Figure 2.
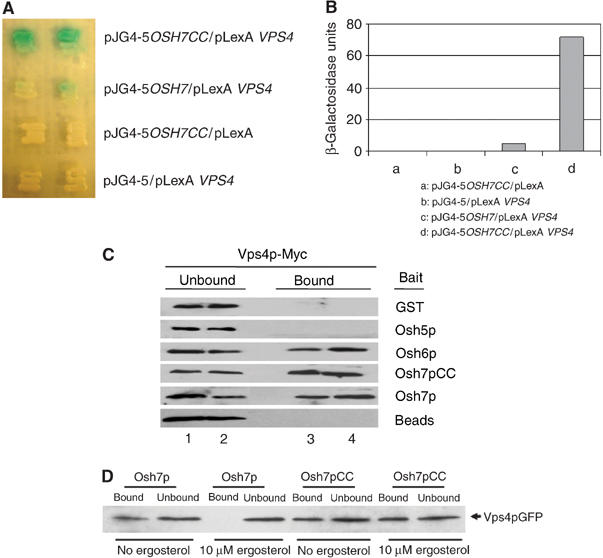
Osh6p and Osh7p interact with Vps4p in vivo and in vitro. (A) Two-hybrid interaction. The LexA-based bait plasmids pLexA and pLexA-VPS4 and the pB42AD-based prey plasmids pJG4-5, pJGOSH7CC and pJGOSH7 were introduced into EGY48 together with the reporter plasmid PSH18-34 and grown in synthetic galactose/raffinose medium containing X-gal at 30°C for 2 days. (B) Quantification of yeast two-hybrid interactions. Cells were lysed by freeze–thaw cycles using liquid nitrogen and β-galactosidase activity was assayed using ONPG as a substrate. (C) GST pull-down. GST fusion proteins were purified from E. coli using glutathione (GSH) agarose beads. The fusion proteins were incubated with yeast lysates prepared from Vps4p-Myc expressing Y10000 cells. After stringency washes, bound proteins were eluted and separated on SDS–PAGE. Vps4p-Myc was detected using an anti-Myc monoclonal antibody. Lanes 1 and 2: unbound fraction; lanes 3 and 4: bound fraction. (D) Incubation with ergosterol affects the interaction between Osh7p and Vps4p in vitro. GST fusion proteins were purified from E. coli using GSH agarose beads. Fusion proteins containing full-length Osh7p or Osh7pCC were incubated in the presence or absence of 10 μM ergosterol for 2 h at 30°C, and then mixed with yeast lysates prepared from Vps4p-GFP-expressing Y10000 cells. After stringency washes, bound proteins were eluted and separated on SDS–PAGE.
