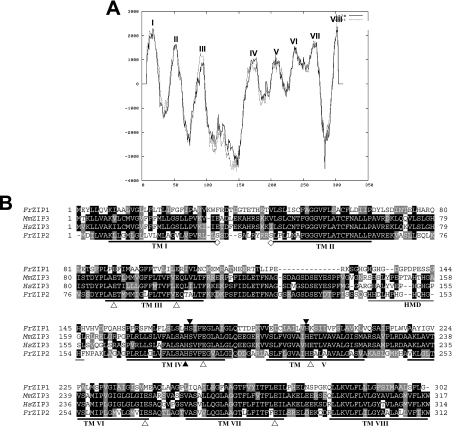
Figure 1. Structural characterization of FrZIP2 protein.
(A) Hydrophobicity analysis of pufferfish ZIP transporter 2 (FrZIP2). Eight TM domains (TM I–VIII) of FrZIP2 protein are predicted with TMpred (http://www.ch.embnet.org/software/TMPRED_form.html). TM IV and V have low hydrophobicity in comparison with other TMs. The dotted line indicates outside-to-inside topology (N-terminus outside) that is predicted to be the strongly preferred model, and the straight line indicates inside-to-outside orientation (N-terminus inside). (B) Alignment of amino acid sequences of FrZIP2, FrZIP1 (accession no. AY529485) and mammalian ZIP3 (SLC39A3). FrZIP2 was aligned with FrZIP1, human and mouse ZIP3 [accession numbers BC005869 (HsZIP3) and BC005502 (MmZIP3)]. Shaded residues represent positions of identity or similarity among the sequences. The eight predicted TM domains are underlined and numbered I–VIII. A potential histidine-rich metal-binding motif between TM III and TM IV is underlined in grey. ▲, conserved functional histidine and serine residues; △, glutamate residues conserved between FrZIP2 and mammalian ZIP3 proteins; and ◇, potential phosphorylation sites of protein kinase A. Signature sequence of the ZIP family in TM IV of FrZIP2 is boxed with a grey line. HMD, histidine-rich metal-binding domain.