Fig. 3.
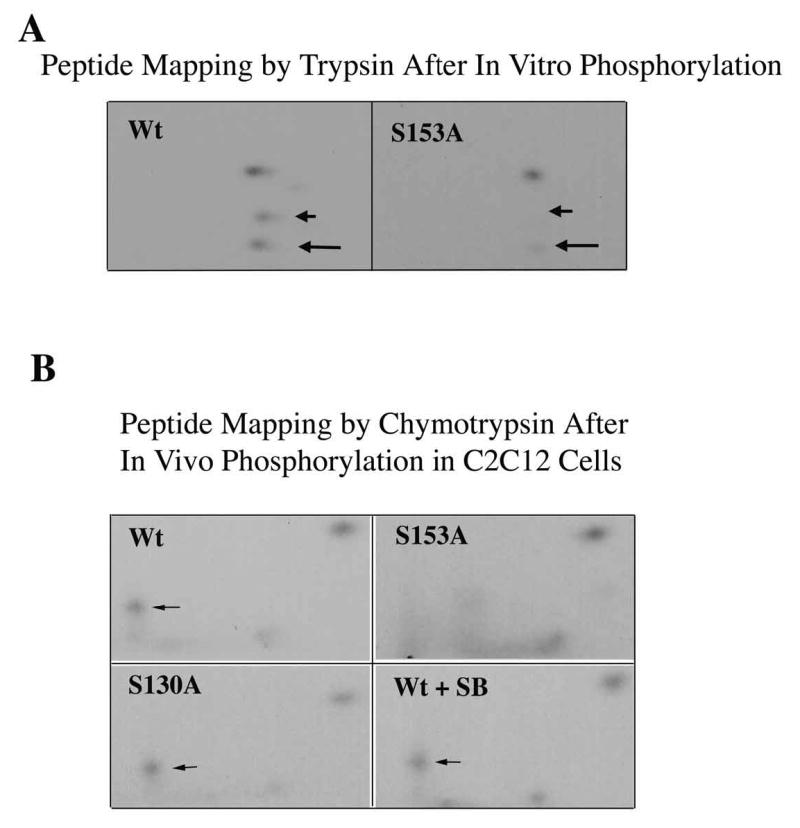
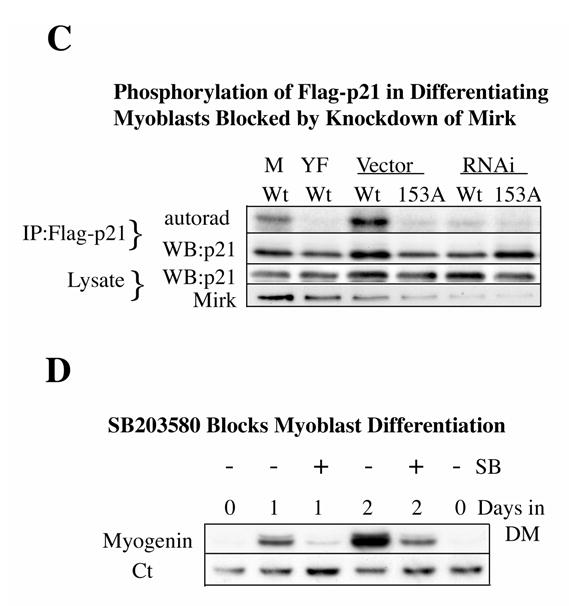
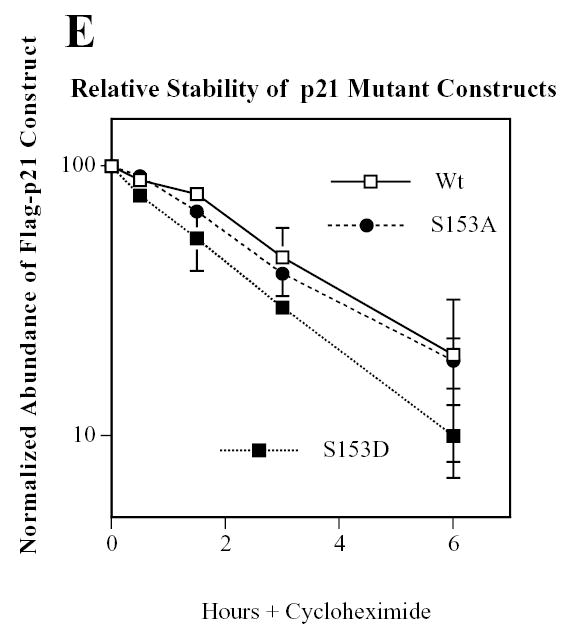
Mirk phosphorylates p21 at S153 in vitro and in differentiating myoblasts. A. Mirk phosphorylates p21 at S153 in vitro as shown by peptide mapping with trypsin. Wild-type (Wt) and mutant p21-S153A constructs were phosphorylated in vitro by purified recombinant Mirk, digested with trypsin and then subjected to two-dimensional peptide mapping. The peptide containing S153 and consisting of amino acids 143–154 is shown by a short arrow in both panels. The peptide identified by the longer arrow may be a partial digestion product containing S153, due to steric interference of the enzyme by the phosphate group. Similar data was seen in two additional peptide maps. B. Mirk phosphorylates p21 at S153 in vivo as shown by peptide mapping with chymotrypsin. Wild-type Flag-p21, mutant p21-S153A, and mutant p21-S130A were each cotransfected with wild-type Mirk into C2C12 cells. Constructs were allowed to express overnight, then cells were placed in myoblast differentiation medium for 24 hours, the last 4 hours of which cells were labeled with [32P]-orthophosphate. In one dish transfected with wild-type p21, 10 uM SB203580 was added at the same time as the label. Flag-p21 was immunoprecipitated with anti-Flag M2 antibody, the immunoprecipitates were digested with chymotrypsin, and then subjected to two-dimensional peptide mapping. The p21-S153A mutant incorporated about 40% as much label as wild-type p21 when normalized to the total amount of p21 immunoprecipitated. Chymotrypsin was used because it yields a simpler map with a broader distribution of peptides. The peptide indicated by the arrow is lost in the p21-S153A mutant, and is the presumed 152-159 amino acid peptide. C. Depletion of endogenous Mirk by RNA interference blocks the phosphorylation of transfected wild-type p21, but not p21-S153A mutant at the Mirk phosphorylation site. Cells were plated at 5x105 per 60 mm dish, cultured for 16 hours, then were transfected for 4 hours in serum-free medium with 2.5 ug of either Flag-p21 or Flag-p21-S153A, and 2.5 ug of pSilencer DNA encoding either RNAi to Mirk (RNAi) or vector. As controls, Flag-p21 was co-transfected with either wild-type Mirk (M) or kinase-inactive YF-Mirk (YF). Fetal bovine serum was then added to 10% to maintain cell viability during overnight expression, and cells were switched to OptiMEM differentiation medium for 24 hours, with 325 uCi 32P-orthophosphate added to each dish for the last 4 hours following 1 hour in phosphate-free medium. Anti-Flag epitope immunoprecipitates were separated by SDS-PAGE and the Flag-p21 bands were detected by autoradiography (top lanes), then by western blotting for Flag. The amount of p21 and Mirk in the lysates were determined by western blotting (lower 2 bands). D. SB203580 inhibits myoblast differentiation as measured by the level of expression of the myogenic regulatory factor myogenin which controls the differentiation program. C2C12 cells were placed in differentiation medium +/− 10 uM SB203580 for 1 and 2 days and the abundance of myogenin determined by western blotting. Ct, cross-reacting protein used as a loading control. E. Relative stability of mutant p21 constructs. C2C12 cells were transfected with either mutant Flag-p21-S153D, Flag-p21-S153A or wild-type Flag-p21, and constructs were allowed to express for 24 hours. Cycloheximide (CH) at 20 ug/ml was added to each culture and Flag-p21 and tubulin abundance were determined at the indicated times by western blotting, and normalized to the 0 time values. Mean +/− SE shown of 2 separate experiments.
