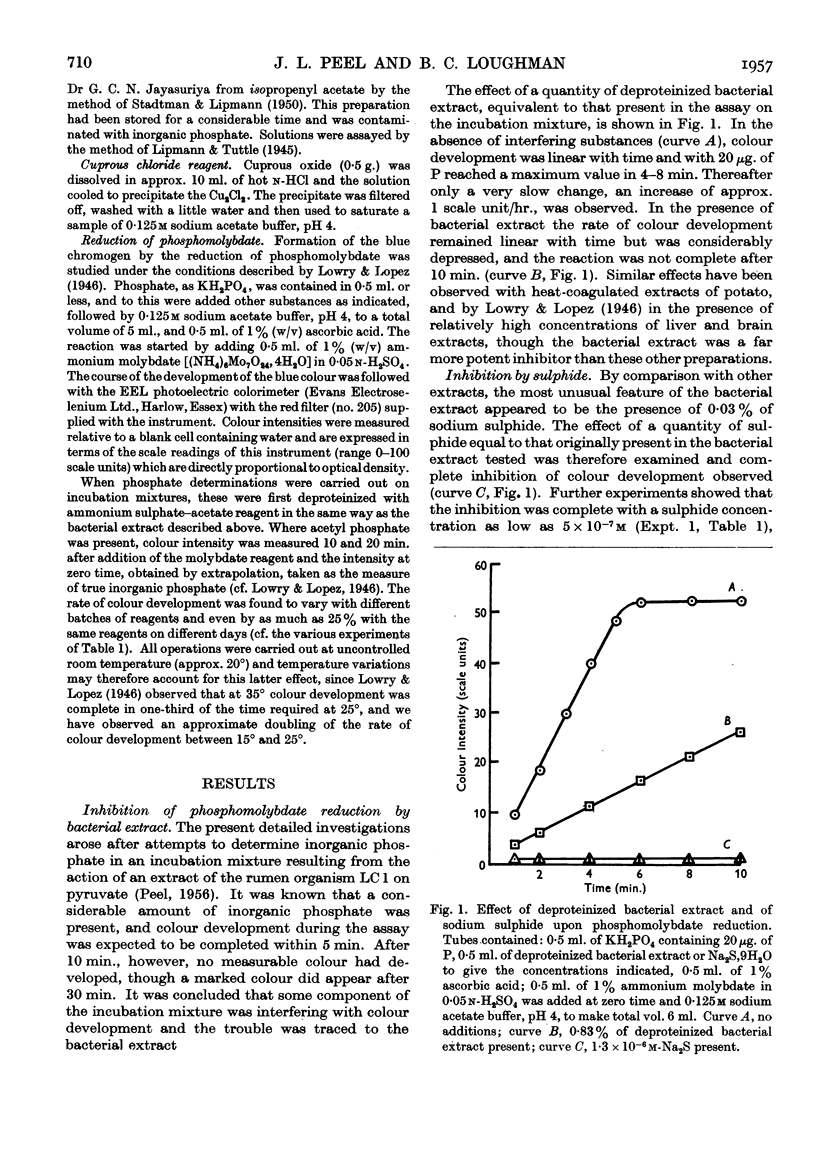
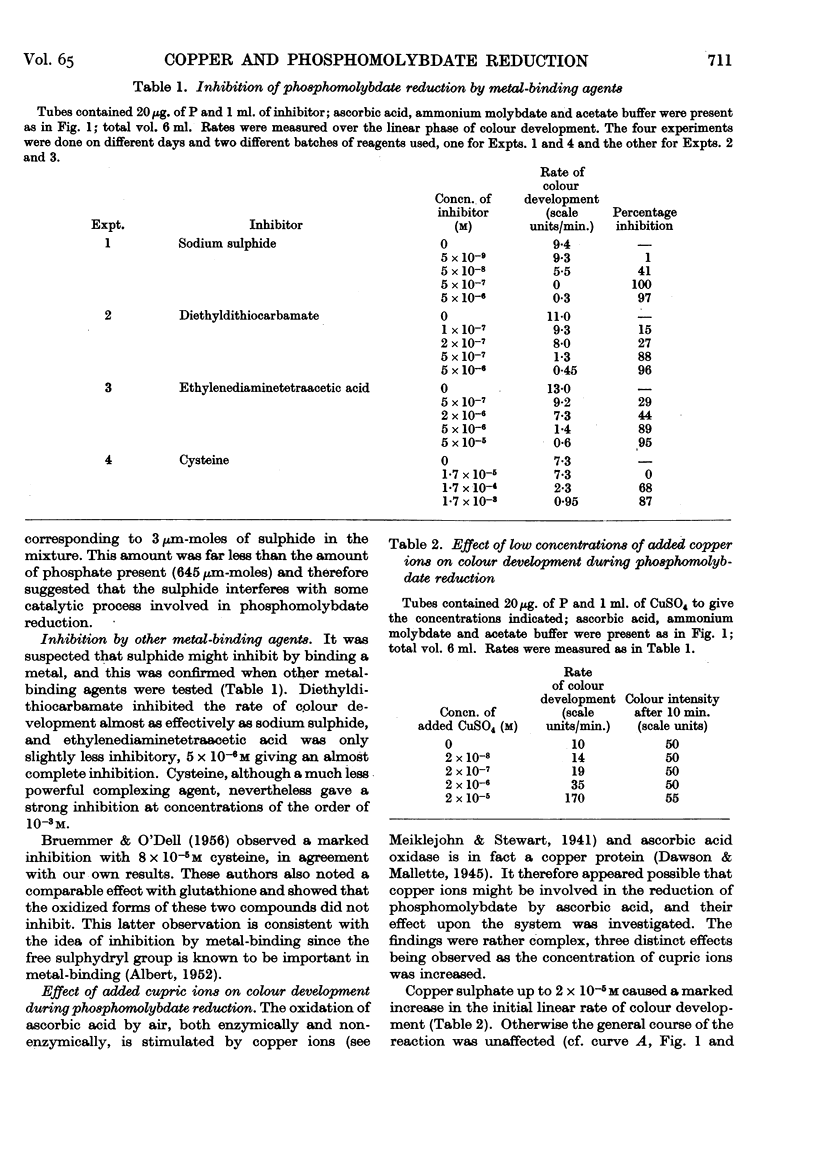
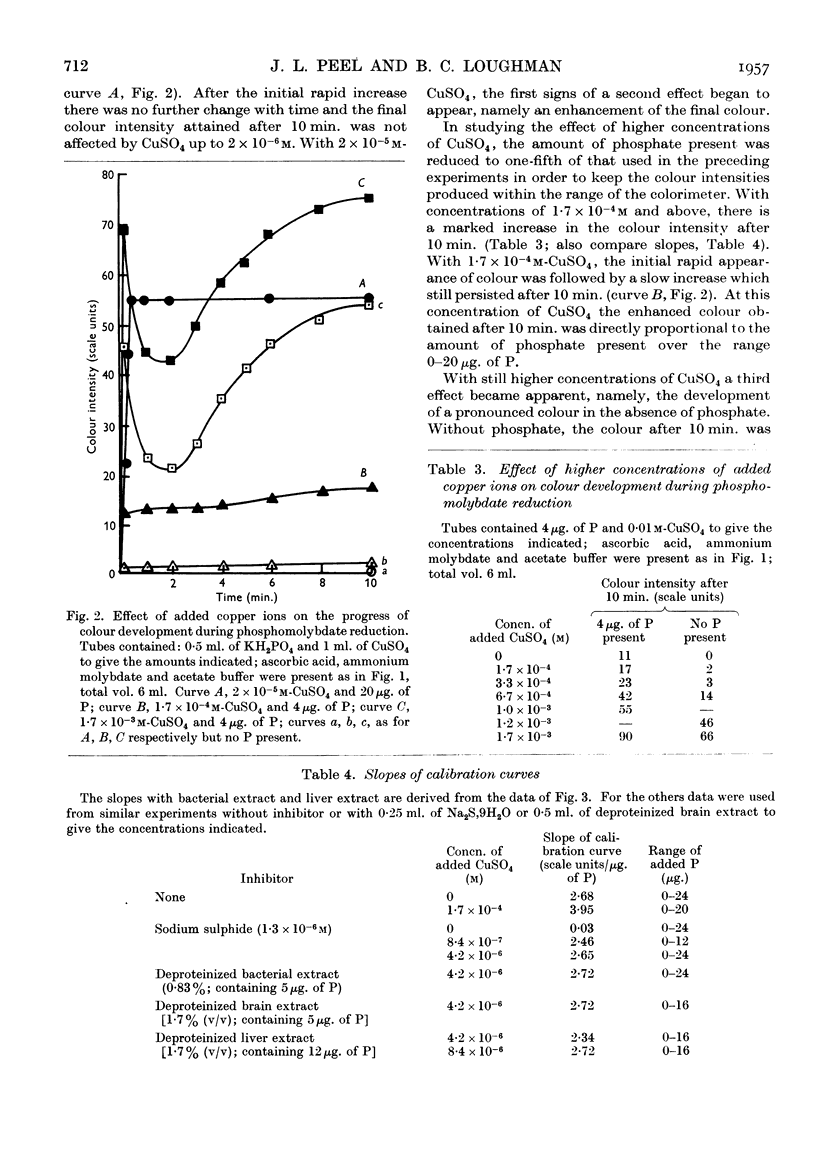
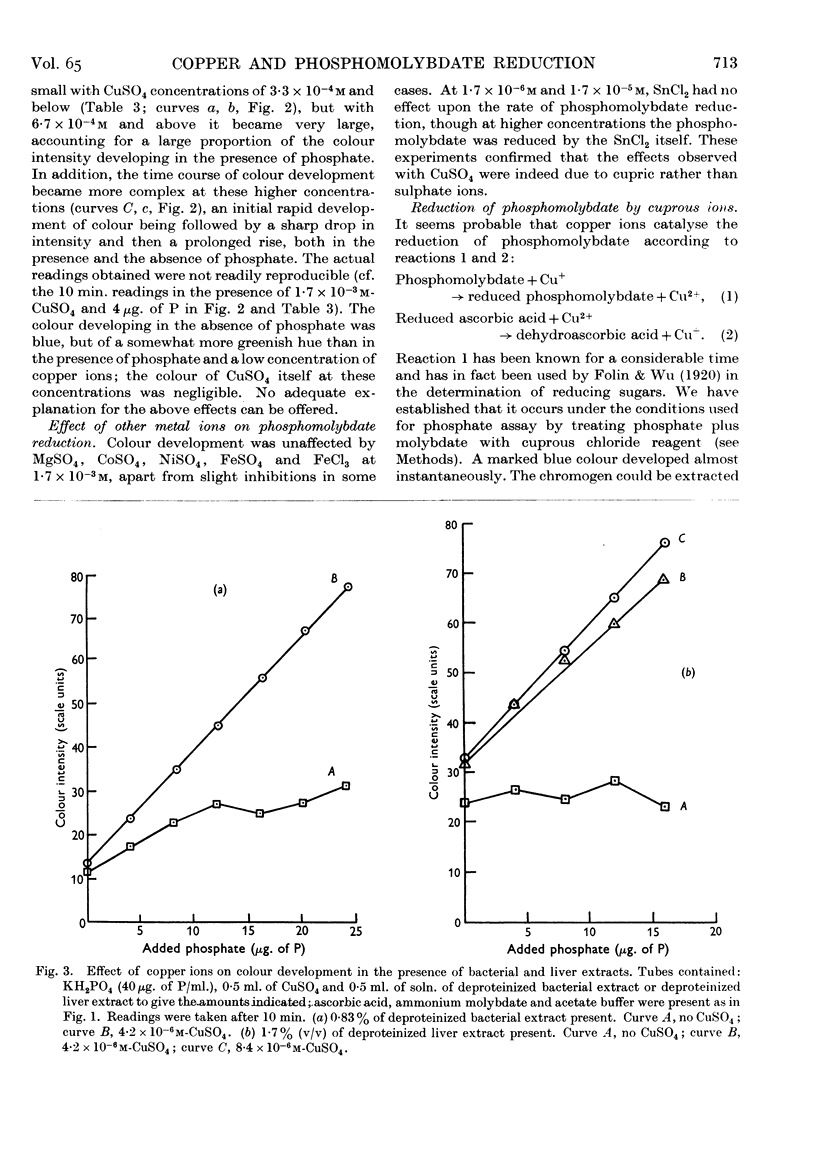
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALBERT A. Quantitative studies of the avidity of naturally occurring substances for trace metals. II. Amino-acids having three ionizing groups. Biochem J. 1952 Mar;50(5):690–697. doi: 10.1042/bj0500690. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ALBERT A. Quantitative studies of the avidity of naturally occurring substances for trace metals. III. Pteridines, riboflavin and purines. Biochem J. 1953 Jul;54(4):646–654. doi: 10.1042/bj0540646. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ALBERT A. Quantitative studies of the avidity of naturally occurring substances for trace metals; amino-acids having only two ionizing groups. Biochem J. 1950 Nov-Dec;47(5):531–538. doi: 10.1042/bj0470531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRUEMMER J. H., O'DELL B. L. Inhibition of color development in the Lowry-Lopez phosphorus method by sulfhydryl compounds and its counteraction by copper. J Biol Chem. 1956 Mar;219(1):283–286. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berenblum I., Chain E. An improved method for the colorimetric determination of phosphate. Biochem J. 1938 Feb;32(2):295–298. doi: 10.1042/bj0320295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELSDEN S. R., GILCHRIST F. M., LEWIS D., VOLCANI B. E. Properties of a fatty acid forming organism isolated from the rumen of sheep. J Bacteriol. 1956 Nov;72(5):681–689. doi: 10.1128/jb.72.5.681-689.1956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meiklejohn G. T., Stewart C. P. Ascorbic acid oxidase from cucumber. Biochem J. 1941 Jul;35(7):755–760. doi: 10.1042/bj0350755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PEEL J. L., FOX M., ELSDEN S. R. Interference by sulphide with inorganic phosphate determinations by the method of Lowry & Lopez and its elimination by the addition of copper ions. Biochem J. 1955 Aug;60(4):xxxiii–xxxiii. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STADTMAN E. R., LIPMANN F. Acetyl phosphate synthesis by reaction of isopropenyl acetate and phosphoric acid. J Biol Chem. 1950 Aug;185(2):549–551. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


