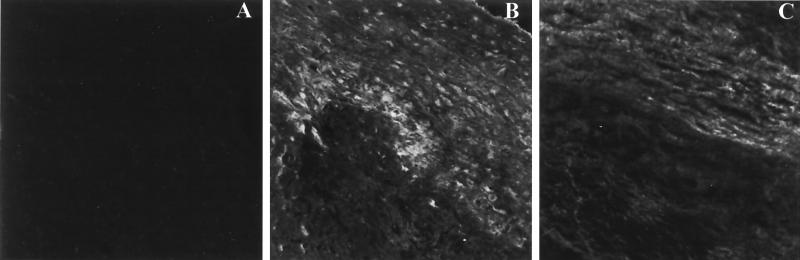
FIG. 2.
Confocal images of immunofluorescence microscopy studies carried out on 4-μm-thick cross-sections of a carotid artery from a subject with atherosclerosis made with a cryocut microtome. The images document the deposition of APP along the vessel walls of carotid arteries obtained from patients who underwent endarterectomies. The vessels tested positive for the presence of DNA from periodontal pathogens (24). (A) Negative control. The vessel was incubated sequentially with normal rabbit serum and FITC-labeled anti-chicken IgG. Similarly, the vessels incubated sequentially with normal rabbit serum and FITC-labeled anti-rabbit IgG or incubations with secondary antibodies alone did not exhibit staining (data not shown). (B) CRP. The vessel was incubated sequentially with antibodies to CRP raised in chickens and fluorochrome-labeled anti-chicken IgG antibodies. (C) SAA. The vessel was incubated sequentially with antibodies to SAA raised in rabbits and fluorochrome-labeled anti-rabbit IgG antibodies. Deposition of SAA and CRP was observed along the intimal wall of the vessels. The extent of deposition varied among patients and was proportional to the severity of the atheromatous lesion formed along the vessel wall. The photomicrographs were obtained by using a Nikon epifluorescence microscope and the Bio-Rad MRC-024 three-channel laser scanning confocal imaging system equipped with a krypton argon laser operating at 514 nm at 100% power. The images were stored at 47 × 47 pixels (512 × 512 μ, full field) with a pixel size of 0.093 μ (final magnification, ×340).