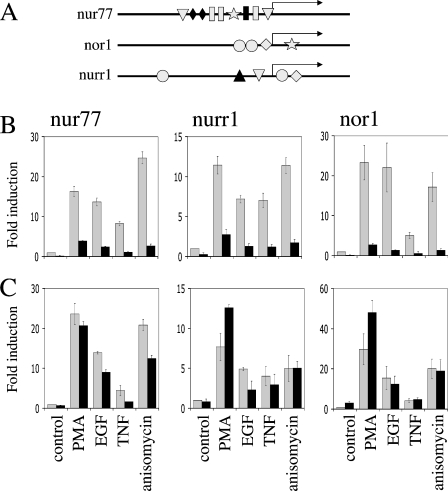
Figure 1. NR4A gene transcription requires CREB.
(A) The promoter region bp −2000 to bp +1000 of the transcriptional start of the Nur77, Nor1 and Nurr1 transcription factors were analysed by GALA prediction software (http://gala.cse.psu.edu/). Potential CRE (closed circle) or AP-1-like (grey rectangle in human, mouse, rat and canine promoters, black rectangle indicating a non-conserved region in the canine promoter) as well as potential sites for MEF cells (black diamond), Elk (star), USF (upstream stimulatory factor; black triangle) and nuclear factor κB (grey triangle) were identified. Sequences predicted as CRE sites were TGACGTAG and TGACGTCT in Nor1, and TGACG.CA and TGACGTCA in Nurr1, against a concensus CRE site of TGACGT(A/C)A. (B) HeLa cells were transfected with either an empty vector (light grey bars) or A-CREB expression vector (dark grey bars). After 24 h transfected cells were serum-starved for 16 h and left unstimulated (control) or stimulated for 60 min with 400 ng/ml PMA, 100 ng/ml EGF, 10 ng/ml TNF or 10 μg/ml anisomycin. Cells were then lysed and RNA isolated and analysed by real-time PCR. Levels of Nur77 mRNA were determined relative to β2-microglobulin controls as described in the Materials and methods section. Error bars represent the S.E.M. of three individual stimulations. (C) As in (B) except a dominant-negative junD vector (black bars) was used in place of A-CREB.