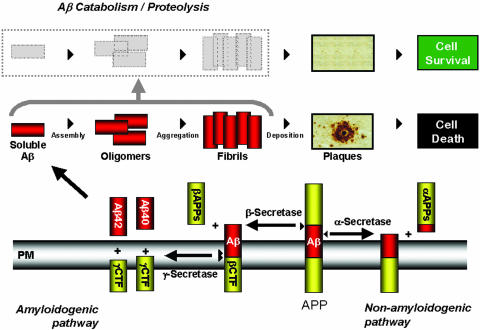
FIG. 2.
The amyloid cascade hypothesis. The amyloid precursor protein APP is processed by β and γ-secretases via the amyloidogenic pathway to yield a variety of toxic Aβ-containing species, ultimately resulting in neuronal cell death. These amyloidogenic species can be degraded by a number of catabolic proteases such as neprilysin, IDE, and plasmin, thereby clearing Aβ and preventing cell death. The nonamyloidogenic pathway results from α-secretase cleavage within the Aβ sequence of APP.