Figure 2.
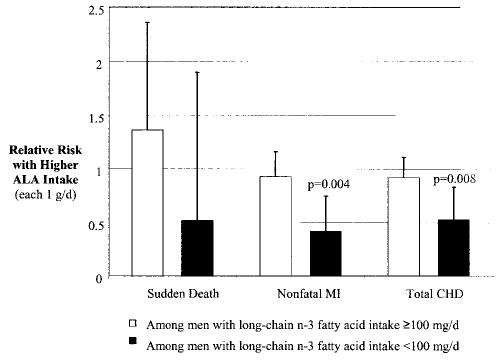
Relative risks (hazards) of CHD associated with each 1 g/d of ALA intake, among participants with long-chain n-3 PUFA intake ≥ 100 mg/d (n = 38 367, open columns) and among participants with little or no long-chain n-3 PUFA intake (<100 mg/d, n = 7355, filled columns). Long-chain n-3 PUFA intake modified effects of ALA intake for both nonfatal MI (P interaction = 0.003) and total CHD (P interaction = 0.006). Error bars indicate upper limit of 95% CI; probability values for significant relative risks are shown. Adjustments as in multivariate model, Table 2. Abbreviations are as defined in text.
