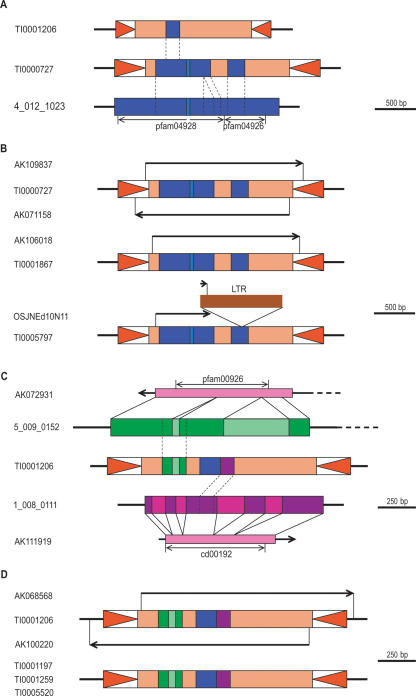
Figure 2.
Transduplication and diversification of a poly(A) polymerase (PAP) gene fragment in the rice genome. (A) The central region of a putative PAP gene on chromosome 4 (4_012_1023) was transduplicated in a MULE that later replicated and, in one branch of the group, internal deletions reduced the size of the transduplicate. (B) Three highly similar copies in the rice genome possess the larger transduplicate, each having a different pattern of expression, including TI0000727, which generates sense and antisense transcripts and TI0005797 with the transcript terminating in a retrotransposon solo long terminal repeat (LTR). (C) The MULE copy with the smaller transduplicate subsequently transduplicated regions from two additional rice genes, a ribA-like gene (5_009_0152) and a serine/threonine protein kinase (1_008_0111). (D) There are four MULEs with these three transduplicates and one of them is transcribed in both the sense and antisense direction. Mapped cDNAs and ESTs are represented by arrows, pink bars represent ORFs, and regions containing conserved protein domains are indicated by double-headed arrows. Genes are shown in blue, green, and purple, and introns are shown in a lighter shade. Inverted triangles represent TIRs.