECO INTERMEDIATES. Biochemistry. 1963 Nov-Dec;2:1238–1243. doi: 10.1021/bi00906a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


